Biscuit porcelain offers a matte, unglazed finish with a porous texture ideal for detailed sculptural vases. Faience, a tin-glazed earthenware, provides a glossy, colorful surface suitable for decorative vases with intricate painted designs.
Table of Comparison
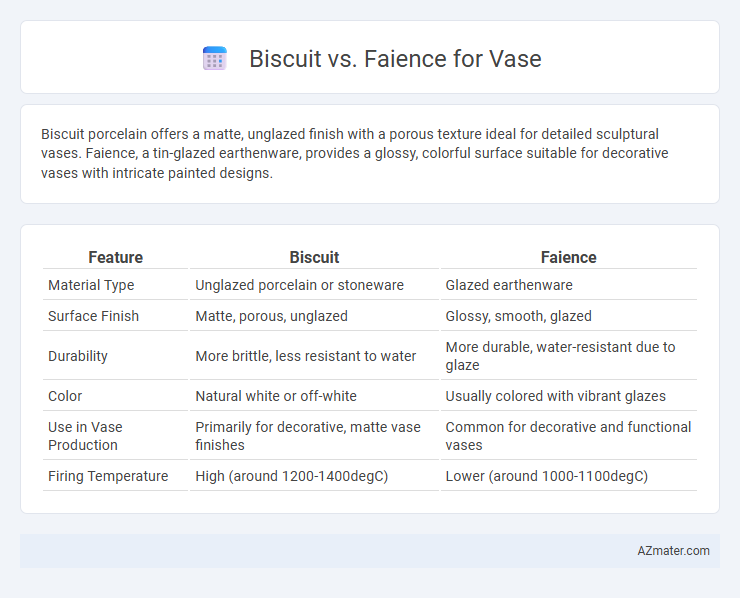
| Feature | Biscuit | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Unglazed porcelain or stoneware | Glazed earthenware |
| Surface Finish | Matte, porous, unglazed | Glossy, smooth, glazed |
| Durability | More brittle, less resistant to water | More durable, water-resistant due to glaze |
| Color | Natural white or off-white | Usually colored with vibrant glazes |
| Use in Vase Production | Primarily for decorative, matte vase finishes | Common for decorative and functional vases |
| Firing Temperature | High (around 1200-1400degC) | Lower (around 1000-1100degC) |
Introduction: Understanding Biscuit and Faience
Biscuit refers to unglazed, fired porcelain or earthenware known for its matte, porous surface that enhances intricate detailing and a natural aesthetic. Faience is a glazed ceramic material dating back to antiquity, characterized by its glossy finish and vibrant colors achieved through a silica-based glaze. Understanding the distinct properties of biscuit and faience is crucial for selecting the appropriate technique for vase production, balancing durability, texture, and visual appeal.
Historical Origins of Biscuit and Faience Vases
Biscuit vases, originating in the 18th century, are unglazed porcelain pieces celebrated for their matte, delicate texture resembling sculptural art, primarily produced in European manufactories like Sevres and Meissen. Faience vases trace back to 15th-century Italy and were widely popularized in French and Dutch pottery, characterized by tin-glazed earthenware with vibrant, glossy surfaces and intricate painted decorations. The historical development of biscuit and faience vases reflects the evolving ceramic techniques that distinguished porcelain's refined elegance from faience's colorful, rustic appeal.
Material Composition: Biscuit vs Faience
Biscuit porcelain is an unglazed, matte-finish ceramic made primarily from refined kaolin clay fired at high temperatures, resulting in a durable yet porous material. Faience is a glazed earthenware composed of a porous ceramic body coated with a tin or alkaline glaze, producing a glossy, colorful surface commonly enriched with intricate painted designs. The key distinction lies in biscuit's unglazed, natural clay texture versus faience's glazed, decorative finish, affecting both aesthetic qualities and durability in vases.
Production Techniques: Biscuit and Faience Methods
Biscuit vases are created through a firing process without glazing, resulting in a matte, unglazed surface achieved by firing the clay body once at high temperatures, enhancing fine detail and texture. Faience vases are produced using a tin-glazing technique, where the ceramic is dipped in a glaze made from a mixture of silica, tin oxide, and lead, then fired to create a shiny, opaque, and brightly colored surface. The production of biscuit relies on porcelain or stoneware clay fired at approximately 1200-1400degC, whereas faience employs earthenware clay fired at lower temperatures around 900-1050degC before glazing and refiring.
Surface Finish: Matte Texture vs Glazed Shine
Biscuit vases feature a matte texture achieved through unglazed porcelain, offering a soft, natural surface that highlights intricate sculptural details. Faience vases are characterized by a glossy, glazed finish that creates a vibrant, reflective shine, enhancing color depth and surface smoothness. The choice between biscuit and faience hinges on whether a muted, tactile feel or a bright, polished look best suits the vase's decorative intent.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Biscuit porcelain and faience both offer unique durability traits for vases, with biscuit porcelain excelling in strength due to its higher firing temperature, resulting in a vitrified, non-porous surface that resists chipping and cracking. Faience, characterized by its tin-glazed earthenware composition, is more porous and prone to surface wear over time, making it less durable for long-term use compared to biscuit porcelain. When prioritizing longevity, biscuit porcelain vases maintain structural integrity better under environmental stress, while faience requires more careful handling and maintenance to preserve its aesthetic appeal.
Aesthetic Appeal: Design and Color Possibilities
Biscuit porcelain offers a matte, unglazed surface that highlights intricate sculptural details with a soft, understated elegance, ideal for classical or minimalist vase designs. Faience, with its glazed, glossy finish, enables vibrant color palettes and intricate painted patterns, enhancing the vase's decorative appeal and making it a focal point in varied interior settings. The choice between biscuit and faience significantly impacts the vase's aesthetic versatility, with biscuit favoring subtle texture and form, while faience excels in vivid hues and ornamental complexity.
Common Uses of Biscuit and Faience Vases
Biscuit vases, characterized by their unglazed, matte finish, are commonly used for decorative purposes in antique and art collections due to their fine porcelain texture and detailed craftsmanship. Faience vases, made from glazed earthenware, are frequently found in functional and ornamental roles such as flower containers and colorful interior decor elements because of their vibrant glazes and durability. Both materials serve distinct purposes: biscuit emphasizes artistic value and delicate appearance, while faience prioritizes practicality and vivid coloration.
Collectibility and Market Value Differences
Biscuit porcelain vases, known for their unglazed, matte finish, appeal to collectors seeking fine texture and classical artistry, often commanding higher market values due to their detailed craftsmanship and rarity. Faience vases, characterized by their colorful, glazed surfaces and tin-based enamel, attract buyers interested in vibrant, durable decorative pieces, typically featuring lower but steady market prices. The collectibility of biscuit vases is driven by their historical prestige and artisanal quality, while faience's market value depends on style trends and condition within folk art and decorative ceramics sectors.
Choosing Between Biscuit and Faience for Vase Selection
Choosing between biscuit and faience for vase selection depends on the desired texture and finish; biscuit porcelain offers a matte, unglazed surface ideal for detailed sculptural effects, while faience features a glossy, glazed coating that enhances color vibrancy and durability. Biscuit vases are prized for their natural, earthy appearance and subtle tactile qualities, making them suitable for classic or antique-style decor. Faience vases provide a smooth, reflective surface resistant to moisture, making them practical for floral arrangements and contemporary interior designs.
Infographic: Biscuit vs Faience for Vase
 azmater.com
azmater.com