Structural ceramics offer superior mechanical strength and fracture toughness compared to porcelain ceramics, making them highly durable for heavy-use dinnerware. Porcelain ceramics excel in aesthetic appeal and are more resistant to thermal shock, ideal for elegant and versatile tableware.
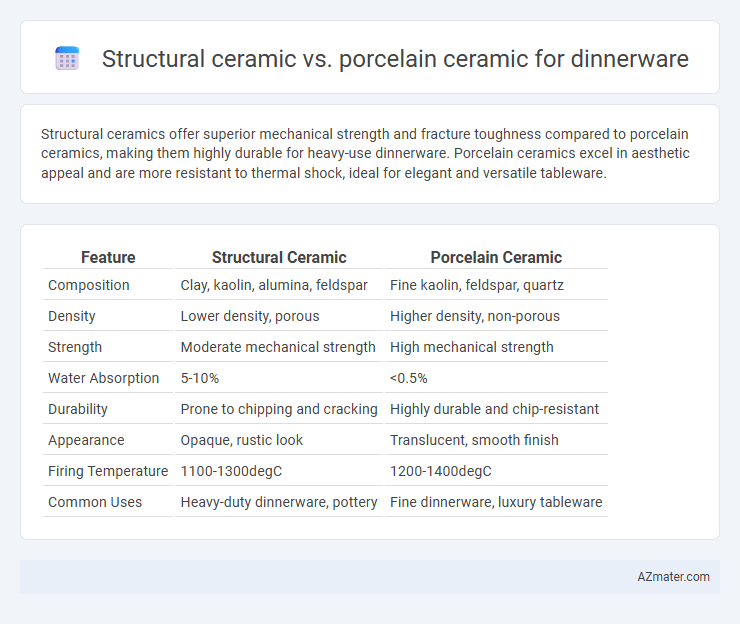
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Structural Ceramic | Porcelain Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay, kaolin, alumina, feldspar | Fine kaolin, feldspar, quartz |
| Density | Lower density, porous | Higher density, non-porous |
| Strength | Moderate mechanical strength | High mechanical strength |
| Water Absorption | 5-10% | <0.5% |
| Durability | Prone to chipping and cracking | Highly durable and chip-resistant |
| Appearance | Opaque, rustic look | Translucent, smooth finish |
| Firing Temperature | 1100-1300degC | 1200-1400degC |
| Common Uses | Heavy-duty dinnerware, pottery | Fine dinnerware, luxury tableware |
Introduction to Structural and Porcelain Ceramics
Structural ceramics, known for their high strength, hardness, and thermal resistance, are engineered materials primarily used in industrial applications where durability and performance under stress are critical. Porcelain ceramics, a subtype of structural ceramics, combine kaolin, feldspar, and quartz to create a dense, vitrified material prized for its translucency, non-porosity, and aesthetic qualities ideal for fine dinnerware. Both ceramics offer excellent durability, but porcelain's refined composition ensures superior resistance to chipping and staining, making it more suitable for everyday and formal table settings.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Structural ceramics for dinnerware primarily consist of alumina, zirconia, and silicon carbide, offering high strength and fracture toughness due to advanced sintering and hot pressing techniques. Porcelain ceramics are composed mainly of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, produced through traditional slip casting and high-temperature firing, resulting in a translucent and vitrified surface. Manufacturing differences influence durability and aesthetics, with structural ceramics favoring mechanical resilience, while porcelain emphasizes refined texture and translucency.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Structural ceramics used in dinnerware typically exhibit higher mechanical strength due to their dense microstructure and advanced manufacturing processes, making them highly resistant to chipping and cracking under stress. Porcelain ceramics, while prized for their translucency and aesthetic appeal, generally have lower mechanical strength but offer excellent durability through their vitrified surface that resists moisture and staining. The inherent toughness of structural ceramics outperforms porcelain in impact resistance, prolonging the lifespan of dinnerware subjected to frequent use and handling.
Aesthetic Qualities and Finish
Structural ceramics offer a matte, earthy finish with a robust texture that emphasizes natural, handcrafted aesthetics, making them ideal for rustic or artisanal dinnerware designs. Porcelain ceramics provide a smooth, glossy finish with a translucent quality, highlighting refined elegance and intricate detailing suited for formal dining settings. The choice between the two depends on desired visual appeal: the warm, tactile surface of structural ceramics versus the sleek, luminous surface of porcelain.
Weight and Handling Comfort
Structural ceramic dinnerware typically offers a lighter weight compared to porcelain ceramic, enhancing ease of handling during meals. Porcelain ceramics, while denser and heavier, provide a smooth, refined feel that some users find more comfortable to grip due to its balanced weight distribution. The choice between the two depends on whether lightweight convenience or sturdy comfort in handling is prioritized for daily use.
Thermal Resistance and Usage Safety
Structural ceramics offer superior thermal resistance, withstanding rapid temperature changes and exposure to high heat without cracking, making them ideal for oven-to-table applications. Porcelain ceramics, while elegant and non-porous, have moderate thermal shock resistance and are better suited for everyday dining and microwave use rather than direct heat exposure. Usage safety in structural ceramics is enhanced by their durability under thermal stress, reducing the risk of breakage, whereas porcelain's smooth surface provides ease of cleaning and resistance to bacterial contamination.
Porosity and Stain Resistance
Porcelain ceramic dinnerware features low porosity, making it highly resistant to moisture absorption and staining compared to more porous structural ceramics. This dense, vitrified material creates a durable, non-porous surface that resists food and liquid penetration, ensuring easier cleaning and long-lasting stain resistance. Structural ceramics typically exhibit higher porosity, which can lead to increased susceptibility to stains and reduced hygiene over time.
Cost Comparison and Value
Structural ceramic dinnerware generally offers a lower cost compared to porcelain ceramic, making it a budget-friendly option for everyday use. Porcelain ceramics, although more expensive, provide superior durability, resistance to chipping, and a refined aesthetic that adds long-term value to dinnerware collections. The higher initial investment in porcelain is often justified by its enhanced longevity and timeless appeal, making it a cost-effective choice over time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Structural ceramics demonstrate superior durability and lower resource consumption during manufacturing compared to porcelain ceramics, resulting in reduced environmental impact. Porcelain ceramics, though favored for their aesthetic appeal and translucency, require higher firing temperatures that increase energy use and carbon emissions. Choosing structural ceramics for dinnerware supports sustainability by minimizing waste through their enhanced strength and longer lifespan.
Ideal Applications for Dinnerware
Structural ceramics suit dinnerware requiring high mechanical strength and resistance to chipping, ideal for everyday, heavy-use settings such as restaurants and catering services. Porcelain ceramics offer superior translucency, smooth surface finish, and excellent resistance to stains and thermal shock, making them optimal for fine dining and elegant table settings. Both materials provide hygienic, non-porous surfaces crucial for food safety but differ primarily in durability and aesthetic appeal tailored to their respective applications.
Infographic: Structural ceramic vs Porcelain ceramic for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com