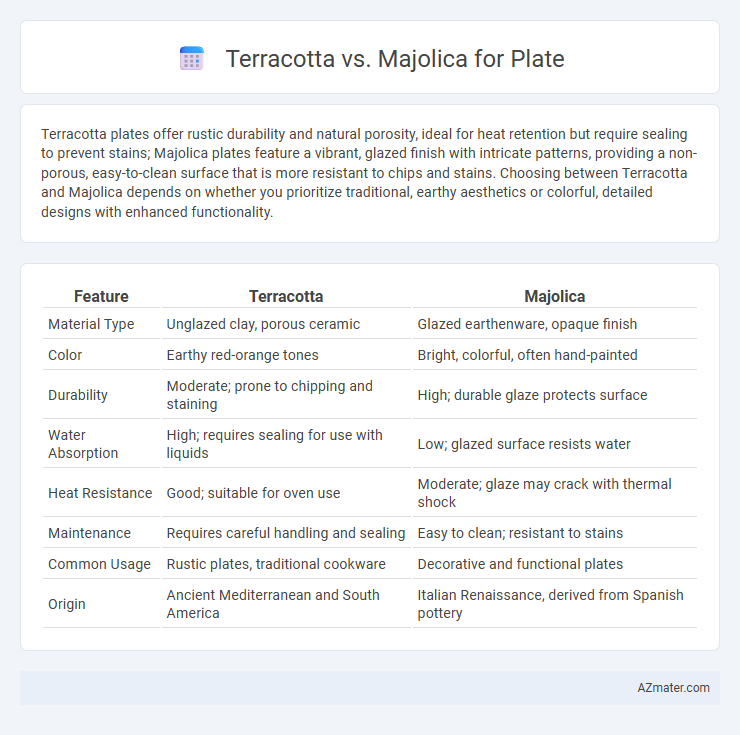
Terracotta plates offer rustic durability and natural porosity, ideal for heat retention but require sealing to prevent stains; Majolica plates feature a vibrant, glazed finish with intricate patterns, providing a non-porous, easy-to-clean surface that is more resistant to chips and stains. Choosing between Terracotta and Majolica depends on whether you prioritize traditional, earthy aesthetics or colorful, detailed designs with enhanced functionality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Terracotta | Majolica |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Unglazed clay, porous ceramic | Glazed earthenware, opaque finish |
| Color | Earthy red-orange tones | Bright, colorful, often hand-painted |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to chipping and staining | High; durable glaze protects surface |
| Water Absorption | High; requires sealing for use with liquids | Low; glazed surface resists water |
| Heat Resistance | Good; suitable for oven use | Moderate; glaze may crack with thermal shock |
| Maintenance | Requires careful handling and sealing | Easy to clean; resistant to stains |
| Common Usage | Rustic plates, traditional cookware | Decorative and functional plates |
| Origin | Ancient Mediterranean and South America | Italian Renaissance, derived from Spanish pottery |
Introduction to Terracotta and Majolica Plates
Terracotta plates are crafted from natural clay, offering porous, rustic, and earthy textures ideal for casual dining and traditional culinary presentations. Majolica plates, coated with a tin-glazed earthenware surface, provide vibrant, colorful designs and a non-porous, glossy finish, making them both decorative and functional. The choice between terracotta and majolica plates depends on desired aesthetics, durability, and intended use in tableware collections.
Material Composition of Terracotta vs Majolica
Terracotta plates are crafted from natural clay that is porous and unglazed, giving them a rustic, earthy texture with a reddish-brown hue due to the iron content in the soil. Majolica plates are made from a finer clay base coated with a white tin glaze, creating a smooth, non-porous surface that allows for vibrant, colorful hand-painted designs. The key difference in material composition is terracotta's raw, breathable clay versus majolica's refined clay with a protective, glossy glaze.
Historical Origins and Cultural Significance
Terracotta, originating from ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley, is valued for its porous, earthenware quality and widespread use in functional pottery and architectural elements. Majolica developed during the Italian Renaissance, characterized by its tin-glazed, vividly painted surface, reflecting Mediterranean artistic traditions and symbolizing social status and artistic expression. Both materials embody distinct cultural heritages, with terracotta representing utilitarian simplicity and majolica showcasing decorative sophistication.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Terracotta plates are made by shaping natural clay and firing it at lower temperatures, typically between 1000degC and 1150degC, resulting in a porous, earthy material that requires sealing for food safety. Majolica plates undergo a two-step firing process: first, a bisque firing of shaped clay at higher temperatures around 1000degC, followed by glazing with tin-oxide enamel and a second firing at slightly lower temperatures to create a glossy, non-porous surface with vibrant colors. The manufacturing difference primarily lies in terracotta's simpler, single firing and porous nature versus majolica's complex glazing and dual firing process that enhances durability and decorative appeal.
Design and Artistic Styles
Terracotta plates showcase earthy, rustic aesthetics with a warm, natural reddish-brown tone, often featuring hand-painted motifs that emphasize traditional and folk art styles. Majolica plates are known for their vibrant, glossy glazes and intricate, colorful designs inspired by Renaissance and Mediterranean artistry, offering a more decorative and ornate appearance. The design versatility of Majolica allows for detailed scenes and floral patterns, while Terracotta typically maintains a simpler, organic look that highlights craftsmanship and texture.
Durability and Daily Use
Terracotta plates offer excellent durability due to their dense, porous clay composition, making them resistant to chipping and suitable for everyday use. Majolica plates, characterized by their tin-glazed earthenware surface, provide a vibrant finish but are more prone to scratching and require gentle handling to maintain their appearance. For daily use, terracotta's robustness and heat retention make it ideal, while majolica is better suited for decorative or occasional serving contexts.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Terracotta plates are porous and often untreated, making them more susceptible to absorbing liquids and bacteria, which can pose safety concerns unless properly glazed and sealed. Majolica plates feature a non-porous, lead-free tin glaze that ensures excellent food compatibility by preventing contamination and making them safer for serving acidic or oily dishes. Choosing majolica for plates guarantees better hygiene and durability, while terracotta requires careful consideration of glazing quality to ensure food safety.
Maintenance and Care Tips
Terracotta plates require regular sealing to prevent moisture absorption and stains, with gentle hand washing recommended to avoid cracking or chipping. Majolica plates, being glazed and more durable, tolerate dishwasher cleaning but should still be handled carefully to preserve the vibrant enamel and prevent glaze damage. Both materials benefit from avoiding extreme temperature changes to maintain integrity and longevity.
Cost Analysis: Terracotta vs Majolica
Terracotta plates generally offer a lower cost due to their simpler production process and abundant raw materials, making them an economical choice for everyday use. Majolica plates, characterized by their intricate glazing and vibrant designs, involve higher production expenses contributing to a more premium price point. Evaluating cost effectiveness requires balancing Terracotta's affordability against Majolica's decorative appeal and durability for specific dining needs.
Best Applications for Each Plate Type
Terracotta plates excel in rustic and casual dining settings due to their porous nature, which enhances flavor absorption and retains heat, making them ideal for serving warm, hearty dishes like stews and grilled vegetables. Majolica plates feature a glazed finish with vibrant colors and intricate designs, perfect for decorative presentations and formal occasions where visual appeal is crucial, such as serving appetizers or desserts. Terracotta suits artisanal, earthy-themed meals, while Majolica complements refined, elegant dining experiences needing durability and aesthetic charm.
Infographic: Terracotta vs Majolica for Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com