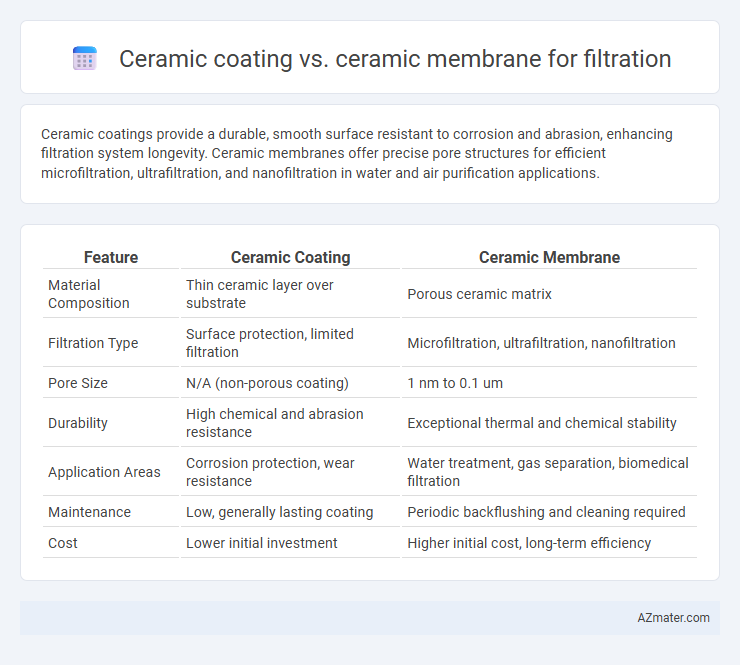
Ceramic coatings provide a durable, smooth surface resistant to corrosion and abrasion, enhancing filtration system longevity. Ceramic membranes offer precise pore structures for efficient microfiltration, ultrafiltration, and nanofiltration in water and air purification applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ceramic Coating | Ceramic Membrane |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Thin ceramic layer over substrate | Porous ceramic matrix |
| Filtration Type | Surface protection, limited filtration | Microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration |
| Pore Size | N/A (non-porous coating) | 1 nm to 0.1 um |
| Durability | High chemical and abrasion resistance | Exceptional thermal and chemical stability |
| Application Areas | Corrosion protection, wear resistance | Water treatment, gas separation, biomedical filtration |
| Maintenance | Low, generally lasting coating | Periodic backflushing and cleaning required |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher initial cost, long-term efficiency |
Introduction to Filtration Technologies
Ceramic coatings provide a thin, durable layer that enhances the surface properties of filtration substrates, improving resistance to corrosion and wear in industrial filtration systems. Ceramic membranes, composed of porous ceramic materials, enable high precision filtration with superior chemical and thermal stability, allowing for effective separation of fine particles and contaminants in water treatment and gas filtration. Both technologies play crucial roles in advanced filtration applications, with ceramic membranes offering enhanced selectivity and ceramic coatings contributing to extended filter lifespan.
Understanding Ceramic Coating in Filtration
Ceramic coating in filtration involves applying a thin, durable layer of ceramic material onto a substrate to enhance surface properties such as chemical resistance, thermal stability, and fouling resistance. This coating improves filter longevity and performance by protecting the base material from corrosion and mechanical wear while maintaining high permeability for efficient particle separation. Compared to ceramic membranes, which are porous and serve as the primary filtration medium, ceramic coatings act as protective or functional layers that complement filtration systems without solely relying on pore structure for separation.
What Are Ceramic Membranes?
Ceramic membranes are advanced filtration technologies composed of inorganic materials like alumina, zirconia, or titania, designed for high chemical, thermal, and mechanical stability. These membranes offer precise separation capabilities at the micro-, ultra-, and nanofiltration levels, making them ideal for harsh industrial applications involving aggressive chemicals and extreme temperatures. Unlike ceramic coatings that serve as protective layers, ceramic membranes function as selective barriers to remove particles, bacteria, and dissolved impurities from liquids and gases.
Material Properties: Coating vs Membrane
Ceramic coatings offer a dense, smooth, and chemically inert surface that enhances corrosion resistance and provides excellent thermal stability, making them ideal for protective applications. Ceramic membranes, in contrast, possess a porous, rigid structure with controlled pore sizes that enable precise microfiltration or ultrafiltration, combining high permeability with mechanical strength. The key difference lies in the ceramic coating's solid, impermeable characteristics versus the ceramic membrane's porous architecture designed for selective filtration.
Filtration Efficiency Comparison
Ceramic coatings offer moderate filtration efficiency by providing a protective layer that repels contaminants and enhances surface durability, typically capturing larger particles above 1 micron. Ceramic membranes achieve superior filtration efficiency with pore sizes as small as 0.1 microns, enabling effective removal of fine particles, bacteria, and viruses through precise microfiltration or ultrafiltration processes. The nanoporous structure of ceramic membranes results in higher contaminant retention and longer operational lifespan compared to the thin, often less porous ceramic coating layers.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Ceramic coatings offer excellent surface protection with moderate durability, typically lasting 3 to 5 years under harsh conditions, whereas ceramic membranes exhibit superior structural integrity and can operate efficiently for over 10 years with proper maintenance. The dense, microporous structure of ceramic membranes enhances resistance to chemical, thermal, and mechanical stress, making them ideal for long-term filtration applications. Durability analysis favors ceramic membranes due to their ability to withstand repeated cleaning cycles and high-pressure environments without significant degradation.
Chemical and Thermal Resistance
Ceramic coatings provide excellent chemical resistance by forming a dense, inert barrier that withstands acids, alkalis, and solvents, making them ideal for protecting surfaces in aggressive chemical environments. Ceramic membranes offer superior thermal stability, operating efficiently at temperatures up to 900degC while maintaining structural integrity and filtration performance. Both technologies leverage the inherent durability of ceramic materials, but ceramic membranes excel in high-temperature filtration applications due to their porous, rigid microstructure.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Ceramic coating in filtration systems offers enhanced surface durability but requires periodic reapplication to maintain efficiency, especially under abrasive conditions. Ceramic membranes provide superior chemical and thermal resistance, allowing for aggressive cleaning methods like backflushing and chemical cleaning without damaging the filtration matrix. Maintenance of ceramic membranes is generally simpler and less frequent compared to ceramic-coated filters, resulting in lower long-term operational costs and extended service life.
Cost Implications: Installation and Operation
Ceramic membranes generally incur higher initial installation costs compared to ceramic coatings due to their complex manufacturing and specialized module requirements. Operational expenses for ceramic membranes often include periodic membrane cleaning and replacement, which can be cost-intensive depending on the filtration application. Ceramic coatings, while cheaper to install, may require more frequent maintenance or replacement in aggressive environments, potentially increasing overall lifecycle costs.
Application Suitability and Recommendations
Ceramic membranes offer superior filtration precision and chemical resistance, making them ideal for wastewater treatment and pharmaceutical applications requiring ultra-filtration and micro-filtration. Ceramic coatings provide enhanced surface durability and anti-corrosion properties, best suited for protecting filtration equipment exposed to abrasive or high-temperature environments. For selecting between the two, prioritize ceramic membranes when high pore-size control and separation efficiency are critical, while ceramic coatings are recommended for extending the lifespan of filter surfaces in harsh operational conditions.
Infographic: Ceramic coating vs Ceramic membrane for Filtration
 azmater.com
azmater.com