Alumina tiles exhibit superior hardness and thermal resistance compared to porcelain tiles, making them ideal for industrial and high-wear applications. Porcelain tiles offer better water absorption rates and aesthetic versatility, suited for residential and decorative flooring.
Table of Comparison
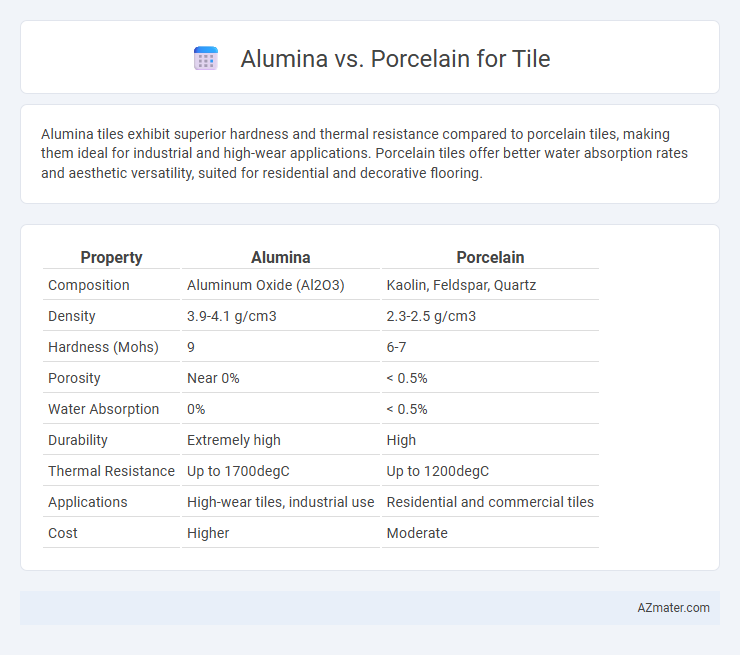
| Property | Alumina | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) | Kaolin, Feldspar, Quartz |
| Density | 3.9-4.1 g/cm3 | 2.3-2.5 g/cm3 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 9 | 6-7 |
| Porosity | Near 0% | < 0.5% |
| Water Absorption | 0% | < 0.5% |
| Durability | Extremely high | High |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 1700degC | Up to 1200degC |
| Applications | High-wear tiles, industrial use | Residential and commercial tiles |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate |
Introduction to Alumina and Porcelain Tiles
Alumina tiles consist primarily of aluminum oxide, offering superior hardness and high wear resistance ideal for industrial applications and heavy-traffic areas. Porcelain tiles, made from refined clay fired at high temperatures, feature low porosity and excellent moisture resistance, making them perfect for residential and commercial flooring. Both materials provide durability but differ significantly in composition, mechanical properties, and typical use cases.
Composition and Material Structure
Alumina tiles consist primarily of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), offering high hardness and excellent wear resistance due to their dense, crystalline microstructure. Porcelain tiles are made from a mixture of finely ground clays, kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, sintered at high temperatures to create a vitrified, non-porous surface. Alumina's rigid ceramic lattice enhances durability for industrial applications, while porcelain's glass-like matrix provides moisture resistance and aesthetic versatility for residential flooring.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Alumina tiles are produced through a high-temperature sintering process using aluminum oxide powders, resulting in dense, wear-resistant surfaces ideal for industrial applications. Porcelain tiles undergo a combination of fine clay, feldspar, and quartz, fired at ultra-high temperatures to achieve a vitrified, water-resistant finish favored in residential and commercial flooring. The manufacturing of alumina emphasizes purity and strength, while porcelain prioritizes aesthetic versatility and moisture resistance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Alumina tiles exhibit superior mechanical strength due to their high aluminum oxide content, making them highly resistant to wear, impact, and abrasion. Porcelain tiles, composed primarily of refined clay and quartz, offer excellent durability and strong resistance to moisture and staining but generally have lower impact resistance compared to alumina. The choice between alumina and porcelain tiles depends on application demands, with alumina favored in industrial or high-traffic areas and porcelain preferred for aesthetic and versatile residential settings.
Chemical and Thermal Resistance
Alumina tiles exhibit superior chemical resistance due to their high purity aluminum oxide content, making them ideal for environments with exposure to acids, alkalis, and solvents. Porcelain tiles, composed primarily of refined clay and quartz, offer excellent thermal resistance, maintaining structural integrity under rapid temperature changes and high heat. Alumina's thermal stability surpasses that of porcelain, enabling its use in extreme industrial applications where both chemical inertness and heat resistance are crucial.
Aesthetic Options and Surface Finishes
Alumina tiles offer a sleek, modern aesthetic with a smooth, polished surface finish that enhances their durability and resistance to wear. Porcelain tiles provide a broader range of aesthetic options, including matte, glossy, textured, and patterned finishes, allowing for versatile design applications. The dense composition of porcelain supports high-quality surface finishes that mimic natural stone, wood, or concrete, making it ideal for diverse interior or exterior projects.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Alumina tiles excel in high-wear industrial applications such as chemical processing, metal fabrication, and mining due to their superior hardness and chemical resistance, making them ideal for environments requiring abrasion and corrosion protection. Porcelain tiles are favored in architectural and commercial spaces for their aesthetic versatility, water resistance, and durability, commonly used in flooring, wall cladding, and exterior facades. The choice between alumina and porcelain tiles hinges on the specific industry use case, with alumina dominating heavy-duty industrial contexts and porcelain preferred in design-centric construction projects.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Alumina tiles generally cost more upfront than porcelain tiles due to their superior hardness and durability, making them an ideal choice for high-traffic or industrial areas. Porcelain tiles offer a more budget-friendly option with good resistance to wear and moisture, appealing to residential and moderate-traffic commercial spaces. When considering long-term economic value, alumina's extended lifespan and lower maintenance requirements can result in greater overall savings despite the higher initial investment.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Alumina tiles offer easier installation due to their consistent size and lightweight nature compared to heavier, more fragile porcelain tiles requiring specialized cutting tools. Maintenance of alumina is simpler, as its non-porous surface resists stains and requires only regular cleaning, whereas porcelain tiles demand periodic sealing to prevent moisture infiltration and grout discoloration. Choosing alumina reduces long-term upkeep costs, while porcelain provides higher durability but involves more complex installation and maintenance routines.
Choosing the Right Tile: Alumina or Porcelain?
Selecting between alumina and porcelain tiles hinges on performance needs and aesthetic preferences; alumina tiles offer superior hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for high-traffic or industrial settings. Porcelain tiles, prized for their low porosity and diverse design options, excel in residential and commercial installations requiring moisture resistance and elegant finishes. Evaluating factors such as durability, water absorption rate, and style versatility ensures the right choice for flooring or wall applications.
Infographic: Alumina vs Porcelain for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com