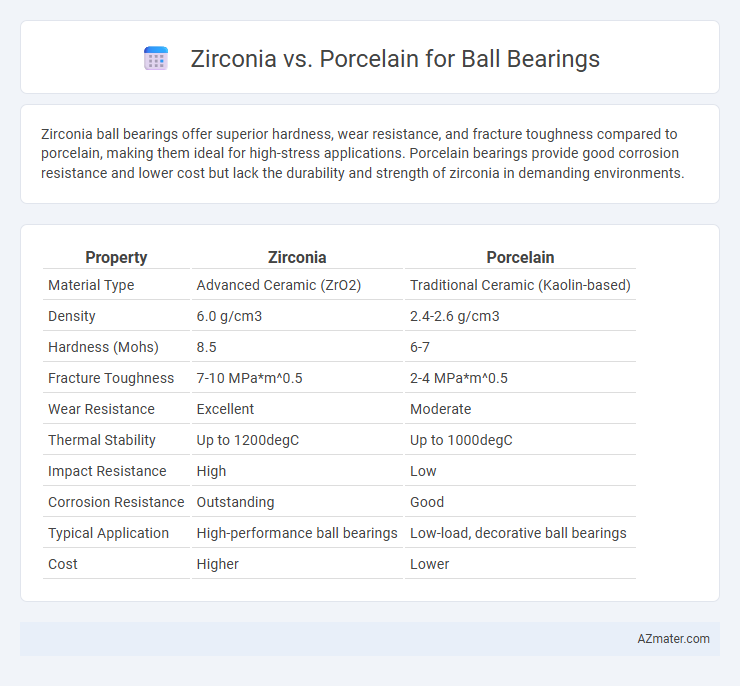
Zirconia ball bearings offer superior hardness, wear resistance, and fracture toughness compared to porcelain, making them ideal for high-stress applications. Porcelain bearings provide good corrosion resistance and lower cost but lack the durability and strength of zirconia in demanding environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zirconia | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Advanced Ceramic (ZrO2) | Traditional Ceramic (Kaolin-based) |
| Density | 6.0 g/cm3 | 2.4-2.6 g/cm3 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 8.5 | 6-7 |
| Fracture Toughness | 7-10 MPa*m^0.5 | 2-4 MPa*m^0.5 |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1000degC |
| Impact Resistance | High | Low |
| Corrosion Resistance | Outstanding | Good |
| Typical Application | High-performance ball bearings | Low-load, decorative ball bearings |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Zirconia and Porcelain Ball Bearings
Zirconia ball bearings offer exceptional hardness, high resistance to wear, and excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for demanding applications. Porcelain ball bearings, composed primarily of alumina ceramic, provide good thermal stability and electrical insulation but generally have lower toughness than zirconia. Both materials deliver superior performance compared to steel bearings, with zirconia excelling in durability and porcelain favored for lightweight, non-conductive environments.
Material Composition and Properties
Zirconia ball bearings are composed of zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), offering exceptional hardness, high fracture toughness, and excellent wear resistance, making them suitable for high-load and high-speed applications. Porcelain ball bearings, typically made from alumina (Al2O3), provide good corrosion resistance and electrical insulation but exhibit lower toughness and higher brittleness compared to zirconia. The superior mechanical properties of zirconia, including higher flexural strength and thermal stability, position it as the preferred material for demanding bearing environments requiring durability and precision.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Zirconia ball bearings outperform porcelain in strength due to their higher fracture toughness and resistance to impact, making them ideal for high-stress applications. Zirconia's superior durability is attributed to its ability to withstand wear and thermal fluctuations without significant degradation, whereas porcelain bearings are more prone to chipping and cracking under heavy loads. The combination of zirconia's toughness and long service life establishes it as a preferred material for ball bearings demanding exceptional mechanical performance.
Wear Resistance and Longevity
Zirconia ball bearings exhibit superior wear resistance and longevity compared to porcelain counterparts due to their high fracture toughness and resistance to chipping. The dense microstructure of zirconia minimizes surface degradation under high-stress rotational conditions, extending operational lifespan. Porcelain bearings, while corrosion-resistant, typically suffer from brittleness and lower durability under heavy loads, resulting in faster wear and reduced service life.
Friction Performance and Efficiency
Zirconia ball bearings exhibit significantly lower friction coefficients compared to porcelain, resulting in enhanced rotational efficiency and reduced energy loss. Their superior tribological properties and higher wear resistance contribute to consistent performance under high-speed and load conditions. Porcelain bearings, while durable and corrosion-resistant, generally display higher friction levels, limiting their efficiency in precision applications.
Temperature and Chemical Resistance
Zirconia ball bearings exhibit superior temperature resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 1200degC compared to porcelain's lower tolerance around 700degC. Chemically, zirconia offers exceptional resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents, making it ideal for harsh environments, whereas porcelain can degrade under prolonged chemical exposure. These properties make zirconia a preferred choice in demanding industrial applications requiring high thermal stability and chemical durability.
Cost Analysis: Zirconia vs Porcelain
Zirconia ball bearings typically cost more upfront than porcelain due to their advanced material properties and manufacturing complexity. Porcelain ball bearings offer a more budget-friendly option but may require more frequent replacements or maintenance, impacting long-term expenses. Cost analysis should factor in durability, performance, and lifecycle to determine the most economical choice for specific applications.
Applications in Industry and Machinery
Zirconia ball bearings are preferred in high-performance industrial and machinery applications due to their exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. Porcelain bearings, while corrosion-resistant and electrically insulating, are typically used in less demanding environments such as chemical processing or electrical equipment where lower impact resistance is acceptable. The superior mechanical strength and wear resistance of zirconia make it ideal for heavy-duty machinery, robotics, and precision instruments requiring long service life and minimal maintenance.
Maintenance and Lifespan Considerations
Zirconia ball bearings offer superior maintenance advantages due to their high resistance to wear, corrosion, and temperature fluctuations, resulting in longer service intervals compared to porcelain counterparts. Porcelain ball bearings, while cost-effective, typically require more frequent inspections and replacements due to their brittleness and susceptibility to chipping under stress. Lifespan considerations favor zirconia for applications demanding durability and minimal downtime, as they provide enhanced toughness and sustained performance in harsh environments.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Zirconia ball bearings offer superior hardness, wear resistance, and higher load capacity compared to porcelain, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications requiring durability and precision. Porcelain ball bearings provide excellent corrosion resistance and electrical insulation, suitable for environments exposed to moisture or chemical exposure but with lower mechanical strength. Selecting between zirconia and porcelain depends on operational conditions, including load demands, exposure to corrosive elements, and the need for electrical insulation to optimize performance and longevity.
Infographic: Zirconia vs Porcelain for Ball Bearing
 azmater.com
azmater.com