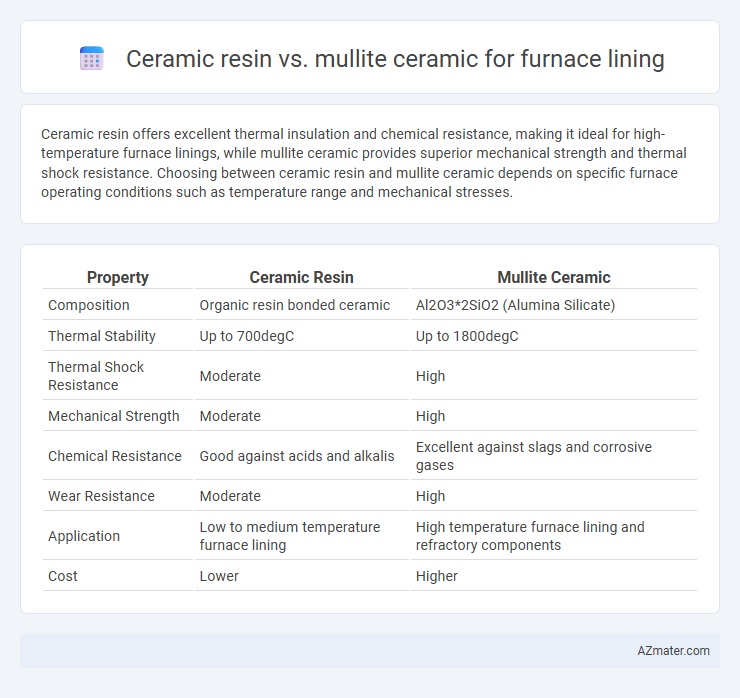
Ceramic resin offers excellent thermal insulation and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature furnace linings, while mullite ceramic provides superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance. Choosing between ceramic resin and mullite ceramic depends on specific furnace operating conditions such as temperature range and mechanical stresses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Resin | Mullite Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Organic resin bonded ceramic | Al2O3*2SiO2 (Alumina Silicate) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 700degC | Up to 1800degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and alkalis | Excellent against slags and corrosive gases |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Application | Low to medium temperature furnace lining | High temperature furnace lining and refractory components |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Ceramic resin and mullite ceramic are two commonly used materials for furnace lining, each offering distinct thermal and mechanical properties. Ceramic resin provides excellent adhesion and resistance to thermal shock, making it suitable for applications requiring rapid temperature changes. Mullite ceramic, composed mainly of alumina and silica, delivers superior high-temperature stability and corrosion resistance, ideal for prolonged exposure to extreme furnace environments.
Overview of Ceramic Resin
Ceramic resin, used in furnace lining, offers excellent thermal insulation and chemical resistance due to its polymer-ceramic composite structure that enhances durability under high temperatures. This material provides superior bonding capabilities and flexibility compared to traditional mullite ceramic, resulting in improved mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock. Ceramic resin linings are preferred in applications requiring lightweight and easily moldable solutions, optimizing furnace performance and service life.
Overview of Mullite Ceramic
Mullite ceramic, primarily composed of 3Al2O3*2SiO2, offers exceptional thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for furnace linings subject to high temperatures. Its low thermal conductivity and excellent mechanical strength ensure durability and energy efficiency in industrial kiln applications. Compared to ceramic resin linings, mullite ceramic provides superior corrosion resistance and longer service life in harsh thermal environments.
Key Properties Comparison
Ceramic resin exhibits excellent chemical resistance and superior bonding strength, making it effective for sealing furnace linings and providing thermal shock resistance up to 1000degC. Mullite ceramic offers higher mechanical strength, outstanding thermal stability, and can withstand temperatures exceeding 1700degC, ideal for structural furnace components exposed to intense heat and abrasion. The choice between ceramic resin and mullite ceramic in furnace linings depends on the balance between temperature tolerance, mechanical durability, and chemical resistance required for specific industrial applications.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Ceramic resin offers moderate thermal stability with excellent adhesion properties but typically withstands temperatures up to 1200degC, making it suitable for low- to medium-temperature furnace linings. Mullite ceramic, composed mainly of 3Al2O3*2SiO2, provides superior thermal stability and heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity above 1700degC, which ensures enhanced performance in high-temperature furnace environments. The high melting point and low thermal expansion of mullite ceramics reduce thermal shock risks, making them ideal for industrial furnace lining applications requiring prolonged exposure to extreme heat.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Ceramic resin exhibits superior mechanical strength with enhanced impact resistance, making it ideal for furnace linings subjected to thermal shocks and mechanical stress. Mullite ceramic offers exceptional durability due to its high-temperature stability and resistance to thermal expansion, ensuring prolonged lifespan in furnace environments. Choosing between ceramic resin and mullite ceramic depends on specific operational demands, with ceramic resin providing flexibility and toughness, while mullite ensures consistent performance under extreme heat.
Chemical Resistance and Corrosion Protection
Ceramic resin offers superior chemical resistance against acidic and alkaline environments, making it ideal for furnace linings exposed to aggressive corrosive agents. Mullite ceramic demonstrates excellent corrosion protection due to its high thermal stability and resistance to molten slags and alkali vapors in high-temperature furnace applications. Choosing between ceramic resin and mullite ceramic depends on the specific chemical exposure and temperature conditions within the furnace environment.
Installation Process and Maintenance
Ceramic resin linings offer faster installation due to their adhesive properties and require minimal curing time compared to mullite ceramic, which involves a more labor-intensive setting and drying process. Maintenance of ceramic resin linings is often simpler, with easier patch repairs and less downtime, whereas mullite ceramic linings, being more rigid and brittle, may necessitate periodic inspections to address potential cracking or spalling. The choice between ceramic resin and mullite ceramic for furnace lining installation and maintenance hinges on balancing installation speed, operational conditions, and long-term durability requirements.
Cost Analysis and Longevity
Ceramic resin furnace linings typically offer lower initial installation costs due to easier application and faster curing times, making them suitable for budget-conscious projects with moderate temperature requirements. Mullite ceramic linings, although more expensive upfront, provide superior thermal stability, resistance to thermal shock, and enhanced durability under high-temperature conditions, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance expenses. Cost analysis favors ceramic resin for short-term use and mullite ceramic for long-term investment in industrial furnace efficiency and reliability.
Best Applications: Ceramic Resin vs Mullite Ceramic
Ceramic resin is optimal for furnace linings requiring superior chemical resistance and lightweight thermal barriers, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation and corrosion-prone environments. Mullite ceramic excels in applications demanding exceptional thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, suitable for high-temperature furnaces with rapid temperature fluctuations and heavy mechanical loads. Selecting between ceramic resin and mullite ceramic depends on specific operational conditions such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress within the furnace lining.
Infographic: Ceramic resin vs Mullite ceramic for Furnace lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com