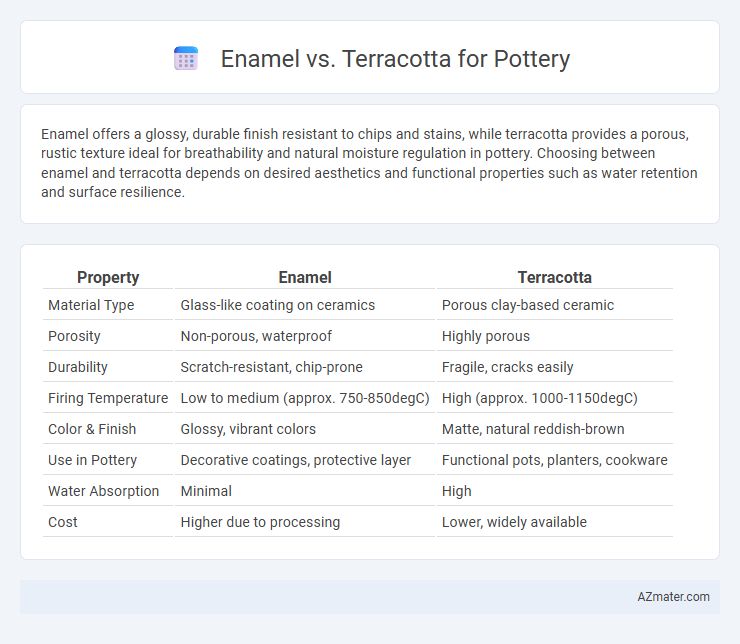
Enamel offers a glossy, durable finish resistant to chips and stains, while terracotta provides a porous, rustic texture ideal for breathability and natural moisture regulation in pottery. Choosing between enamel and terracotta depends on desired aesthetics and functional properties such as water retention and surface resilience.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Enamel | Terracotta |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glass-like coating on ceramics | Porous clay-based ceramic |
| Porosity | Non-porous, waterproof | Highly porous |
| Durability | Scratch-resistant, chip-prone | Fragile, cracks easily |
| Firing Temperature | Low to medium (approx. 750-850degC) | High (approx. 1000-1150degC) |
| Color & Finish | Glossy, vibrant colors | Matte, natural reddish-brown |
| Use in Pottery | Decorative coatings, protective layer | Functional pots, planters, cookware |
| Water Absorption | Minimal | High |
| Cost | Higher due to processing | Lower, widely available |
Introduction to Pottery Materials
Enamel and terracotta represent two distinct pottery materials, each offering unique properties and aesthetics. Terracotta, a porous clay fired at low temperatures, is prized for its natural, earthy tones and breathability, making it ideal for plant pots and traditional crafts. Enamel, a glassy coating fused onto pottery surfaces, provides durability, a glossy finish, and color versatility, enhancing both functionality and decorative appeal in ceramic ware.
What is Enamel in Pottery?
Enamel in pottery refers to a glassy coating fused onto the surface of ceramic pieces through high-temperature firing, providing a smooth, glossy finish that enhances durability and aesthetic appeal. This vitreous layer acts as a protective barrier against moisture and stains, making enamel-coated pottery highly resistant to wear and easy to clean. Unlike terracotta, which is porous and unglazed, enamel offers a non-porous surface that preserves the integrity of the pottery over time.
What is Terracotta in Pottery?
Terracotta in pottery refers to a type of earthenware made from natural clay, characterized by its reddish-brown color due to iron oxide content. It is porous and typically unglazed, requiring sealing or glazing for water resistance and durability. Terracotta is known for its rustic aesthetic, breathability, and thermal insulation, making it ideal for decorative and functional pottery pieces.
Physical Properties: Enamel vs Terracotta
Enamel pottery features a smooth, glossy surface created by fusing powdered glass to a substrate, resulting in a highly durable, non-porous finish that resists stains and scratches. Terracotta is a porous, unglazed clay characterized by its earthy, reddish-brown color and relatively low fired hardness, making it more susceptible to chipping and water absorption. The thermal properties of enamel allow for resistance to high temperatures and easy cleaning, while terracotta's porous nature provides excellent breathability but requires sealing for longevity in moisture-prone environments.
Aesthetic Differences and Finishes
Enamel pottery features a smooth, glossy finish achieved through a glassy coating that enhances vibrant colors and intricate designs, offering a modern and polished aesthetic. Terracotta pottery showcases a matte, rustic texture with earthy tones ranging from red to brown, emphasizing natural textures and a handmade, organic appearance. The choice between enamel and terracotta influences the overall visual impact, with enamel providing a sleek, reflective surface and terracotta highlighting warmth and traditional craftsmanship.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Enamel pottery offers superior durability due to its glass-like coating that resists chipping, scratching, and staining, making it ideal for long-term use. Terracotta, while valued for its rustic aesthetic and breathability, is more porous and prone to cracking or chipping over time, especially if not properly sealed. Therefore, enamel-coated pottery generally ensures greater longevity and maintains its appearance better under frequent use and exposure to moisture.
Suitability for Different Pottery Types
Enamel is ideal for decorative and functional pottery that requires a smooth, glossy finish and enhanced durability, such as tableware and ornamental vases. Terracotta suits rustic and artisanal pottery styles, offering porous and breathable qualities that make it perfect for plant pots, cookware, and traditional earthenware. Both materials cater to distinct aesthetic and functional needs, with enamel favored for modern, polished designs and terracotta valued for its natural, earthy appeal.
Maintenance and Care Factors
Enamel pottery requires regular cleaning with non-abrasive sponges to prevent chipping and maintain its glossy finish, and it is resistant to stains and odors. Terracotta pottery demands gentle handling due to its porous nature, often needing sealing to prevent moisture absorption and occasional reapplication of sealant to protect from cracking and mold growth. Both materials benefit from avoiding sudden temperature changes to prolong durability and ensure longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Enamel pottery involves coating metal or ceramic surfaces with glass-like substances, which requires high-energy kilns and emits pollutants during production, contributing to a larger carbon footprint compared to terracotta. Terracotta, made from natural clay fired at lower temperatures, is more environmentally sustainable due to its renewable raw materials and lower energy consumption. The biodegradability of terracotta pottery further reduces its environmental impact, making it an eco-friendlier choice over enamel-coated alternatives.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Pottery Project
Enamel offers a durable, glossy finish that is resistant to stains and scratches, making it ideal for functional pottery like kitchenware. Terracotta, known for its porous and earthy texture, provides excellent breathability, perfect for decorative pieces or plant pots that benefit from natural moisture regulation. Selecting between enamel and terracotta depends on the intended use, with enamel suited for everyday use and terracotta favored for aesthetic and natural appeal.
Infographic: Enamel vs Terracotta for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com