Photonic ceramics offer superior thermal shock resistance and higher heat conductivity compared to glass ceramics, making them ideal for high-performance cooktops. Glass ceramics provide excellent durability and aesthetic versatility but typically have lower thermal efficiency than photonic ceramics.
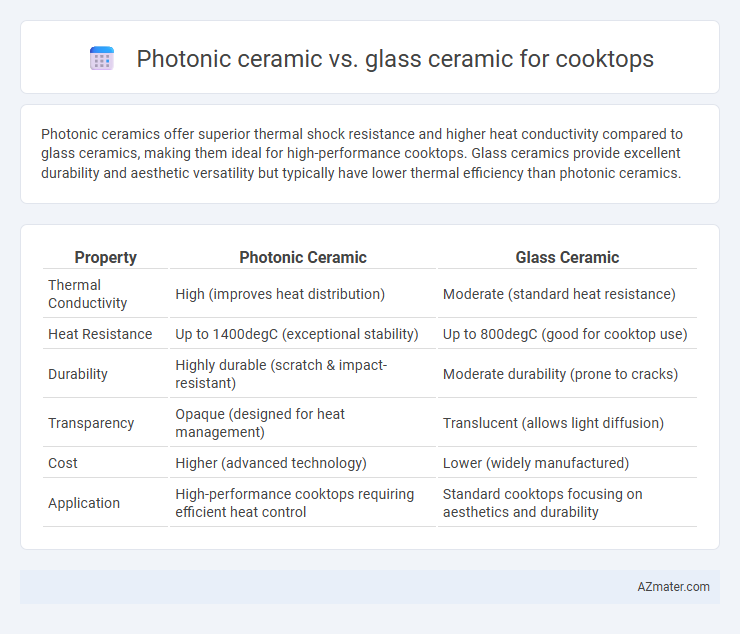
Table of Comparison
| Property | Photonic Ceramic | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High (improves heat distribution) | Moderate (standard heat resistance) |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 1400degC (exceptional stability) | Up to 800degC (good for cooktop use) |
| Durability | Highly durable (scratch & impact-resistant) | Moderate durability (prone to cracks) |
| Transparency | Opaque (designed for heat management) | Translucent (allows light diffusion) |
| Cost | Higher (advanced technology) | Lower (widely manufactured) |
| Application | High-performance cooktops requiring efficient heat control | Standard cooktops focusing on aesthetics and durability |
Introduction to Cooktop Materials
Photonic ceramics offer superior thermal stability and rapid heat distribution compared to traditional glass ceramics used in cooktops. These advanced materials exhibit enhanced durability and resistance to thermal shock, ensuring longer lifespan and safety during high-temperature cooking. Glass ceramics, while cost-effective and widely used, typically provide moderate heat retention and may be more prone to cracking under extreme temperature changes.
What is Photonic Ceramic?
Photonic ceramic is an advanced material engineered with nanostructures that optimize light absorption and heat distribution, making it highly efficient for cooktop surfaces. Unlike traditional glass ceramic, photonic ceramic offers superior thermal conductivity and greater resistance to thermal shock, enhancing cooking performance and durability. Its ability to evenly radiate infrared heat results in faster cooking times and improved energy efficiency.
What is Glass Ceramic?
Glass ceramic is a type of material engineered through controlled crystallization of glass, resulting in exceptional heat resistance and thermal stability ideal for cooktop surfaces. Unlike photonic ceramics, glass ceramics combine transparency and durability, allowing even heat distribution while maintaining resistance to thermal shock. Their low thermal expansion coefficient ensures minimal deformation under high temperatures, making them a preferred choice for efficient and safe cooking applications.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Distribution
Photonic ceramics exhibit superior thermal resistance compared to glass ceramics, with a higher tolerance for rapid temperature changes and extreme heat levels, reducing the risk of cracking or warping during cooking. The advanced crystalline structure in photonic ceramics enables more uniform heat distribution across the cooktop surface, enhancing cooking efficiency and preventing hot spots. Glass ceramics, while offering good thermal shock resistance, generally provide less optimal heat spread and lower maximum temperature endurance than photonic ceramic cooktops.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Photonic ceramics exhibit superior durability compared to glass ceramics due to their dense microstructure and enhanced thermal stability, resisting cracks under high heat. Scratch resistance in photonic ceramics is significantly higher as the material composition includes harder crystalline phases, reducing wear from cookware movement. Glass ceramics offer moderate durability but are more prone to surface scratches and chip formation under mechanical stress, limiting their lifespan on cooktops.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Photonic ceramic cooktops utilize advanced light-based technology to deliver rapid and precise heating, resulting in higher energy efficiency compared to traditional glass ceramic surfaces. Glass ceramic cooktops typically consume more energy due to slower heat conduction and retention properties, causing longer cooking times and increased power usage. Photonic ceramic's superior thermal responsiveness translates to reduced energy waste and cost savings over prolonged kitchen use.
Safety Features and Chemical Stability
Photonic ceramics used in cooktops exhibit superior chemical stability due to their resistance to thermal shock, corrosion, and high-temperature degradation, ensuring long-lasting durability and safety during cooking. Glass ceramics provide excellent safety features with their smooth, non-porous surface that resists staining and prevents bacterial growth, while also maintaining high resistance to heat and mechanical stress. Both materials ensure safe cooking environments, but photonic ceramics generally offer enhanced chemical inertness and thermal stability that reduce the risk of cracks or breaks under extreme temperature changes.
Aesthetic Appeal and Customization Options
Photonic ceramic cooktops offer a sleek, high-gloss finish with vibrant color options that enhance modern kitchen aesthetics, while glass ceramic cooktops provide a smooth, matte or glossy surface with more traditional, neutral tones. Photonic ceramic materials allow for advanced customization, including embedded lighting and print patterns, boosting personalized design possibilities beyond the standard solid colors of glass ceramic. The innovative photonic ceramic technology facilitates unique visual effects that appeal to contemporary tastes, making it ideal for those prioritizing a distinctive and customizable kitchen appearance.
Cost and Availability
Photonic ceramics generally offer higher durability and thermal resistance than glass ceramics, but they come at a significantly higher cost, making them less common in budget cooktops. Glass ceramics dominate the market due to their affordable price point and widespread availability, providing efficient heat distribution suitable for most household cooking needs. The balance between cost-effectiveness and performance often leads consumers to prefer glass ceramic cooktops over photonic ceramic alternatives.
Summary: Choosing the Right Cooktop Material
Photonic ceramic cooktops offer superior thermal conductivity and durability compared to glass ceramic, enhancing cooking efficiency and heat distribution. Glass ceramic cooktops provide a smooth, aesthetically pleasing surface with good heat resistance but are generally less impact-resistant and slower to heat. Selecting the right cooktop material depends on balancing performance needs, durability, and budget preferences for optimal kitchen functionality.
Infographic: Photonic ceramic vs Glass ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com