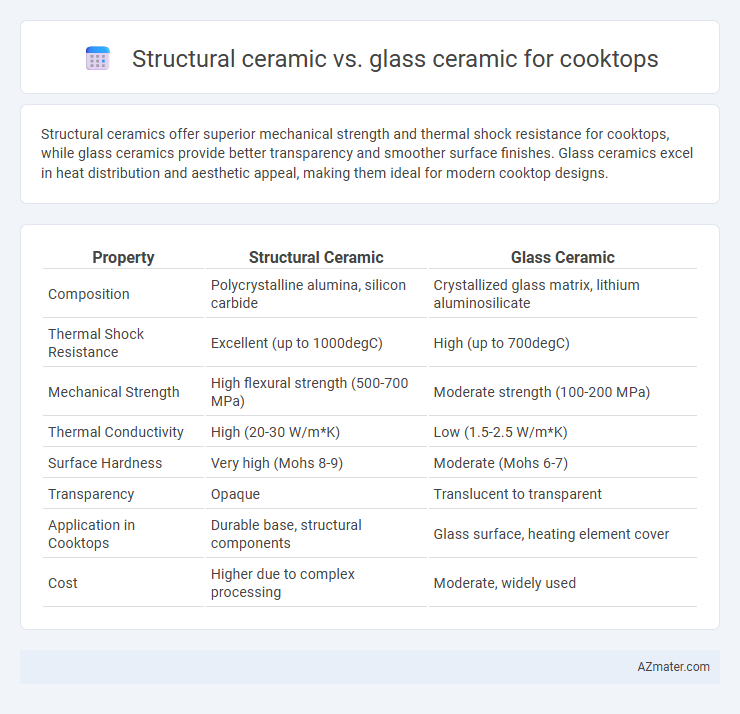
Structural ceramics offer superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance for cooktops, while glass ceramics provide better transparency and smoother surface finishes. Glass ceramics excel in heat distribution and aesthetic appeal, making them ideal for modern cooktop designs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Structural Ceramic | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Polycrystalline alumina, silicon carbide | Crystallized glass matrix, lithium aluminosilicate |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent (up to 1000degC) | High (up to 700degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | High flexural strength (500-700 MPa) | Moderate strength (100-200 MPa) |
| Thermal Conductivity | High (20-30 W/m*K) | Low (1.5-2.5 W/m*K) |
| Surface Hardness | Very high (Mohs 8-9) | Moderate (Mohs 6-7) |
| Transparency | Opaque | Translucent to transparent |
| Application in Cooktops | Durable base, structural components | Glass surface, heating element cover |
| Cost | Higher due to complex processing | Moderate, widely used |
Introduction to Cooktop Surface Materials
Structural ceramics used in cooktop surfaces provide exceptional thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, making them ideal for high-heat cooking environments. Glass ceramics offer a smooth, sleek appearance with excellent heat distribution and easy cleaning properties, often preferred for their aesthetic appeal and durability. Selecting between structural and glass ceramics depends on balancing performance needs such as durability and heat management with design preferences in modern kitchen appliances.
Overview of Structural Ceramics
Structural ceramics, made from materials such as alumina, zirconia, and silicon carbide, exhibit exceptional mechanical strength, high-temperature resistance, and superior wear resistance, making them ideal for demanding applications like cooktops. These ceramics maintain structural integrity under thermal stress and mechanical loads, providing long-term durability and stability compared to glass ceramics. Glass ceramics, while thermally resistant and aesthetically pleasing, generally lack the mechanical robustness of structural ceramics, limiting their use in high-stress cooktop components.
Overview of Glass Ceramics
Glass ceramics for cooktops consist of crystalline structures embedded within a glass matrix, offering superior thermal shock resistance and smooth surfaces ideal for induction and radiant heating elements. Their ability to maintain strength at high temperatures and resist scratches makes them popular for modern kitchen appliances. Compared to structural ceramics, glass ceramics provide enhanced aesthetic appeal and ease of cleaning while delivering reliable durability under frequent thermal cycling.
Thermal Resistance: Structural vs Glass Ceramic
Structural ceramics exhibit superior thermal resistance due to their dense microstructure and high melting points, typically above 2000degC, making them highly durable under extreme temperature fluctuations in cooktops. Glass ceramics, like vitroceramics, combine properties of both glass and ceramics, offering excellent thermal shock resistance and can withstand sudden temperature changes up to around 800degC without cracking. The higher thermal conductivity and stability of glass ceramics provide faster heat transfer and improved efficiency, while structural ceramics excel in maintaining integrity under prolonged high-heat exposure.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Structural ceramics used in cooktops, such as alumina and silicon carbide, exhibit superior mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock compared to glass ceramics, making them ideal for environments subjected to heavy impacts and rapid temperature changes. Glass ceramics, like those made from lithium aluminosilicate, offer good durability and heat resistance but generally have lower fracture toughness and are more prone to cracking under mechanical stress. The enhanced toughness and wear resistance of structural ceramics contribute to longer lifespan and improved performance in demanding kitchen applications.
Heat Distribution and Cooking Performance
Structural ceramics offer superior heat resistance and even heat distribution, ensuring consistent cooking temperatures across the cooktop surface. Glass ceramics provide rapid heat response and excellent thermal shock resistance, allowing for quick temperature adjustments and enhanced cooking precision. Both materials deliver reliable performance, but structural ceramics excel in durability, while glass ceramics optimize energy efficiency and cooking speed.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Structural ceramics offer superior scratch resistance compared to glass ceramics due to their dense, crystalline microstructure and higher hardness levels, making them highly durable for cooktop surfaces. In terms of impact resistance, glass ceramics exhibit better thermal shock resistance and can absorb impact energy more effectively, minimizing cracks and fractures under sudden temperature changes. Choosing between the two materials depends on prioritizing either scratch resistance (structural ceramics) or impact and thermal shock resilience (glass ceramics) for cooktop applications.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Options
Structural ceramics offer high design flexibility due to their superior mechanical strength and thermal stability, allowing for thinner, more intricate cooktop designs that withstand heavy use and high temperatures. Glass ceramics provide a sleek, smooth surface with excellent aesthetic options, including customizable colors and patterns, enhancing modern kitchen appeal while maintaining heat resistance. Combining both materials can optimize cooktop design by balancing durability with diverse visual styles to meet various consumer preferences.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Structural ceramics used in cooktops offer high durability and resistance to scratches, making maintenance straightforward with regular wiping using mild detergents. Glass ceramics, while visually appealing with their smooth and glossy surface, require careful cleaning to avoid streaks and scratches; specialized non-abrasive cleaners are recommended. Both materials benefit from quick cleanup of spills to prevent staining, but structural ceramics generally provide greater longevity under rigorous use.
Cost, Longevity, and Consumer Choice
Structural ceramics for cooktops typically offer higher durability and thermal resistance compared to glass ceramics, making them a longer-lasting investment despite a higher upfront cost. Glass ceramics are generally more affordable and provide smoother surfaces that enhance aesthetic appeal, though they may be more prone to scratches and thermal stress over time. Consumer choice often hinges on balancing budget constraints with the desired longevity and surface performance, with structural ceramics favored in professional kitchens and glass ceramics popular in residential settings.
Infographic: Structural ceramic vs Glass ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com