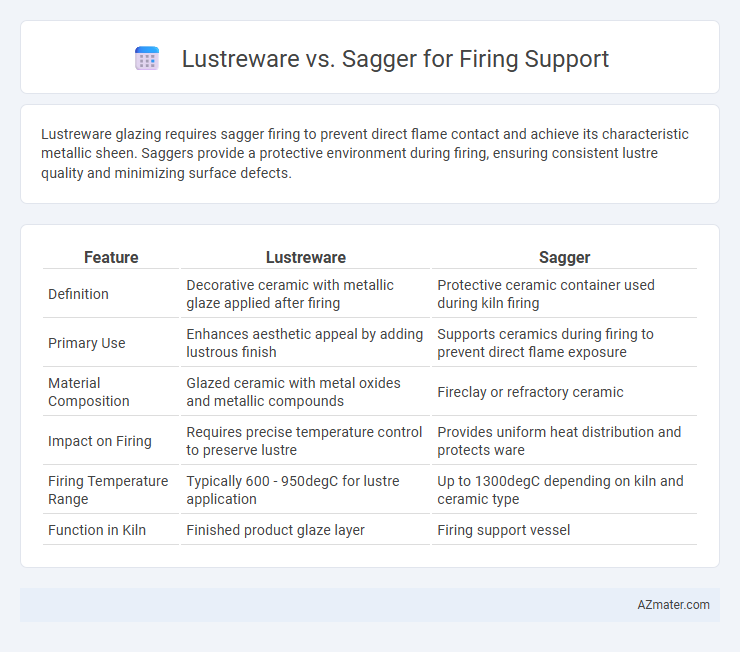
Lustreware glazing requires sagger firing to prevent direct flame contact and achieve its characteristic metallic sheen. Saggers provide a protective environment during firing, ensuring consistent lustre quality and minimizing surface defects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lustreware | Sagger |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decorative ceramic with metallic glaze applied after firing | Protective ceramic container used during kiln firing |
| Primary Use | Enhances aesthetic appeal by adding lustrous finish | Supports ceramics during firing to prevent direct flame exposure |
| Material Composition | Glazed ceramic with metal oxides and metallic compounds | Fireclay or refractory ceramic |
| Impact on Firing | Requires precise temperature control to preserve lustre | Provides uniform heat distribution and protects ware |
| Firing Temperature Range | Typically 600 - 950degC for lustre application | Up to 1300degC depending on kiln and ceramic type |
| Function in Kiln | Finished product glaze layer | Firing support vessel |
Introduction to Lustreware and Sagger in Ceramics
Lustreware refers to ceramics decorated with metallic glazes that create an iridescent sheen, achieved through complex firing techniques involving multiple firings in a reducing atmosphere. Sagger is a protective container used during firing to shield ceramics from direct flame and contaminants, ensuring even heat distribution and preserving glaze quality. Together, lustreware decoration relies on precise firing conditions that saggers help maintain, making them essential tools in advanced ceramic production.
Historical Background of Lustreware Firing Techniques
Lustreware firing techniques originated in the Islamic Golden Age, particularly in 9th-century Mesopotamia, where artisans developed complex metallic glazes using metallic salts and reducing atmospheres to create iridescent surfaces. This firing method involved multiple firings at controlled temperatures to achieve the characteristic shimmering effect, contrasting with the more straightforward Sagger firing that primarily protects ceramics from direct flame contact. Lustreware's historical significance lies in its intricate chemistry and precise kiln environments, which differentiated it from conventional ceramic firing methods like those employing Sagger supports.
What is a Sagger? Purpose and Benefits
A sagger is a protective container used in ceramic firing to shield pottery from direct exposure to flames, ash, and kiln debris, ensuring even temperature distribution and preventing surface defects. Its primary purpose is to maintain the integrity of delicate finishes, such as lustreware glazes, by minimizing contamination and firing irregularities. Using a sagger improves the quality and consistency of fired ceramics, reduces the risk of warping and cracking, and enhances the final aesthetic of the piece.
Material Composition: Lustreware vs. Sagger
Lustreware utilizes a metallic oxide glaze containing elements like silver, copper, or gold, creating iridescent finishes during firing. Sagger, composed primarily of refractory materials such as fireclay, silica, and sometimes organic additives, acts as a protective container to shield ceramics from direct flame and ash during firing. The differing compositions dictate Lustreware's decorative surface effects versus Sagger's functional role in controlled kiln atmospheres.
Firing Process: Differences and Similarities
Lustreware requires a lower firing temperature, typically around 600-700degC, to preserve the delicate metallic sheen, while sagger firing involves enclosing pottery in a container to control the atmosphere and prevent direct flame contact, which can be applied at higher temperatures up to 1300degC. Both methods utilize controlled kiln environments to achieve specific surface effects, but lustreware emphasizes chemical reduction to produce iridescence, whereas sagger firing focuses on protection and subtle color development through shielding. The firing duration for lustreware is relatively short to avoid damaging the metallic finish, contrasting with longer sagger firing cycles that enhance clay body maturation and surface texture.
Impact on Glaze and Surface Finish
Lustreware enhances glaze depth and creates a shimmering, iridescent surface finish due to its metallic oxides that react uniquely in the kiln atmosphere. Sagger firing offers controlled environments that minimize surface defects and reduce oxidation, preserving vibrant glaze colors and ensuring a smooth, consistent finish. Choosing Lustreware results in complex surface textures and metallic sheens, while Sagger firing guarantees optimal glaze clarity and uniformity by isolating the piece during firing.
Heat Distribution and Protection During Firing
Lustreware offers superior heat distribution due to its metallic glaze, which allows for even thermal conduction and reduces the risk of scorching during firing. Sagger provides enhanced protection by enclosing ceramics in a protective container, shielding pieces from direct flame contact and contaminants, thus preventing surface damage and uneven firing. Both methods optimize firing outcomes, with Lustreware focusing on heat diffusion across the surface and Sagger ensuring isolation from harsh kiln environments.
Durability and Reusability Comparison
Lustreware offers moderate durability with its delicate glaze, making it suitable for decorative use but less ideal for repeated firings. Sagger, constructed from heat-resistant refractory materials, provides superior durability and excellent reusability, ensuring consistent kiln support across multiple firings. The thermal stability of Sagger significantly reduces breakage and deformation compared to Lustreware when exposed to high-temperature kiln schedules.
Cost Implications: Lustreware vs. Sagger Use
Lustreware typically incurs higher costs due to its delicate materials and intricate glazing processes compared to the more durable and reusable sagger supports. Saggers, often made from refractory ceramics, offer cost-efficiency by reducing damage risk during firing and allowing multiple uses, minimizing material replacement expenses. Choosing between lustreware and sagger use directly impacts the overall firing budget, balancing artistic quality against long-term cost sustainability.
Choosing the Right Support: Factors to Consider
Choosing between Lustreware and Sagger for firing support depends on the type of glaze and firing temperature, as Lustreware suits intricate, shiny finishes requiring delicate handling, while Saggers offer versatile protection against flame and ash for various ceramic types. Consider the firing atmosphere, with Saggers optimizing oxidation and reduction conditions, and Lustreware demanding precise temperature control for optimal luster results. Material durability, ease of reuse, and compatibility with the kiln environment also play critical roles in selecting the appropriate support to ensure quality and efficiency.
Infographic: Lustreware vs Sagger for Firing Support
 azmater.com
azmater.com