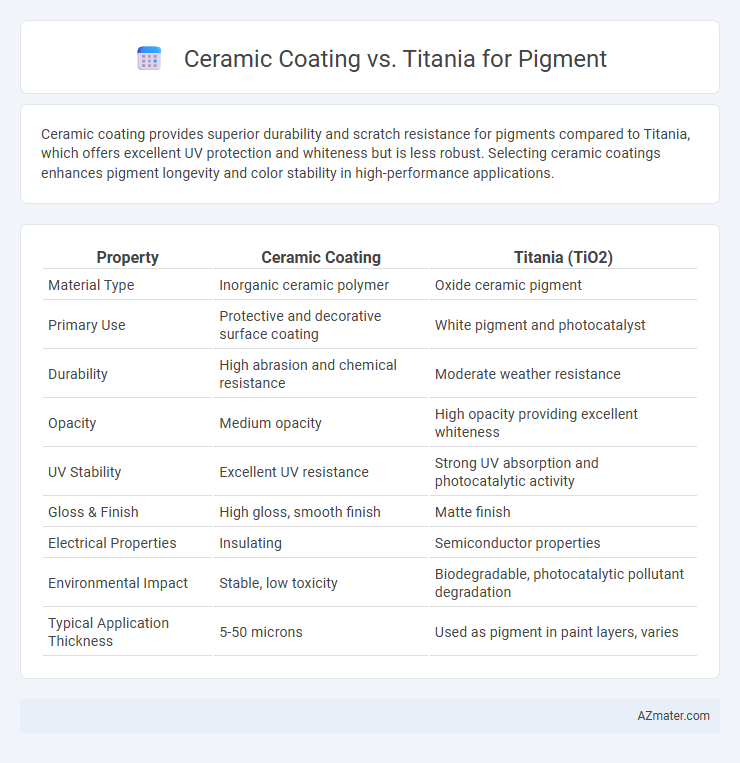
Ceramic coating provides superior durability and scratch resistance for pigments compared to Titania, which offers excellent UV protection and whiteness but is less robust. Selecting ceramic coatings enhances pigment longevity and color stability in high-performance applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Coating | Titania (TiO2) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Inorganic ceramic polymer | Oxide ceramic pigment |
| Primary Use | Protective and decorative surface coating | White pigment and photocatalyst |
| Durability | High abrasion and chemical resistance | Moderate weather resistance |
| Opacity | Medium opacity | High opacity providing excellent whiteness |
| UV Stability | Excellent UV resistance | Strong UV absorption and photocatalytic activity |
| Gloss & Finish | High gloss, smooth finish | Matte finish |
| Electrical Properties | Insulating | Semiconductor properties |
| Environmental Impact | Stable, low toxicity | Biodegradable, photocatalytic pollutant degradation |
| Typical Application Thickness | 5-50 microns | Used as pigment in paint layers, varies |
Introduction to Ceramic Coating and Titania Pigments
Ceramic coatings offer advanced protection and enhanced durability for surfaces by forming a strong, inert layer resistant to heat, chemicals, and abrasion. Titania pigments, primarily composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), provide exceptional whiteness and opacity, widely used in paints, plastics, and coatings due to their high refractive index and photostability. Selecting between ceramic coatings and titania pigments depends on whether the application prioritizes protective surface enhancements or pigment-based color and opacity performance.
Chemical Composition: Ceramic vs Titania Pigments
Ceramic coatings typically utilize silica (SiO2) and alumina (Al2O3) as primary components, providing excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance. Titania pigments primarily consist of titanium dioxide (TiO2), known for its high opacity, brightness, and UV resistance. The chemical structure of ceramic coatings offers superior durability in harsh environments, while titania pigments enhance color vibrancy and protection against photodegradation in coatings.
Application Methods: Ceramic Coating and Titania Compared
Ceramic coating application typically involves spray, dip, or brush methods, ensuring an even, durable layer with enhanced chemical resistance for pigments. Titania, commonly applied via sol-gel processes, spray, or immersion, offers superior photocatalytic properties but requires precise control for uniform pigment coverage. Comparing both, ceramic coating provides stronger mechanical protection, while titania excels in UV blocking, influencing their suitability based on pigment performance needs.
Durability and Longevity of Pigment Coatings
Ceramic coatings offer superior durability for pigment protection, providing a hard, scratch-resistant layer that enhances longevity against environmental factors like UV rays and oxidation. Titania-based coatings, while effective in enhancing pigment stability through photocatalytic properties, generally exhibit less mechanical resistance and may degrade faster under harsh conditions. For prolonged pigment preservation, ceramic coatings maintain color vibrancy and structural integrity significantly longer than titania alternatives.
Optical Properties: Color Vibrancy and Brightness
Ceramic coatings enhance color vibrancy and brightness by providing a high refractive index layer that intensifies light reflection and minimizes surface imperfections. Titania pigments, known for their exceptional light-scattering properties, offer superior brightness and opacity, making colors appear more vivid and luminous. Comparing both, ceramic coatings deliver improved gloss and depth, while titania pigments primarily boost the brightness and saturation of painted surfaces.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ceramic coatings offer long-lasting protection with high durability, reducing the need for frequent repainting and lowering environmental waste. Titania-based pigments, derived from titanium dioxide, provide excellent UV resistance and photocatalytic properties that help degrade pollutants, enhancing air quality and sustainability. Both materials contribute to eco-friendly applications, but Titania's ability to break down organic contaminants gives it a unique advantage in promoting environmental health.
Cost Analysis: Ceramic Coating vs Titania Pigments
Ceramic coatings typically exhibit higher initial costs due to advanced formulation and application technology, whereas Titania pigments offer a more cost-effective solution given their widespread availability and lower production expenses. The durability and longevity of ceramic coatings can result in reduced long-term maintenance costs compared to Titania-based pigments, which may require more frequent reapplication. Cost analysis should consider both upfront investment and lifecycle expenses to determine the most economical option for specific industrial or cosmetic applications.
Performance in Industrial Uses
Ceramic coatings offer exceptional durability, chemical resistance, and high-temperature stability, making them ideal for industrial pigment applications requiring long-term performance and protection against harsh environments. Titania pigments provide superior opacity, brightness, and UV resistance, enhancing color vibrancy while also contributing photocatalytic properties that can improve surface cleanliness and self-cleaning capabilities. Industrial uses benefit from ceramic coatings' protective qualities combined with titania's pigment efficiency, optimizing both performance and lifespan in demanding operational settings.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
Ceramic coatings and titania pigments both undergo rigorous safety assessments to meet regulatory standards, but ceramic coatings often exhibit lower toxicity and greater chemical stability, reducing potential health risks during application. Titania pigments, classified as safe by organizations like the FDA and EPA when used within prescribed limits, require careful handling to avoid inhalation hazards from nanoparticle forms. Compliance with OSHA guidelines and REACH regulations is critical for both materials, ensuring that exposure limits are maintained to protect workers and consumers.
Choosing the Right Pigment Coating for Your Needs
Choosing the right pigment coating depends on durability, UV resistance, and desired finish quality. Ceramic coatings offer superior hardness and long-lasting protection against scratches and chemical damage, making them ideal for automotive applications. Titania coatings provide excellent photocatalytic properties and UV stability, suitable for self-cleaning surfaces and outdoor durability.
Infographic: Ceramic coating vs Titania for Pigment
 azmater.com
azmater.com