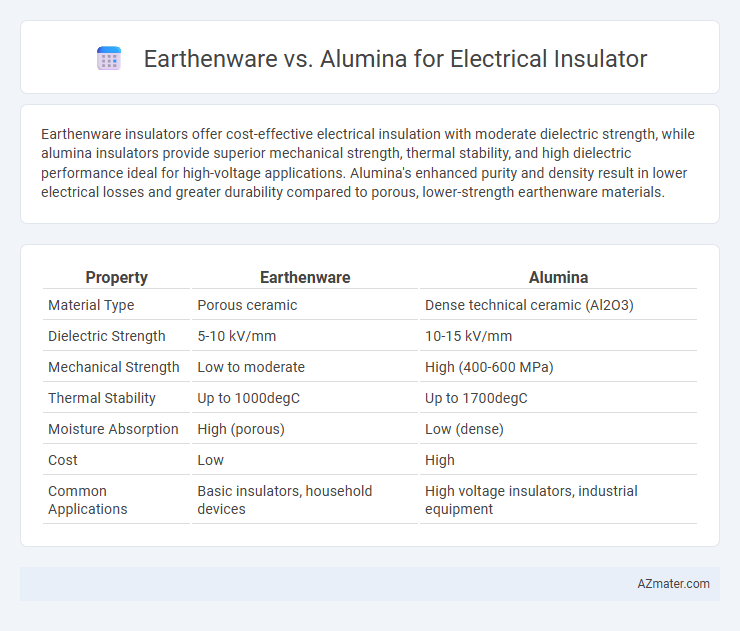
Earthenware insulators offer cost-effective electrical insulation with moderate dielectric strength, while alumina insulators provide superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and high dielectric performance ideal for high-voltage applications. Alumina's enhanced purity and density result in lower electrical losses and greater durability compared to porous, lower-strength earthenware materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Earthenware | Alumina |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Porous ceramic | Dense technical ceramic (Al2O3) |
| Dielectric Strength | 5-10 kV/mm | 10-15 kV/mm |
| Mechanical Strength | Low to moderate | High (400-600 MPa) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1000degC | Up to 1700degC |
| Moisture Absorption | High (porous) | Low (dense) |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Common Applications | Basic insulators, household devices | High voltage insulators, industrial equipment |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators prevent the flow of electric current by providing high resistance, ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical systems. Earthenware, a traditional insulator made from fired clay, offers cost-effectiveness and moderate dielectric strength but tends to absorb moisture, reducing insulation performance. Alumina, a ceramic material with high purity and superior dielectric properties, provides excellent mechanical strength, thermal stability, and resistance to electrical breakdown, making it ideal for advanced electrical insulating applications.
Overview of Earthenware Insulators
Earthenware insulators consist primarily of clay and are widely used in electrical applications due to their cost-effectiveness and adequate dielectric properties. They offer moderate mechanical strength and thermal resistance, making them suitable for low to medium voltage power distribution systems. Despite lower durability compared to alumina, earthenware insulators provide reliable performance in less demanding environments with good moisture resistance and electrical insulation capabilities.
Properties of Alumina Insulators
Alumina insulators exhibit exceptional dielectric strength, thermal conductivity, and mechanical hardness compared to earthenware, making them ideal for high-voltage electrical applications. Their low porosity and excellent resistance to chemical corrosion enhance reliability and longevity in harsh environments. High purity alumina materials provide superior insulation performance with minimal moisture absorption, ensuring consistent electrical properties under varied operating conditions.
Mechanical Strength: Earthenware vs Alumina
Alumina exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to earthenware, making it more durable under mechanical stress and impact. While earthenware typically has lower flexural strength and is more prone to cracking, alumina's superior hardness and fracture toughness enhance its reliability in demanding electrical insulator applications. This mechanical robustness of alumina ensures better resistance to thermal and mechanical shocks, contributing to longer service life in high-performance environments.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Earthenware insulators exhibit lower dielectric strength and higher electrical conductivity compared to alumina, resulting in increased leakage currents and reduced insulation efficiency. Alumina insulators demonstrate superior electrical performance due to their high dielectric constant, excellent resistivity, and minimal dielectric loss, making them ideal for high-voltage applications. The enhanced purity and material density of alumina contribute to its ability to withstand higher electrical stresses and temperature variations without degradation.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Earthenware offers moderate thermal stability with its heat resistance typically limited to around 800degC, making it suitable for low to medium-temperature electrical insulation applications. Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) excels in thermal stability with a high melting point above 2000degC, providing superior heat resistance and maintaining insulating properties in extreme thermal environments. The high thermal conductivity and dielectric strength of alumina make it ideal for electrical insulators requiring excellent performance under rigorous thermal stress.
Durability and Longevity Factors
Earthenware insulators typically offer moderate durability but are more prone to cracking and moisture absorption compared to alumina insulators, which possess superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance. Alumina insulators exhibit enhanced longevity due to their high thermal stability and resistance to wear, making them ideal for harsh electrical environments. The low porosity and high density of alumina contribute significantly to its extended service life, outperforming earthenware in long-term reliability.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Earthenware offers a cost-effective solution for electrical insulators due to inexpensive raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes, making it ideal for low-voltage applications. Alumina, though significantly more expensive, provides superior electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and thermal stability, justifying higher production costs in high-performance or high-voltage environments. Manufacturing alumina insulators requires advanced equipment and precise control, increasing complexity and expense compared to the more straightforward, energy-efficient firing methods used for earthenware.
Typical Applications in Electrical Systems
Earthenware insulators are commonly used in low-voltage electrical distribution systems, such as overhead power lines and domestic wiring, due to their cost-effectiveness and adequate dielectric strength. Alumina insulators, made from high-purity aluminum oxide, are preferred in high-voltage and high-frequency applications like transformers, circuit breakers, and insulating components in electronic devices because of their excellent thermal conductivity and superior mechanical strength. The choice between earthenware and alumina depends on the required operating voltage, mechanical durability, and environmental conditions of the electrical system.
Choosing the Right Insulator Material
Choosing the right insulator material involves evaluating earthenware and alumina based on their dielectric strength and thermal stability. Earthenware offers cost-effective insulation with good mechanical strength but lower thermal resistance compared to alumina, which provides superior dielectric properties and high-temperature endurance essential for demanding electrical applications. Selecting alumina is ideal for environments requiring robust insulation performance under extreme conditions, while earthenware suits applications with moderate electrical and thermal demands.
Infographic: Earthenware vs Alumina for Electrical Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com