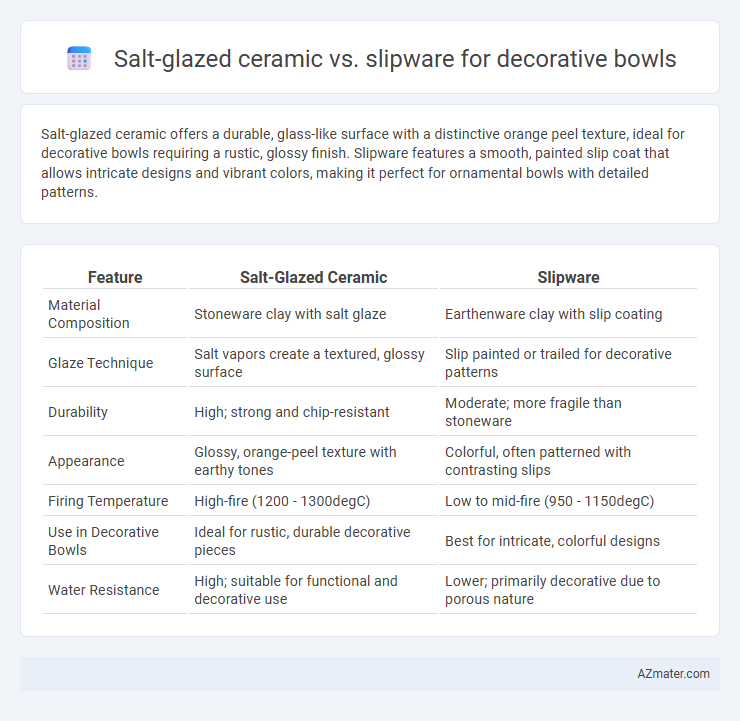
Salt-glazed ceramic offers a durable, glass-like surface with a distinctive orange peel texture, ideal for decorative bowls requiring a rustic, glossy finish. Slipware features a smooth, painted slip coat that allows intricate designs and vibrant colors, making it perfect for ornamental bowls with detailed patterns.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Salt-Glazed Ceramic | Slipware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Stoneware clay with salt glaze | Earthenware clay with slip coating |
| Glaze Technique | Salt vapors create a textured, glossy surface | Slip painted or trailed for decorative patterns |
| Durability | High; strong and chip-resistant | Moderate; more fragile than stoneware |
| Appearance | Glossy, orange-peel texture with earthy tones | Colorful, often patterned with contrasting slips |
| Firing Temperature | High-fire (1200 - 1300degC) | Low to mid-fire (950 - 1150degC) |
| Use in Decorative Bowls | Ideal for rustic, durable decorative pieces | Best for intricate, colorful designs |
| Water Resistance | High; suitable for functional and decorative use | Lower; primarily decorative due to porous nature |
Overview of Salt-Glazed Ceramics
Salt-glazed ceramics feature a distinctive glossy, textured surface created by introducing salt into a hot kiln, where it reacts with the silica in the clay to form a durable glassy coating. This technique, originating in 15th-century Germany, produces vessels with a unique orange-peel effect and enhanced resistance to liquids, making it ideal for decorative bowls. Compared to slipware, salt-glazed pieces often display a more rustic, natural aesthetic with subtle variations in color and finish.
Introduction to Slipware Techniques
Slipware techniques involve applying liquid clay slip to a ceramic surface before firing, creating intricate patterns and textures ideal for decorative bowls. Unlike salt-glazed ceramics, which develop a glossy, textured finish through salt vapor at high temperatures, slipware offers greater versatility in color and detailed design through various slip application methods such as trailing, painting, and marbling. Mastery of slipware enhances the aesthetic appeal of bowls by combining tactile surface interest with vibrant, layered decoration.
Historical Background and Origins
Salt-glazed ceramics originated in 15th-century Germany, where salt was introduced into the kiln to create a distinctive glossy, textured surface on stoneware, making it highly prized for decorative bowls. Slipware dates back to ancient times, with significant development during the Medieval period in England, utilizing liquid clay (slip) to create painted or trailed designs, offering vibrant and intricate decoration. Both techniques have rich historical roots that influenced decorative pottery styles across Europe, with salt glazing emphasizing texture and durability, while slipware focused on colorful, detailed ornamentation.
Key Differences in Materials Used
Salt-glazed ceramics are created by introducing salt into a hot kiln, resulting in a distinctive glossy, textured surface formed through a chemical reaction with the silica in the clay. Slipware involves coating the pottery with a liquid clay mixture called slip, which allows for intricate painted designs and a smoother surface texture. The key difference lies in salt-glazing's reactive, textured finish versus slipware's decorative, painted slip coating applied before firing.
Surface Texture and Visual Appeal
Salt-glazed ceramic bowls feature a distinctive glossy, slightly orange-peel texture created by vaporized salt reacting with the clay during firing, offering a rustic and tactile surface that enhances visual depth. Slipware bowls exhibit smooth or slightly raised patterns formed by applying liquid clay (slip) decorated with contrasting colors, resulting in intricate, painterly designs with vibrant and matte finishes. The choice between salt-glazed and slipware for decorative bowls depends on whether a more organic, textured aesthetic or detailed, colorful ornamentation is desired.
Durability and Functional Qualities
Salt-glazed ceramic offers exceptional durability due to its dense, vitrified surface created by the salt-firing process, making it highly resistant to chipping and scratching. Slipware, characterized by its decorative slip coating, provides moderate durability but is more prone to surface wear and requires careful handling to prevent damage. For functional qualities, salt-glazed ceramics excel in heat retention and are generally more food-safe, whereas slipware prioritizes intricate design and aesthetic appeal, often making it better suited for decorative rather than everyday functional use.
Artistic Styles and Decorative Potential
Salt-glazed ceramics exhibit a distinctive glossy, textured surface achieved through vaporized salt during firing, enhancing the tactile and visual depth ideal for rustic, earthy decorative bowls. Slipware utilizes liquid clay (slip) for intricate patterns and contrasting colors, enabling refined, detailed artistic styles from traditional to contemporary motifs. Both methods offer unique decorative potentials: salt-glazing emphasizes natural, organic aesthetics, while slipware allows versatile, controlled embellishments for expressive artistry.
Common Uses for Decorative Bowls
Salt-glazed ceramic decorative bowls are prized for their glassy, textured surfaces that enhance visual appeal and durability, making them ideal for rustic or artisanal home decor. Slipware bowls feature intricate, painted slip designs and smooth finishes, often used in traditional or folk-inspired decorative settings. Both styles serve as focal points on shelves or tables, with salt-glazed ceramics leaning toward a natural, earthy aesthetic and slipware offering vibrant patterns and color contrasts.
Collectibility and Market Value
Salt-glazed ceramics exhibit a distinctive textured surface created by spraying salt during firing, making them highly collectible due to their unique craftsmanship and historical significance, often commanding strong market values among antique enthusiasts. Slipware, characterized by its colorful slip decorations and smoother finish, attracts collectors who appreciate its vibrant designs and folk art heritage, typically resulting in variable market prices depending on artistic detail and provenance. Both types hold niche appeal, but salt-glazed pieces generally achieve higher auction prices due to rarity and specific regional interest.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Salt-glazed ceramics offer a distinctive glossy and textured surface created by introducing salt into the kiln at high temperatures, making them ideal for rustic, durable decorative bowls with a natural, earthy appeal. Slipware, characterized by its vibrant, painted slip designs applied before firing, provides greater flexibility in pattern and color, perfect for decorative bowls requiring intricate, colorful motifs. Choosing the right technique depends on the desired aesthetic, texture, and firing process, with salt glazing enhancing tactile depth and slipware emphasizing detailed, artistic expression.
Infographic: Salt-glazed ceramic vs Slipware for Decorative bowl
 azmater.com
azmater.com