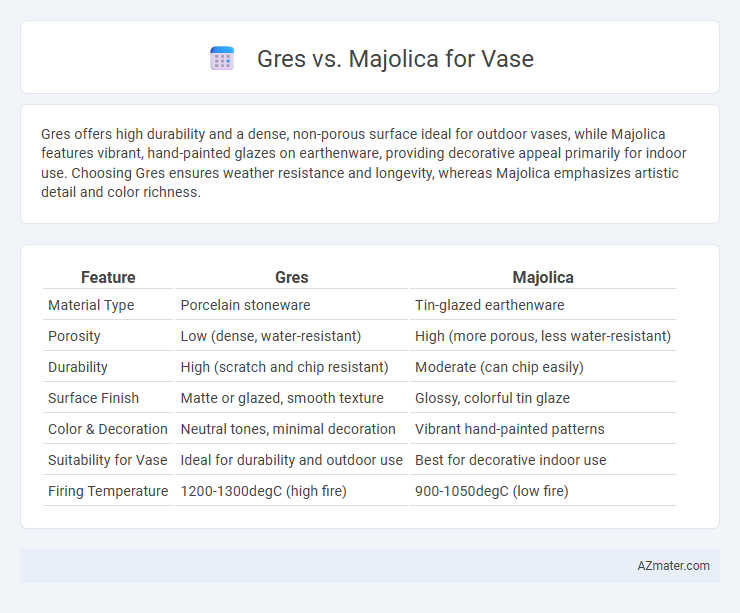
Gres offers high durability and a dense, non-porous surface ideal for outdoor vases, while Majolica features vibrant, hand-painted glazes on earthenware, providing decorative appeal primarily for indoor use. Choosing Gres ensures weather resistance and longevity, whereas Majolica emphasizes artistic detail and color richness.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gres | Majolica |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Porcelain stoneware | Tin-glazed earthenware |
| Porosity | Low (dense, water-resistant) | High (more porous, less water-resistant) |
| Durability | High (scratch and chip resistant) | Moderate (can chip easily) |
| Surface Finish | Matte or glazed, smooth texture | Glossy, colorful tin glaze |
| Color & Decoration | Neutral tones, minimal decoration | Vibrant hand-painted patterns |
| Suitability for Vase | Ideal for durability and outdoor use | Best for decorative indoor use |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1300degC (high fire) | 900-1050degC (low fire) |
Understanding Gres and Majolica: Key Differences
Gres, a dense and durable stoneware, is fired at high temperatures, making it highly resistant to water and mechanical wear, ideal for vase durability. Majolica, distinguished by its tin-glazed earthenware surface, features vibrant, glossy colors and intricate designs but is more porous and delicate compared to gres. Understanding these differences helps in selecting gres for robustness and majolica for decorative appeal in vase production.
Material Composition: Gres vs Majolica
Gres vases are made from high-fired stoneware, characterized by dense, durable clay that is fired at temperatures around 1200-1300degC, resulting in a strong, vitrified body with low porosity. Majolica vases, in contrast, are crafted from earthenware clay fired at lower temperatures, typically 950-1050degC, and feature a porous body coated with a tin-glaze that creates a glossy, decorative surface. The fundamental material composition difference--gres's stoneware base versus majolica's earthenware base--affects their durability, water absorption, and finish quality in vase applications.
Production Techniques: Traditional and Modern Methods
Gres vases are crafted using high-fired stoneware techniques, ensuring durability through vitrification at temperatures above 1200degC, utilizing traditional wheel-throwing methods and modern kiln technology. Majolica vases, characterized by their tin-glazed earthenware production, involve a multi-step process where an opaque white glaze is applied before hand-painting colorful motifs and firing at lower temperatures around 1000degC. Both methods combine handcrafted artistry with advancements in kiln precision and glazing chemistry to enhance the aesthetic and functional qualities of each vase.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Gres, a dense and highly vitrified stoneware, offers superior durability and strength compared to majolica, which is a less dense earthenware known for its decorative glaze but increased fragility. Gres vases resist chipping and cracking under impact due to their compact, non-porous structure, making them ideal for both indoor and outdoor use. In contrast, majolica vases require careful handling as their porous body and colorful glaze are more susceptible to damage from physical shocks and weather elements.
Aesthetic Qualities: Colors, Patterns, and Finishes
Gres vases showcase a matte, earthy finish with muted tones and natural textures, emphasizing rustic elegance and subtle color variations. Majolica vases feature vibrant, glossy glazes with intricate hand-painted patterns, often displaying bright blues, greens, and yellows that create a visually striking and ornate appearance. The choice between gres and majolica depends on whether a subdued, tactile aesthetic or a bold, colorful statement is desired.
Suitability for Vase Making
Gres clay offers exceptional durability and low porosity, making it highly suitable for vase making due to its strength and resistance to water absorption. Majolica, characterized by its porous bisque body coated with a tin glaze, provides vibrant decorative finishes but requires careful sealing to prevent water leakage. Choosing gres ensures structural integrity and longevity, while majolica excels in aesthetic appeal with its colorful, glossy surfaces.
Maintenance and Cleaning: Gres vs Majolica Vases
Gres vases, made from dense stoneware, offer superior resistance to stains and scratches, making maintenance straightforward with simple wiping and occasional gentle washing. Majolica vases, crafted from porous earthenware with a tin glaze, require careful handling to avoid chipping and glaze damage; cleaning with mild soap and a soft cloth is essential to preserve their colorful finish. Both materials benefit from avoiding harsh chemicals, but gres vases generally provide easier long-term upkeep due to their durability and lower porosity.
Price and Market Availability
Gres vases, known for their durability and high firing temperature, generally command moderate prices and enjoy broad market availability due to mass production in contemporary ceramics. Majolica vases, characterized by their intricate hand-painted glazes and historical artisan techniques, tend to be priced higher and are often found in specialty markets or as collectible items. Market demand for gres vases favors functionality and affordability, whereas majolica appeals to buyers seeking artistic value and uniqueness.
Environmental Impact of Gres and Majolica
Gres vases, made from high-fired stoneware clay, are more environmentally sustainable due to their durability and lower porosity, reducing the need for frequent replacement and minimizing waste. Majolica, characterized by its tin-glazed earthenware, requires lower firing temperatures but often involves lead-based glazes and higher emissions from glaze production, posing environmental and health concerns. Choosing gres supports eco-friendly ceramics by emphasizing longevity and non-toxic materials, whereas majolica demands careful consideration of glaze composition and disposal impact.
Choosing the Right Material: Gres or Majolica for Your Vase
Choosing between gres and majolica for your vase depends on durability and aesthetic preferences; gres offers high resistance to weather and scratches, making it ideal for outdoor or heavy-use environments, while majolica provides vibrant, hand-painted designs suitable for decorative indoor settings. Gres vases, typically fired at higher temperatures, exhibit a non-porous, stoneware quality that ensures longevity and minimal maintenance. Majolica ceramics feature a tin-glazed surface that enhances color vibrancy but requires more careful handling to prevent chipping or wear over time.
Infographic: Gres vs Majolica for Vase
 azmater.com
azmater.com