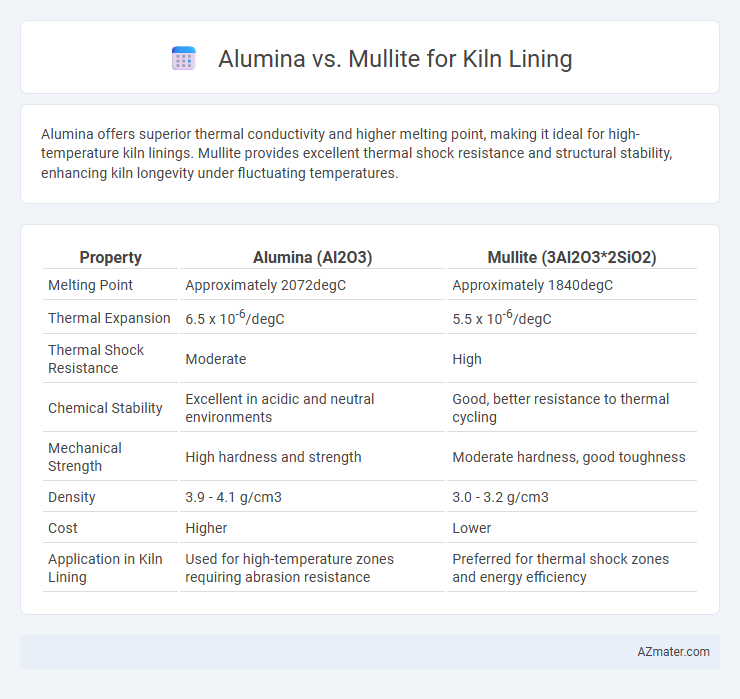
Alumina offers superior thermal conductivity and higher melting point, making it ideal for high-temperature kiln linings. Mullite provides excellent thermal shock resistance and structural stability, enhancing kiln longevity under fluctuating temperatures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alumina (Al2O3) | Mullite (3Al2O3*2SiO2) |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | Approximately 2072degC | Approximately 1840degC |
| Thermal Expansion | 6.5 x 10-6/degC | 5.5 x 10-6/degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Stability | Excellent in acidic and neutral environments | Good, better resistance to thermal cycling |
| Mechanical Strength | High hardness and strength | Moderate hardness, good toughness |
| Density | 3.9 - 4.1 g/cm3 | 3.0 - 3.2 g/cm3 |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Application in Kiln Lining | Used for high-temperature zones requiring abrasion resistance | Preferred for thermal shock zones and energy efficiency |
Overview of Kiln Lining Materials
Alumina and mullite are key refractory materials commonly used for kiln linings due to their high-temperature resistance and thermal stability. Alumina offers excellent hardness and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for areas exposed to intense wear and chemical attack, while mullite provides superior thermal shock resistance and lower thermal expansion, enhancing the kiln's structural integrity during rapid temperature changes. Selecting between alumina and mullite depends on specific kiln operating conditions, such as temperature range, mechanical stress, and chemical environment.
Alumina: Properties and Applications
Alumina is favored in kiln lining due to its high melting point above 2070degC, excellent thermal stability, and superior resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for extreme temperature environments. Its dense structure and high mechanical strength ensure durability under thermal shock and mechanical stress, commonly encountered in ceramic and metallurgical kilns. Applications of alumina-lined kilns include glass production, metal smelting, and advanced ceramics manufacturing, where maintaining structural integrity at high temperatures is critical.
Mullite: Properties and Applications
Mullite offers superior thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, making it an ideal material for kiln lining in high-temperature environments. Its high melting point around 1830degC and good mechanical strength ensure durability under fluctuating temperatures, outperforming alumina in shock resistance and dimensional stability. Widely used in ceramic and glass industries, mullite enhances kiln efficiency, longevity, and energy savings by maintaining structural integrity during prolonged thermal cycles.
Thermal Resistance: Alumina vs Mullite
Alumina offers superior thermal resistance with a melting point above 2072degC and excellent stability in high-temperature kiln conditions, making it ideal for extreme heat applications. Mullite provides good thermal resistance with a melting point around 1840degC and exceptional thermal shock resistance, enhancing durability under rapid temperature fluctuations. The choice depends on specific kiln operating temperatures and thermal cycling requirements, where alumina suits ultra-high heat while mullite excels in thermal shock endurance.
Chemical Durability Comparison
Alumina offers high chemical durability with excellent resistance to acidic slags and molten metals, making it ideal for environments with aggressive chemical exposures. Mullite provides superior resistance to alkali and silica attack due to its stable chemical structure, enhancing its performance in alkaline and siliceous atmospheres. The choice between alumina and mullite for kiln lining depends on the specific chemical environment, with alumina favored for acidic resistance and mullite preferred for alkaline and siliceous conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Wear Resistance
Alumina offers superior mechanical strength with high compressive and flexural strength values, making it ideal for kiln linings subjected to intense thermal and mechanical stresses. Mullite exhibits excellent wear resistance due to its stable microstructure and low thermal expansion, which enhances durability in abrasive and cyclic thermal environments. Combining high alumina content with mullite phases often results in kiln linings that balance mechanical robustness and wear resistance effectively.
Cost Analysis: Alumina vs Mullite
Alumina kiln linings generally offer higher thermal resistance and corrosion durability but come at a significantly greater cost compared to mullite. Mullite provides a more cost-effective solution with adequate thermal stability for many industrial applications, making it preferable where budget constraints exist without sacrificing essential performance. Evaluating the lifecycle expenses, including installation and maintenance, mullite often proves economical, whereas alumina's superior properties justify its premium price in high-demand environments.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Alumina kiln linings offer higher thermal conductivity and lower thermal expansion, making installation less complex due to better fit and reduced cracking risk compared to mullite. Mullite's superior thermal shock resistance and chemical stability demand careful installation to accommodate slight expansion and reduce maintenance frequency. Maintenance for alumina linings involves more frequent inspections due to potential spalling, while mullite linings typically require less frequent repairs but need precise initial installation to maximize service life.
Case Studies: Industrial Performance
Industrial case studies reveal that alumina kiln linings excel in high-temperature environments exceeding 1700degC, offering superior abrasion resistance and thermal conductivity for steel and cement production. Mullite linings demonstrate enhanced thermal shock resistance and lower thermal expansion, making them ideal for ceramic kilns operating between 1400degC and 1600degC. Data from multiple industries indicate alumina's robustness in continuous, high-wear scenarios, while mullite provides longevity in cyclical heating and cooling processes.
Choosing the Optimal Kiln Lining Material
Alumina offers superior thermal conductivity and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature kiln linings that require rapid heat transfer and durability under abrasive conditions. Mullite provides excellent thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion, which enhances kiln structural stability during frequent temperature fluctuations. Choosing the optimal kiln lining material depends on balancing alumina's high-temperature strength with mullite's stability to maximize kiln performance and lifespan.
Infographic: Alumina vs Mullite for Kiln lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com