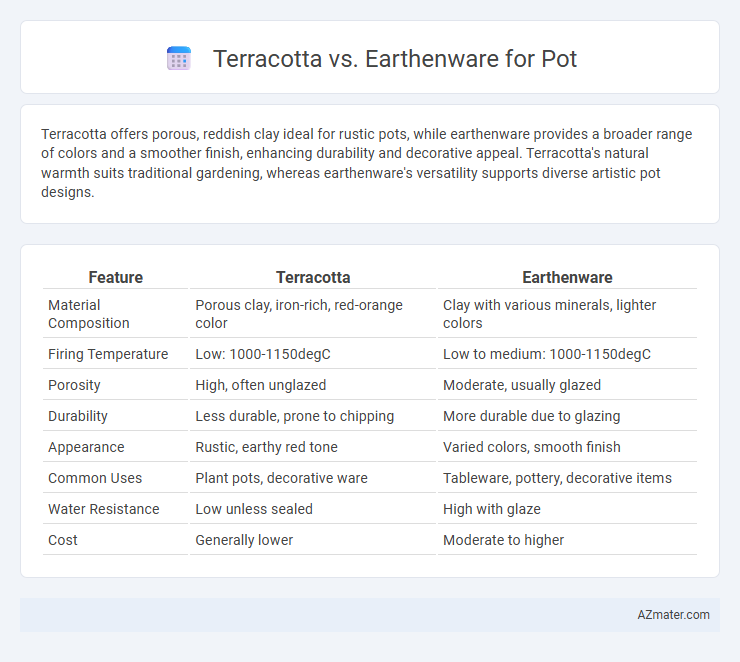
Terracotta offers porous, reddish clay ideal for rustic pots, while earthenware provides a broader range of colors and a smoother finish, enhancing durability and decorative appeal. Terracotta's natural warmth suits traditional gardening, whereas earthenware's versatility supports diverse artistic pot designs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Terracotta | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Porous clay, iron-rich, red-orange color | Clay with various minerals, lighter colors |
| Firing Temperature | Low: 1000-1150degC | Low to medium: 1000-1150degC |
| Porosity | High, often unglazed | Moderate, usually glazed |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to chipping | More durable due to glazing |
| Appearance | Rustic, earthy red tone | Varied colors, smooth finish |
| Common Uses | Plant pots, decorative ware | Tableware, pottery, decorative items |
| Water Resistance | Low unless sealed | High with glaze |
| Cost | Generally lower | Moderate to higher |
Understanding Terracotta and Earthenware
Terracotta and earthenware are both types of porous, low-fired clay materials commonly used for pottery, but terracotta is typically more porous and reddish due to iron oxide content, while earthenware can vary in color and often has a smoother surface finish. Terracotta pots are favored for their breathability, allowing air and moisture to pass through, which benefits plant roots, whereas earthenware pots may be glazed to enhance water retention and durability. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the right pot for specific gardening or decorative needs, balancing aesthetic preferences with functional qualities like drainage and moisture control.
Key Differences Between Terracotta and Earthenware
Terracotta pottery is characterized by its reddish-brown color due to iron-rich clay and is typically porous, requiring sealing for water retention, while earthenware includes a broader range of clay bodies fired at lower temperatures, resulting in varied colors from white to buff and lower porosity. Terracotta is fired at temperatures around 1000-1150degC, which gives it a rustic, porous texture, whereas earthenware is usually fired between 1000-1300degC, allowing for diverse finishes and stronger structures when glazed. Key differences include terracotta's distinct porous nature and iron oxide content versus earthenware's more versatile composition and firing range, affecting durability, appearance, and practical uses in pottery.
Material Composition and Properties
Terracotta is a porous, reddish clay fired at lower temperatures (1,000-1,150degC), resulting in a more porous and softer material ideal for plant pots due to its breathability and water absorption. Earthenware, made from a variety of clays fired at slightly higher temperatures (1,000-1,200degC), is generally less porous, more durable, and often coated with a glaze to enhance water retention and surface hardness. The key difference lies in terracotta's higher permeability and lower firing temperature compared to earthenware's denser composition and glazing options, influencing their suitability for different potting needs.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Terracotta pots are made from red clay fired at lower temperatures between 1000degC and 1150degC, resulting in a porous, breathable material ideal for plant roots. Earthenware, typically fired at slightly higher temperatures ranging from 1000degC to 1200degC, uses a wider variety of clays and often receives a glaze to improve durability and water resistance. The manufacturing process of terracotta emphasizes simplicity and natural aesthetics, while earthenware involves more refined shaping, glazing, and firing techniques to create diverse finishes and enhanced impermeability.
Porosity and Water Retention
Terracotta pots exhibit higher porosity compared to earthenware, allowing for better air circulation and improved root oxygenation but resulting in quicker water evaporation. Earthenware has a denser composition, offering lower porosity and superior water retention, which helps maintain consistent soil moisture levels. Understanding the porosity differences between terracotta and earthenware is crucial for selecting the ideal pot based on plant water needs and environmental conditions.
Strength and Durability
Terracotta pots are known for their moderate strength and porous nature, making them more susceptible to cracking under extreme weather conditions compared to earthenware. Earthenware offers higher durability due to a denser composition and a fired glaze that enhances resistance to moisture and mechanical stress. Gardeners often prefer earthenware pots for long-lasting use, while terracotta is favored for its breathability and natural aesthetic despite lower toughness.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Variations
Terracotta pots showcase a warm, natural reddish-brown hue with a matte finish, offering a rustic and earthy aesthetic that complements Mediterranean and Southwestern decor styles. Earthenware pots provide a broader color palette, including natural browns, reds, and sometimes glazed finishes in vibrant blues, greens, and yellows, enhancing decorative versatility for both traditional and contemporary settings. The porous texture of terracotta contrasts with the often smoother, glazed surface of earthenware, influencing both visual appeal and tactile experience.
Suitability for Indoor and Outdoor Use
Terracotta pots offer excellent breathability and natural insulation, making them ideal for indoor plants that require good airflow and moisture regulation, but they can be prone to cracking in freezing outdoor conditions. Earthenware pots, often glazed, provide better water retention and are more durable against outdoor elements, thus suitable for both indoor decorative use and outdoor gardening in moderate climates. Choosing between terracotta and earthenware depends on the specific environmental conditions and plant needs, with terracotta favored for indoor settings and earthenware preferred for outdoor versatility.
Maintenance and Care Considerations
Terracotta pots require regular sealing to prevent water absorption and cracking, whereas earthenware pots are naturally more porous but often glazed to enhance durability and ease of cleaning. Both materials benefit from gentle washing with mild soap and avoiding harsh chemicals to preserve the surface integrity. Proper storage in dry conditions reduces the risk of mold and frost damage for both terracotta and earthenware pots.
Choosing the Right Pot for Your Plants
Terracotta pots offer excellent breathability and natural insulation, making them ideal for plants requiring well-drained soil and moderate moisture retention, while earthenware pots are typically glazed, providing better water retention and a wider variety of decorative finishes. Choosing the right pot depends on your plant's watering needs, with terracotta suited for drought-tolerant species and earthenware better for moisture-loving plants. Consider factors like porosity, weight, and aesthetic preferences to ensure optimal growth and durability for your specific plant type.
Infographic: Terracotta vs Earthenware for Pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com