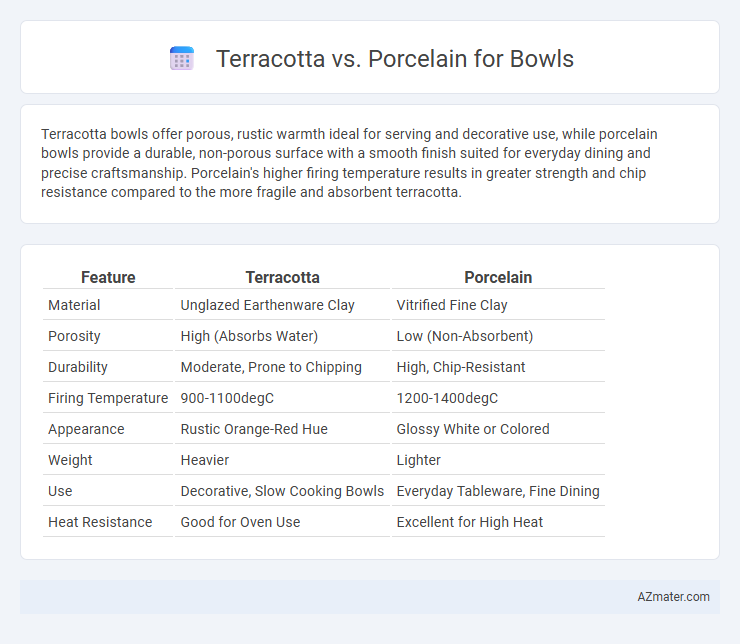
Terracotta bowls offer porous, rustic warmth ideal for serving and decorative use, while porcelain bowls provide a durable, non-porous surface with a smooth finish suited for everyday dining and precise craftsmanship. Porcelain's higher firing temperature results in greater strength and chip resistance compared to the more fragile and absorbent terracotta.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Terracotta | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Unglazed Earthenware Clay | Vitrified Fine Clay |
| Porosity | High (Absorbs Water) | Low (Non-Absorbent) |
| Durability | Moderate, Prone to Chipping | High, Chip-Resistant |
| Firing Temperature | 900-1100degC | 1200-1400degC |
| Appearance | Rustic Orange-Red Hue | Glossy White or Colored |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Use | Decorative, Slow Cooking Bowls | Everyday Tableware, Fine Dining |
| Heat Resistance | Good for Oven Use | Excellent for High Heat |
Introduction to Terracotta and Porcelain Bowls
Terracotta bowls, crafted from porous clay fired at low temperatures, offer natural breathability and rustic charm ideal for traditional cooking and serving. Porcelain bowls, made from refined kaolin clay and fired at high temperatures, provide exceptional strength, non-porous surfaces, and elegant translucency suitable for fine dining. Choosing between terracotta and porcelain bowls depends on preferences for durability, aesthetic appeal, and heat retention in culinary uses.
Material Composition: Terracotta vs. Porcelain
Terracotta bowls are made from natural clay fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a porous, breathable material with a rustic texture ideal for traditional cooking and serving. Porcelain bowls consist of refined kaolin clay fired at very high temperatures, creating a non-porous, dense, and highly durable surface with a smooth, glass-like finish suitable for elegant tableware. The distinct mineral compositions and firing processes between terracotta and porcelain significantly affect their strength, water absorption, and thermal properties.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Terracotta bowls, made from porous clay, are prone to chipping and cracking over time, making them less durable compared to porcelain bowls, which are fired at higher temperatures for increased strength. Porcelain exhibits exceptional longevity due to its non-porous, vitrified surface that resists stains, scratches, and thermal shock. For long-term use and durability, porcelain bowls outperform terracotta by maintaining structural integrity and aesthetic appeal over years of regular use.
Aesthetic Appeal: Colors and Textures
Terracotta bowls offer a warm, earthy aesthetic with rich, natural reddish-brown hues and a slightly rough, porous texture that enhances rustic and artisanal designs. Porcelain bowls present a smooth, glossy surface with a wide range of vibrant colors and intricate patterns, delivering a refined and elegant look suitable for modern and sophisticated settings. The choice between terracotta and porcelain bowls depends on the desired visual impact, where terracotta emphasizes organic charm and porcelain highlights sleek sophistication.
Weight and Handling Differences
Terracotta bowls are generally heavier and offer a rustic, sturdy feel, making them less ideal for frequent handling or carrying. Porcelain bowls are lighter, providing easier maneuverability and a more delicate touch suitable for daily use or serving. The weight difference significantly impacts handling, with porcelain favored for its ease of use and terracotta prized for its durability and heat retention.
Heat Retention & Thermal Properties
Terracotta bowls excel in heat retention due to their porous nature, allowing them to absorb and slowly release heat, making them ideal for serving hot dishes. Porcelain bowls, however, have a denser, vitrified structure that resists thermal shock and retains heat efficiently but cools faster than terracotta. The thermal conductivity of terracotta is lower than porcelain, which means it maintains temperature longer but is more fragile under rapid temperature changes.
Porosity and Stain Resistance
Terracotta bowls exhibit higher porosity, absorbing liquids and stains more readily, which can lead to discoloration and odor retention over time. Porcelain bowls feature low porosity due to their dense, vitrified structure, making them highly resistant to stains and easy to maintain. This difference in porosity significantly impacts the durability and hygienic qualities of each material in everyday use.
Safety: Food-Safe and Non-Toxic Qualities
Terracotta bowls are naturally porous and require proper sealing to ensure they are food-safe, as unglazed terracotta can absorb liquids and harbor bacteria. Porcelain bowls, made from vitrified clay fired at high temperatures, offer a non-porous, non-toxic surface that resists staining and does not leach harmful substances, making them inherently safer for food use. When prioritizing safety, porcelain is generally more reliable due to its durable glazing and resistance to contaminants.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Terracotta bowls require gentle hand washing with mild soap and should be dried thoroughly to prevent mold and cracking due to their porous nature. Porcelain bowls offer easier maintenance, as they are non-porous and dishwasher safe, resisting stains and odors more effectively. Regular sealing of terracotta enhances durability, whereas porcelain's glazed surface provides inherent protection against wear and staining.
Cost and Value Considerations
Terracotta bowls typically offer a lower upfront cost compared to porcelain, making them an affordable choice for everyday use. Porcelain bowls, while more expensive, provide higher durability, resistance to chipping, and a longer lifespan, which enhances their overall value. Choosing between terracotta and porcelain involves balancing initial investment with long-term benefits, where porcelain is often favored for its strength and elegance despite the higher price point.
Infographic: Terracotta vs Porcelain for Bowl
 azmater.com
azmater.com