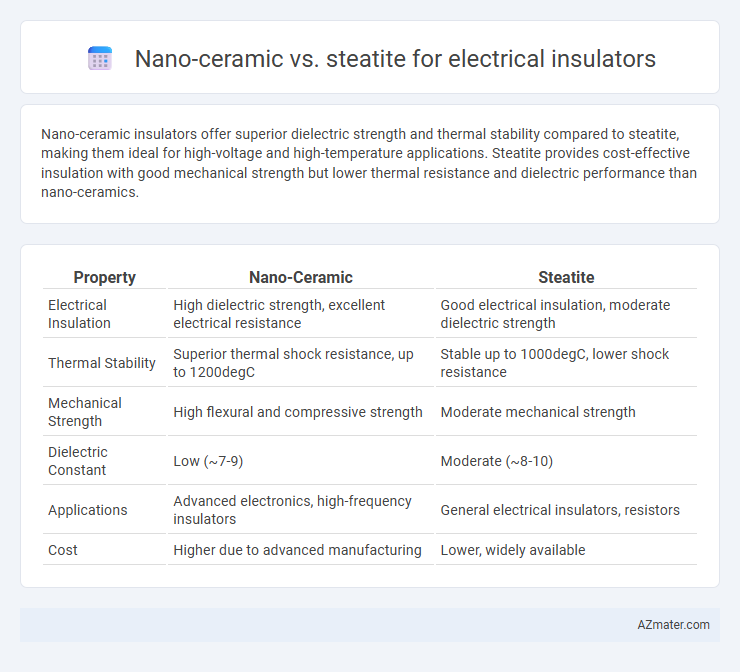
Nano-ceramic insulators offer superior dielectric strength and thermal stability compared to steatite, making them ideal for high-voltage and high-temperature applications. Steatite provides cost-effective insulation with good mechanical strength but lower thermal resistance and dielectric performance than nano-ceramics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nano-Ceramic | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength, excellent electrical resistance | Good electrical insulation, moderate dielectric strength |
| Thermal Stability | Superior thermal shock resistance, up to 1200degC | Stable up to 1000degC, lower shock resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | High flexural and compressive strength | Moderate mechanical strength |
| Dielectric Constant | Low (~7-9) | Moderate (~8-10) |
| Applications | Advanced electronics, high-frequency insulators | General electrical insulators, resistors |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced manufacturing | Lower, widely available |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators are critical materials used to prevent the flow of electric current by providing high resistance and maintaining electrical isolation. Nano-ceramic insulators offer enhanced dielectric strength, thermal stability, and mechanical durability due to their nano-scale grain structure. Steatite, a traditional ceramic insulator, is valued for its excellent thermal shock resistance and stable electrical insulation properties in high-voltage applications.
What Is Nano-Ceramic?
Nano-ceramic materials consist of ceramic particles with nanometer-sized grains that offer superior electrical insulation, thermal stability, and mechanical strength compared to conventional ceramics like steatite. Nano-ceramics provide enhanced dielectric properties and reduce electrical losses, making them ideal for high-performance electrical insulators in demanding applications. Steatite, composed mainly of magnesium silicate, is a traditional insulator known for good dielectric strength and machinability but lacks the advanced nano-scale properties that improve efficiency and durability.
Overview of Steatite Material
Steatite, a magnesium silicate ceramic, offers exceptional electrical insulation with high dielectric strength and thermal stability up to 1000degC, making it ideal for demanding electrical applications. Its low dielectric loss and excellent mechanical toughness enhance reliability in insulating components under thermal and mechanical stress. Compared to nano-ceramic materials, steatite provides cost-effective insulation with well-established manufacturing processes and proven durability in industrial use.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Nano-ceramic electrical insulators exhibit superior dielectric strength, thermal stability up to 1200degC, and enhanced mechanical toughness compared to steatite, which typically offers moderate dielectric strength and thermal resistance near 1000degC. Nano-ceramics have a lower coefficient of thermal expansion, reducing thermal stress in high-voltage applications, whereas steatite's higher porosity results in lower mechanical density and increased electrical losses. The enhanced microstructure of nano-ceramics contributes to improved electrical resistivity and higher resistance to electrical breakdown under harsh operating conditions relative to steatite.
Electrical Performance: Nano-Ceramic vs Steatite
Nano-ceramic electrical insulators exhibit superior dielectric strength and lower dielectric losses compared to steatite, making them ideal for high-frequency and high-voltage applications. Steatite, composed mainly of magnesium silicate, provides good mechanical strength and thermal stability but generally falls short in electrical insulation performance under extreme conditions. The nano-ceramic's fine microstructure allows enhanced electrical performance through improved uniformity and reduced porosity, resulting in higher reliability and efficiency in insulating applications.
Thermal Stability and Endurance
Nano-ceramic electrical insulators exhibit superior thermal stability with operating temperatures often exceeding 1200degC, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. Steatite insulators, composed primarily of magnesium silicate, typically remain stable up to around 1000degC but demonstrate excellent mechanical endurance and resistance to thermal shock. The enhanced grain structure of nano-ceramics contributes to improved thermal endurance and longer lifespan under cyclic thermal stress compared to steatite.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Nano-ceramic electrical insulators exhibit superior mechanical strength due to their fine microstructure, enhancing resistance to cracking and thermal stress compared to traditional steatite insulators. Steatite, composed primarily of magnesium silicate, offers good mechanical durability but tends to be more brittle and less resistant to impact over prolonged usage. The enhanced durability of nano-ceramics makes them ideal for high-performance electrical components requiring long-term reliability under mechanical and thermal stress.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Nano-ceramic electrical insulators offer superior mechanical strength and thermal stability but tend to be more expensive and less readily available compared to steatite ceramics. Steatite, a well-established material, provides cost-effective insulation with widespread availability and sufficient dielectric properties for many industrial applications. Choosing between nano-ceramic and steatite depends on balancing budget constraints against performance requirements and supply chain accessibility.
Application Suitability in Modern Technology
Nano-ceramic insulators exhibit superior thermal stability, high dielectric strength, and excellent resistance to electrical erosion, making them ideal for advanced electronics, high-frequency communication devices, and compact power modules. Steatite insulators offer reliable mechanical strength, low moisture absorption, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for traditional electrical components, ceramic bushings, and medium-power industrial applications. The choice between nano-ceramic and steatite depends on the operational environment, frequency requirements, and thermal management needs in modern technological systems.
Which Is Better: Nano-Ceramic or Steatite?
Nano-ceramic insulators offer superior dielectric strength and thermal stability compared to steatite, making them ideal for high-voltage and high-temperature applications. Steatite, composed mainly of magnesium silicate, provides excellent mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness but falls short in thermal resistance and electrical insulation properties relative to nano-ceramic materials. For critical electrical insulation tasks demanding enhanced durability and performance, nano-ceramics generally outperform steatite in efficiency and longevity.
Infographic: Nano-ceramic vs Steatite for Electrical insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com