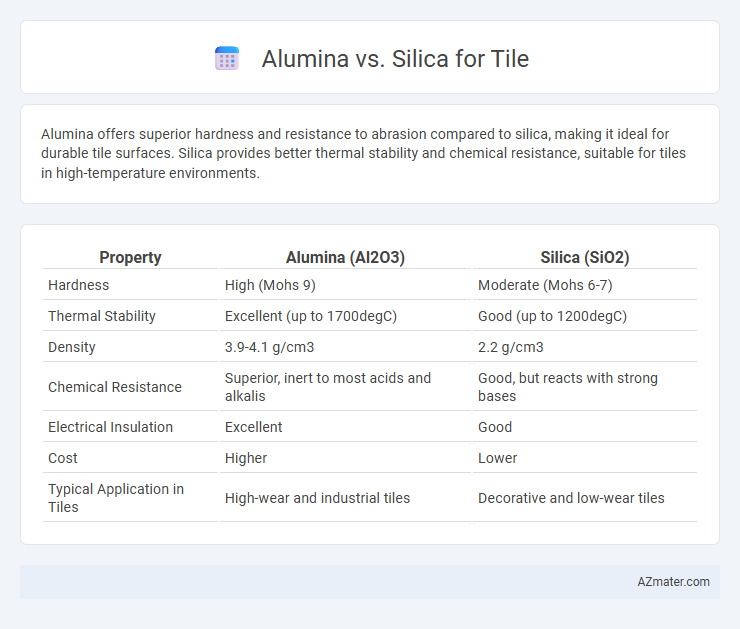
Alumina offers superior hardness and resistance to abrasion compared to silica, making it ideal for durable tile surfaces. Silica provides better thermal stability and chemical resistance, suitable for tiles in high-temperature environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alumina (Al2O3) | Silica (SiO2) |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | High (Mohs 9) | Moderate (Mohs 6-7) |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent (up to 1700degC) | Good (up to 1200degC) |
| Density | 3.9-4.1 g/cm3 | 2.2 g/cm3 |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior, inert to most acids and alkalis | Good, but reacts with strong bases |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Application in Tiles | High-wear and industrial tiles | Decorative and low-wear tiles |
Introduction to Alumina and Silica in Tile Manufacturing
Alumina and silica are critical materials in tile manufacturing, each contributing unique properties to the final product. Alumina enhances wear resistance and mechanical strength due to its high hardness and thermal stability, making it ideal for durable flooring tiles. Silica provides excellent flexibility and thermal insulation, improving the tile's ability to withstand temperature variations and reduce thermal stress during firing processes.
Chemical Properties: Alumina vs Silica
Alumina (Al2O3) exhibits high chemical stability and resistance to acidic and basic environments, making it ideal for tile applications requiring durability against chemical corrosion. Silica (SiO2), while chemically inert and stable under most conditions, can react with strong alkalis, which may limit its effectiveness in environments exposed to high pH levels. The superior hardness and resistance to chemical attack of alumina contribute to enhanced longevity and performance in demanding tile installations compared to silica-based materials.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Alumina tiles exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to silica tiles, with hardness values often exceeding 9 on the Mohs scale, making them highly resistant to wear and abrasion. Alumina's dense microstructure contributes to enhanced durability, allowing it to withstand high-impact and thermal stress environments better than silica tiles, which tend to be more brittle and prone to cracking under similar conditions. The exceptional fracture toughness and compressive strength of alumina make it the preferred choice for industrial applications requiring long-lasting, heavy-duty tile performance.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Alumina exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to silica, making it ideal for tiles exposed to high temperatures. Alumina tiles can withstand temperatures exceeding 1600degC without significant degradation, while silica tiles typically tolerate up to 1200degC before losing structural integrity. This enhanced thermal performance ensures alumina-based tiles maintain durability and mechanical strength in extreme heat environments.
Effects on Tile Aesthetics and Surface Finish
Alumina enhances tile durability and imparts a glossy, smooth surface finish that resists scratches and wear, making it ideal for high-traffic areas. Silica contributes to a matte or satin texture with a more natural, tactile feel, but may be more prone to surface abrasion over time. The choice between alumina and silica significantly influences tile aesthetic, with alumina delivering a sleek, polished look and silica offering a subtle, organic appearance.
Cost Efficiency and Material Availability
Alumina tiles offer higher cost efficiency due to their superior durability and resistance to wear, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance expenses. Silica tiles, while generally less expensive upfront, may incur higher long-term costs because of their lower hardness and susceptibility to thermal shock. Alumina's widespread industrial availability ensures consistent supply and competitive pricing, whereas silica's supply can fluctuate with varying demand in the glass and ceramics industries.
Impact on Water Absorption and Porosity
Alumina-rich tiles exhibit lower water absorption rates and reduced porosity compared to silica-based tiles, enhancing durability and resistance to moisture damage. High alumina content forms a denser microstructure that minimizes pore connectivity, effectively limiting water penetration. Silica tiles, with higher porosity, tend to absorb more water, increasing the risk of cracking and surface degradation over time.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Alumina tiles offer excellent durability and corrosion resistance while requiring significant energy for production, resulting in a higher carbon footprint compared to silica tiles. Silica tiles, often derived from abundant natural quartz, tend to have a lower environmental impact due to more energy-efficient manufacturing processes and greater recyclability. Choosing silica tiles supports sustainability goals through reduced resource consumption and enhanced potential for circular use in construction materials.
Performance in Specialized Tile Applications
Alumina offers superior hardness and abrasion resistance compared to silica, making it ideal for high-wear, specialized tile applications such as industrial flooring and heavy-traffic areas. Its high thermal stability and excellent chemical resistance enhance durability in extreme environments, outperforming silica-based tiles. Silica tiles provide adequate strength and thermal shock resistance but generally lack the robust performance characteristics required for specialized, high-stress tile uses.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Your Tiling Needs
Alumina offers superior hardness and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-traffic tile applications where durability is critical. Silica provides excellent chemical stability and thermal resistance, suitable for decorative or less demanding environments. Selecting between alumina and silica depends on balancing wear resistance with aesthetic and environmental factors to meet specific tiling requirements.
Infographic: Alumina vs Silica for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com