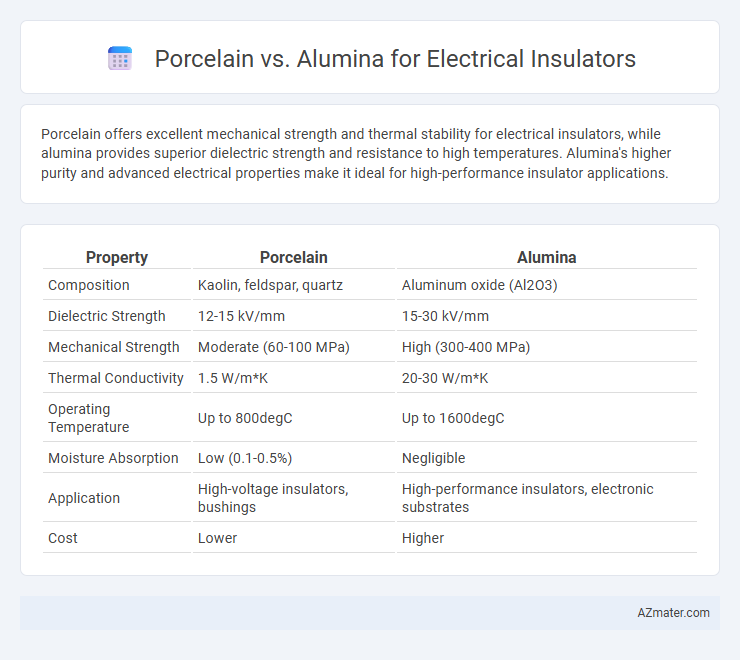
Porcelain offers excellent mechanical strength and thermal stability for electrical insulators, while alumina provides superior dielectric strength and resistance to high temperatures. Alumina's higher purity and advanced electrical properties make it ideal for high-performance insulator applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Porcelain | Alumina |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Kaolin, feldspar, quartz | Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) |
| Dielectric Strength | 12-15 kV/mm | 15-30 kV/mm |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate (60-100 MPa) | High (300-400 MPa) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1.5 W/m*K | 20-30 W/m*K |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 800degC | Up to 1600degC |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (0.1-0.5%) | Negligible |
| Application | High-voltage insulators, bushings | High-performance insulators, electronic substrates |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators such as porcelain and alumina play critical roles in preventing electrical current leakage and ensuring safety in power systems. Porcelain offers excellent mechanical strength, resistance to weathering, and high dielectric strength, making it suitable for outdoor insulators in high-voltage applications. Alumina, a ceramic material with superior thermal conductivity and mechanical hardness, is often preferred in high-temperature and demanding industrial environments requiring robust electrical insulation.
Overview of Porcelain Insulators
Porcelain insulators are widely used in electrical systems due to their excellent mechanical strength and high dielectric strength, making them ideal for high-voltage applications. Composed primarily of clay, kaolin, and feldspar, porcelain exhibits superior resistance to weathering, thermal stress, and electrical degradation. Their smooth surface reduces contamination buildup, ensuring reliable insulation performance in outdoor environments.
Overview of Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) Insulators
Alumina (aluminum oxide) insulators exhibit high dielectric strength and excellent thermal conductivity, making them ideal for high-voltage and high-temperature electrical applications. Their superior mechanical strength and chemical stability enhance durability in harsh environments compared to porcelain insulators. Alumina insulators also feature low moisture absorption and exceptional resistance to electrical arc corrosion, ensuring reliable insulation performance.
Material Properties: Porcelain vs Alumina
Porcelain exhibits excellent dielectric strength and high mechanical robustness, making it a preferred material for traditional electrical insulators, while Alumina offers superior thermal conductivity, higher hardness, and greater resistance to wear and corrosion. Alumina's higher purity and dense microstructure result in enhanced electrical insulation performance under extreme conditions compared to porcelain. The choice between Porcelain and Alumina depends heavily on the specific application requirements such as operating temperature, mechanical stress, and environmental exposure.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Porcelain exhibits excellent dielectric strength and high resistivity, making it highly effective for insulating electrical components in high-voltage applications. Alumina, with its superior thermal conductivity and higher mechanical strength, provides enhanced performance under extreme thermal and mechanical stress while maintaining excellent electrical insulation properties. The choice between porcelain and alumina depends on specific application requirements, with alumina favored for demanding environments requiring both robust electrical insulation and heat dissipation.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Porcelain offers excellent mechanical strength and is highly resistant to thermal shock, making it suitable for high-voltage insulators in harsh environments. Alumina surpasses porcelain in mechanical strength due to its higher hardness and fracture toughness, resulting in superior durability under mechanical stress and abrasion. Both materials exhibit strong electrical insulation properties, but alumina's enhanced mechanical resilience often makes it preferable for demanding industrial applications requiring long-term performance.
Thermal Stability and Resistance
Porcelain exhibits high thermal stability with a melting point around 1,200degC, making it suitable for electrical insulators exposed to moderate heat levels. Alumina offers superior thermal resistance, with melting points exceeding 2,000degC and excellent dielectric strength, ideal for high-temperature electrical insulation applications. Both materials provide robust insulation properties, but alumina's enhanced thermal stability and resistance make it preferable for environments demanding extreme heat endurance.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Porcelain insulators typically offer lower material costs but involve labor-intensive manufacturing processes that can increase overall expenses. Alumina insulators, while more expensive due to high-purity raw materials and precision sintering techniques, provide superior mechanical strength and electrical performance, justifying their cost in high-demand applications. Manufacturing alumina requires advanced equipment and controlled environments, leading to higher production costs compared to the traditional firing and glazing methods used for porcelain.
Typical Applications and Industry Use
Porcelain electrical insulators are widely used in high-voltage transmission lines, substation equipment, and distribution transformers due to their excellent mechanical strength and weather resistance. Alumina insulators find typical applications in high-temperature environments, such as semiconductor manufacturing, electrical discharge machining (EDM), and vacuum systems, owing to their superior thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties. The power utility industry predominantly favors porcelain for outdoor applications, whereas electronics and high-tech industries prefer alumina for precision and high-performance electrical insulation.
Choosing the Right Insulator: Key Factors
Choosing the right electrical insulator between porcelain and alumina depends on factors such as dielectric strength, thermal stability, and mechanical durability. Porcelain offers excellent insulation properties and is cost-effective for high-voltage applications, while alumina provides superior thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for harsh environments. The decision hinges on specific operational requirements, environmental conditions, and longevity expectations to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Alumina for Electrical Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com