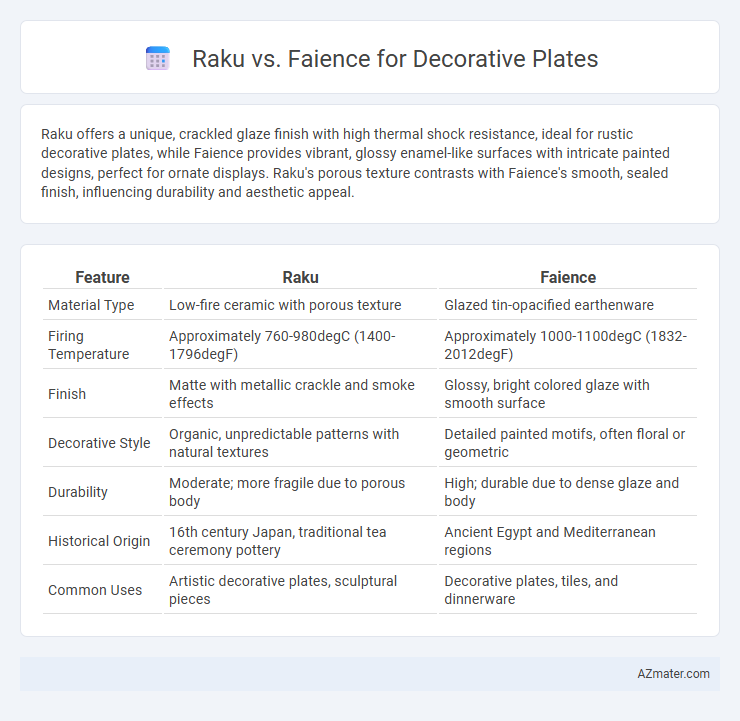
Raku offers a unique, crackled glaze finish with high thermal shock resistance, ideal for rustic decorative plates, while Faience provides vibrant, glossy enamel-like surfaces with intricate painted designs, perfect for ornate displays. Raku's porous texture contrasts with Faience's smooth, sealed finish, influencing durability and aesthetic appeal.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raku | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Low-fire ceramic with porous texture | Glazed tin-opacified earthenware |
| Firing Temperature | Approximately 760-980degC (1400-1796degF) | Approximately 1000-1100degC (1832-2012degF) |
| Finish | Matte with metallic crackle and smoke effects | Glossy, bright colored glaze with smooth surface |
| Decorative Style | Organic, unpredictable patterns with natural textures | Detailed painted motifs, often floral or geometric |
| Durability | Moderate; more fragile due to porous body | High; durable due to dense glaze and body |
| Historical Origin | 16th century Japan, traditional tea ceremony pottery | Ancient Egypt and Mediterranean regions |
| Common Uses | Artistic decorative plates, sculptural pieces | Decorative plates, tiles, and dinnerware |
Introduction to Decorative Plate Materials
Raku and faience represent distinct decorative plate materials with unique historical and compositional characteristics. Raku, originating from Japanese pottery, uses low-firing techniques resulting in distinctive crackled glazes and earthy textures, while faience is a type of tin-glazed ceramic known for its bright, opaque surfaces and vibrant colors, often linked to European and Middle Eastern traditions. Both materials serve as versatile mediums for artistic expression, but Raku emphasizes spontaneity and natural aesthetics compared to the more controlled, colorful artistry of faience.
Overview of Raku Pottery
Raku pottery is a traditional Japanese technique characterized by its rapid firing process and dramatic thermal shock cooling, producing unique crackled glazes and unpredictable textures. Compared to faience, which is a tin-glazed ceramic known for its smooth, opaque surface and vibrant painted designs, raku offers a more organic, rustic aesthetic with a tactile, often metallic finish. Raku plates stand out for their artistic spontaneity and the individual character imparted by the firing method, making them highly valued in contemporary decorative art.
What is Faience?
Faience is a type of glazed ceramic ware characterized by its vibrant, opaque colors and smooth, glossy surface, traditionally made from tin-glazed earthenware. Unlike Raku, which involves a rapid firing and cooling process producing unique crackled effects, Faience emphasizes bright, detailed patterns often inspired by historical and cultural motifs. Its durability and ornate finish make Faience a popular choice for decorative plates, offering both aesthetic appeal and functional strength.
Historical Background: Raku vs Faience
Raku pottery originated in 16th-century Japan, closely tied to the traditional tea ceremony, emphasizing hand-shaped, low-fired ceramics known for their unpredictably textured glaze. Faience, with roots dating back to ancient Egypt and flourishing in Renaissance Europe, is a tin-glazed earthenware characterized by its bright, opaque surface ideal for detailed painted decorations. While Raku embraces spontaneity and wabi-sabi aesthetics, Faience prioritizes vibrant, glossy finishes with intricate, often symbolic motifs, reflecting distinct cultural and historical artisanal traditions.
Differences in Production Techniques
Raku and Faience decorative plates differ significantly in production techniques, with Raku involving a rapid firing process followed by immediate cooling in open air or reduction chambers, which creates unique crackled textures and unpredictable glazes. Faience, a type of tin-glazed pottery, is produced by applying an opaque white glaze to earthenware before painting intricate designs and firing at a steady temperature, resulting in smooth, glossy surfaces with vivid colors. The spontaneous thermal shock in Raku contrasts with the controlled kiln firing of Faience, influencing both the aesthetic and durability of decorative plates.
Aesthetic Qualities Compared
Raku pottery offers a unique aesthetic with its unpredictable crackle glaze and smoky, metallic finishes, creating an organic, rustic appeal ideal for decorative plates. Faience, known for its smooth, glossy surface and vibrant, opaque colors, provides a more polished and refined look that highlights intricate painted designs. While Raku emphasizes texture and spontaneity, Faience excels in detailed artistry and consistent color vibrancy, influencing decorative plate choices based on desired visual impact.
Durability and Practicality
Raku pottery, known for its unique crackled glaze, offers a distinct aesthetic but is less durable due to its porous and fragile nature, making it prone to chipping and unsuitable for everyday use. Faience, a tin-glazed earthenware, provides greater durability and a smoother surface, making it more practical for decorative plates that require longevity and easier maintenance. Choosing faience ensures better resistance to moisture and wear, ideal for both display and functional purposes compared to the more delicate Raku pieces.
Design Versatility and Color Options
Raku pottery offers unique design versatility with its unpredictable crackle patterns and metallic finishes, making each decorative plate one-of-a-kind. Faience provides a broader color palette through its tin-glazed surface, allowing vibrant blues, greens, and yellows that suit intricate, detailed designs. Both materials excel in artistic expression, but Raku emphasizes texture and spontaneity, while Faience prioritizes vivid, consistent color application.
Popular Uses in Modern Decor
Raku and Faience decorative plates each bring distinct artistic value to modern decor, with Raku prized for its unique crackled glaze and organic texture, making it a favorite for rustic and contemporary interiors. Faience, known for its vibrant tin-glazed pottery origins, is popular in Mediterranean and eclectic styles due to its colorful, glossy finish and intricate patterns. Both are widely used as wall accents or centerpiece displays, enhancing spaces with cultural depth and artisanal craftsmanship.
Choosing Between Raku and Faience Plates
Choosing between Raku and Faience decorative plates depends on the desired aesthetic and durability. Raku plates offer unique, crackled glaze effects and an organic, unpredictable finish ideal for rustic or artistic displays, while Faience plates provide a smooth, colorful tin-glazed surface perfect for intricate patterns and a classic, polished look. Consider the environment where the plate will be displayed since Raku is more porous and delicate, whereas Faience is more durable and suitable for both decorative and functional use.
Infographic: Raku vs Faience for Decorative Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com