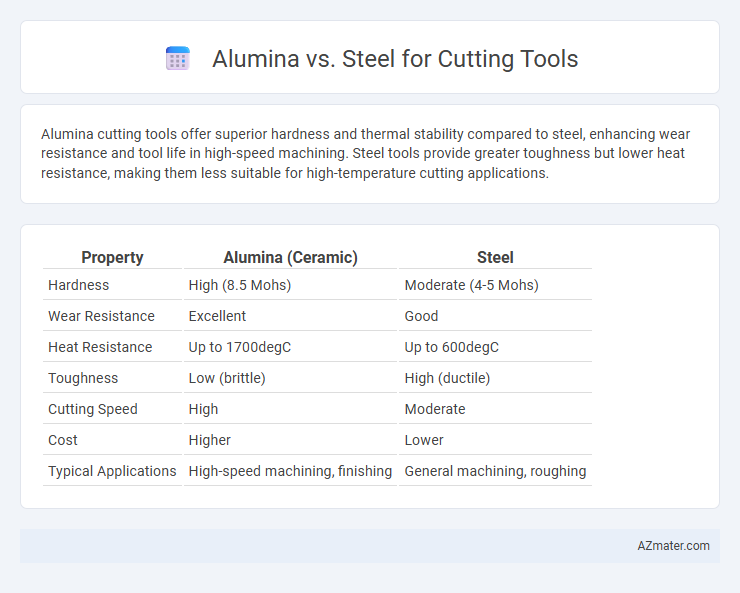
Alumina cutting tools offer superior hardness and thermal stability compared to steel, enhancing wear resistance and tool life in high-speed machining. Steel tools provide greater toughness but lower heat resistance, making them less suitable for high-temperature cutting applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alumina (Ceramic) | Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | High (8.5 Mohs) | Moderate (4-5 Mohs) |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 1700degC | Up to 600degC |
| Toughness | Low (brittle) | High (ductile) |
| Cutting Speed | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Applications | High-speed machining, finishing | General machining, roughing |
Introduction: Alumina vs Steel in Cutting Tools
Alumina and steel are two prominent materials used in cutting tools, each offering distinct advantages based on their physical and chemical properties. Alumina, known for its exceptional hardness and thermal resistance, excels in high-speed cutting applications and abrasive environments. Steel, particularly high-speed steel (HSS), provides superior toughness and flexibility, making it ideal for precision and impact-intensive machining tasks.
Material Composition and Properties
Alumina cutting tools are primarily composed of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), offering exceptional hardness and excellent wear resistance at high temperatures, making them ideal for machining abrasive materials. Steel cutting tools, typically made from high-speed steel (HSS) or tool steels with carbon, chromium, and tungsten, provide toughness, flexibility, and impact resistance but have lower hardness compared to alumina. The thermal conductivity of alumina is lower than steel, resulting in better heat retention in the cutting zone, which enhances tool life when machining hard materials.
Hardness Comparison
Alumina exhibits a hardness of approximately 9 on the Mohs scale, making it highly resistant to wear and suitable for abrasive cutting applications. Steel cutting tools, depending on the alloy and heat treatment, typically range between 7 and 8 on the Mohs hardness scale, offering toughness but lower hardness than alumina. The superior hardness of alumina enhances tool life and precision in cutting hard materials, while steel provides better impact resistance in dynamic machining conditions.
Wear Resistance and Durability
Alumina cutting tools exhibit superior wear resistance due to their high hardness and thermal stability, making them ideal for abrasive machining operations. Steel cutting tools, while tougher and more impact-resistant, generally have lower wear resistance and require coatings or alloys to enhance durability. The choice between alumina and steel depends on the cutting application, with alumina favored for high-speed, high-temperature environments and steel for versatile, moderate-duty tasks.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Alumina cutting tools exhibit superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to steel, allowing them to maintain hardness and cutting efficiency at elevated temperatures above 1000degC. Steel tools typically lose hardness and degrade rapidly under high heat, limiting their use in high-speed or high-temperature machining applications. The superior heat resistance of alumina enhances tool life and performance, especially in cutting hardened metals or during prolonged cutting operations.
Cutting Performance and Efficiency
Alumina cutting tools offer superior hardness and wear resistance compared to steel, enhancing cutting precision and extending tool life in high-speed machining applications. Steel tools, while more cost-effective and tougher under impact loads, tend to wear faster and generate more heat, reducing efficiency in prolonged cutting operations. The choice between alumina and steel directly impacts cutting performance and operational efficiency, with alumina being preferable for high-precision, high-speed tasks and steel suited for general-purpose cutting where flexibility and durability under variable conditions are required.
Application Suitability
Alumina cutting tools excel in high-speed machining of non-ferrous metals and abrasive materials due to their superior hardness and thermal stability. Steel cutting tools, particularly high-speed steel (HSS), provide excellent toughness and are suitable for a wide range of general-purpose applications including cutting soft metals and wood. Selecting alumina tools enhances wear resistance and performance in precision grinding, while steel tools offer cost-effectiveness and impact resistance for rougher cutting operations.
Cost Analysis and Economic Impact
Alumina cutting tools offer a lower initial cost compared to steel tools, making them a cost-effective option for high-volume, low-stress applications. Steel tools, while more expensive upfront, provide greater durability and longer tool life, reducing replacement frequency and overall production downtime expenses. The economic impact of choosing alumina centers on short-term savings, whereas steel tools contribute to long-term cost efficiency through enhanced performance and reduced maintenance costs.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Alumina cutting tools offer significant environmental advantages due to their recyclability and lower energy consumption during production compared to steel tools. Steel cutting tools often require more intensive mining and refining processes, generating higher carbon emissions and hazardous waste. In terms of safety, alumina tools produce less heat and reduce the risk of tool wear-related accidents, while steel tools may pose greater risks due to potential overheating and metal fatigue.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Cutting Tool Material
Alumina cutting tools offer excellent wear resistance and high hardness, making them ideal for machining abrasive materials and maintaining sharp edges under high temperatures. Steel cutting tools provide superior toughness and impact resistance, suitable for applications requiring flexibility and shock absorption during intermittent cuts. Selecting the right cutting tool material depends on balancing hardness with toughness, considering the specific machining conditions and workpiece characteristics to maximize tool life and performance.
Infographic: Alumina vs Steel for Cutting tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com