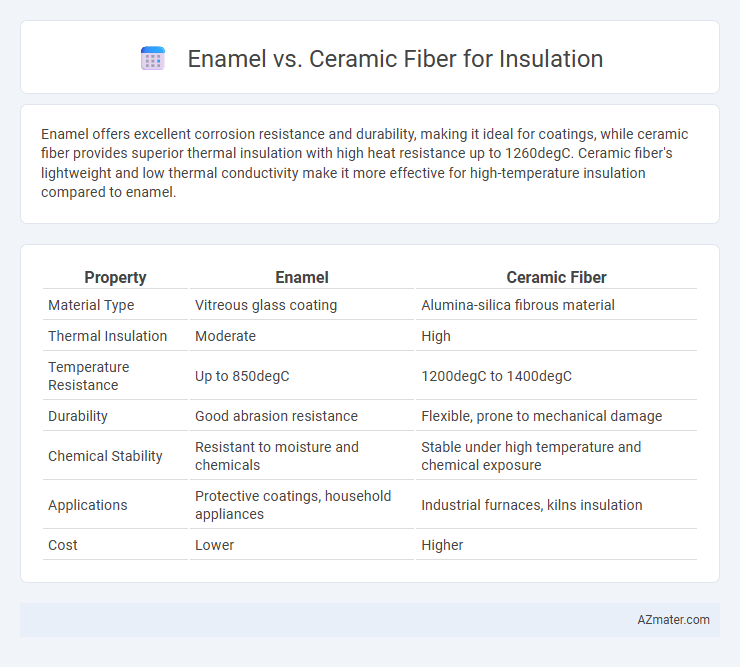
Enamel offers excellent corrosion resistance and durability, making it ideal for coatings, while ceramic fiber provides superior thermal insulation with high heat resistance up to 1260degC. Ceramic fiber's lightweight and low thermal conductivity make it more effective for high-temperature insulation compared to enamel.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Enamel | Ceramic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Vitreous glass coating | Alumina-silica fibrous material |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate | High |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 850degC | 1200degC to 1400degC |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance | Flexible, prone to mechanical damage |
| Chemical Stability | Resistant to moisture and chemicals | Stable under high temperature and chemical exposure |
| Applications | Protective coatings, household appliances | Industrial furnaces, kilns insulation |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Enamel and Ceramic Fiber Insulation
Enamel insulation features a durable, glassy coating that provides excellent resistance to heat, corrosion, and electrical conductivity, making it suitable for high-temperature applications and electrical components. Ceramic fiber insulation consists of alumina-silica fibers known for exceptional thermal stability, low thermal conductivity, and superior mechanical strength at elevated temperatures, widely used in industrial furnaces and kilns. Both materials offer distinct advantages in thermal insulation, with enamel excelling in protective applications and ceramic fiber ideal for intense thermal environments.
Composition and Material Properties
Enamel insulation primarily consists of a glassy coating fused onto metal substrates, offering high electrical resistance and durability, while ceramic fiber insulation comprises alumina and silica-based fibers known for outstanding thermal stability and low thermal conductivity. Enamel's composition provides excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for electrical applications, whereas ceramic fibers excel in high-temperature environments due to their refractory properties and lightweight structure. The material properties of ceramic fiber include resistance to thermal shock and chemical inertness, contrasting with enamel's superior electrical insulation and hardness.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Enamel coatings offer moderate thermal insulation with durability suited for protecting surfaces from high temperatures up to around 500degC, while ceramic fiber insulation excels in thermal performance by withstanding extreme temperatures exceeding 1260degC with minimal heat loss. Ceramic fiber's low thermal conductivity and high stability make it ideal for applications requiring superior heat resistance and energy efficiency, such as furnaces and kilns. In contrast, enamel's insulation value is limited by its relatively thin layer and lower heat tolerance, making it less effective for high-temperature insulation needs.
Temperature Resistance and Stability
Enamel insulation typically offers temperature resistance up to around 550degC, making it suitable for moderate heat applications but less stable under prolonged high-temperature exposure. Ceramic fiber insulation excels with temperature resistance exceeding 1260degC, providing superior thermal stability and durability in extreme heat environments. The choice between enamel and ceramic fiber hinges on the operational temperature range and the need for long-term structural integrity under thermal stress.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Enamel insulation offers superior mechanical strength due to its rigid, glass-like surface, making it highly resistant to abrasion and physical impact. Ceramic fiber insulation provides excellent durability at high temperatures, maintaining structural integrity and flexibility under thermal cycling. While enamel excels in mechanical wear resistance, ceramic fiber outperforms in thermal shock resilience and long-term dimensional stability in extreme environments.
Installation Methods and Ease of Use
Enamel insulation typically requires curing at high temperatures and precise application techniques, making installation more labor-intensive and suited for industrial settings. Ceramic fiber insulation is lightweight and flexible, allowing for easy cutting, shaping, and installation with minimal tools, which enhances speed and adaptability in various environments. The ease of use of ceramic fiber contributes to lower labor costs and faster project completion compared to the more rigid and intricate enamel application processes.
Fire Resistance and Safety Aspects
Enamel insulation offers moderate fire resistance with its glass-like coating that can withstand temperatures up to 850degC, making it suitable for applications requiring moderate heat protection. Ceramic fiber insulation excels in fire resistance, tolerating extreme temperatures up to 1,260degC or higher, providing superior safety in high-temperature environments such as furnaces and kilns. The non-combustible and lightweight nature of ceramic fibers also reduces fire hazards and improves overall safety compared to enamel coatings.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Enamel insulation typically offers lower upfront costs compared to ceramic fiber, making it a cost-effective option for projects with budget constraints. Ceramic fiber insulation, while more expensive initially, provides superior thermal resistance and longer service life, leading to reduced maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including energy savings and durability, is crucial for determining the most economically viable insulation material.
Typical Applications in Industry
Enamel and ceramic fiber insulation materials serve distinct industrial applications based on their properties. Enamel coatings are typically employed in electronics and automotive industries for heat resistance and electrical insulation, while ceramic fiber is favored in high-temperature environments such as furnaces, kilns, and petrochemical plants due to its superior thermal stability and low thermal conductivity. Ceramic fiber's lightweight and flexible nature also make it ideal for insulation in aerospace and power generation sectors where effective heat containment is critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Enamel insulation typically involves metal oxides, which can be energy-intensive to produce but often offer recyclability and durability, reducing waste over time. Ceramic fiber insulation is made from aluminosilicate materials that provide excellent thermal resistance and have a lower environmental footprint due to their natural raw materials and longer lifespan. Sustainable insulation choices prioritize materials with low embodied energy, recyclability, and minimal ecological disruption during production and disposal phases.
Infographic: Enamel vs Ceramic Fiber for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com