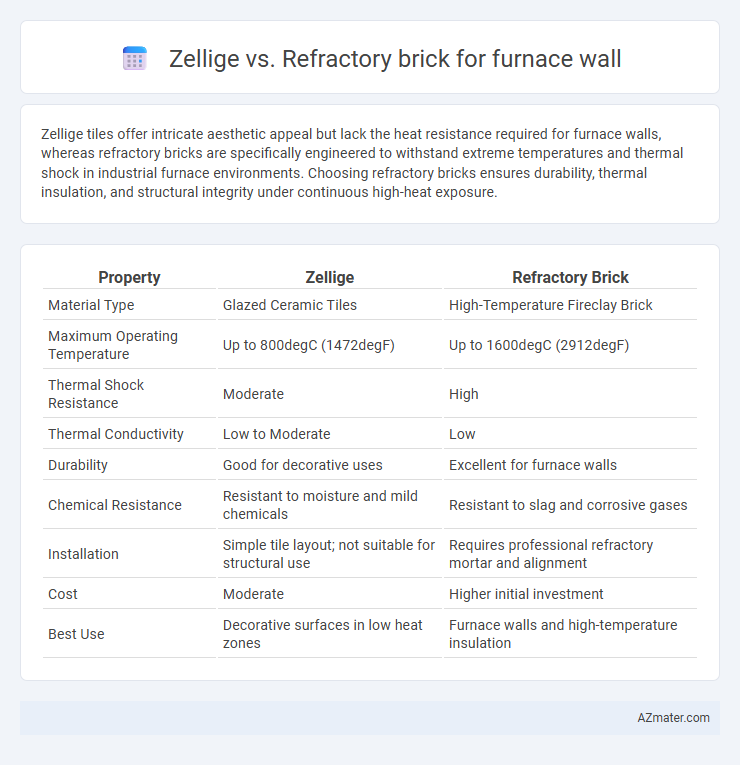
Zellige tiles offer intricate aesthetic appeal but lack the heat resistance required for furnace walls, whereas refractory bricks are specifically engineered to withstand extreme temperatures and thermal shock in industrial furnace environments. Choosing refractory bricks ensures durability, thermal insulation, and structural integrity under continuous high-heat exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zellige | Refractory Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed Ceramic Tiles | High-Temperature Fireclay Brick |
| Maximum Operating Temperature | Up to 800degC (1472degF) | Up to 1600degC (2912degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low to Moderate | Low |
| Durability | Good for decorative uses | Excellent for furnace walls |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to moisture and mild chemicals | Resistant to slag and corrosive gases |
| Installation | Simple tile layout; not suitable for structural use | Requires professional refractory mortar and alignment |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher initial investment |
| Best Use | Decorative surfaces in low heat zones | Furnace walls and high-temperature insulation |
Introduction to Furnace Wall Materials
Furnace wall materials play a crucial role in thermal efficiency and durability, with Zellige and refractory bricks being popular choices. Zellige, a handcrafted ceramic tile, offers aesthetic appeal but lacks the high heat resistance and mechanical strength required for industrial furnace walls. Refractory bricks, made from fireclay or silica, provide superior thermal insulation, high melting points above 1500degC, and resistance to chemical corrosion, making them the preferred material for furnace wall construction.
What is Zellige?
Zellige is a traditional Moroccan tile made from natural clay, known for its intricate geometric patterns and glazed finish, commonly used for decorative purposes rather than high-heat applications. Refractory bricks, by contrast, are specifically engineered to withstand extremely high temperatures, making them ideal for furnace walls where thermal resistance and durability are critical. While Zellige offers aesthetic appeal and cultural significance, refractory bricks ensure structural integrity and heat insulation in industrial furnace environments.
What are Refractory Bricks?
Refractory bricks are specialized ceramic materials designed to withstand high temperatures, thermal shock, and chemical corrosion, making them essential for furnace walls and kilns. They possess high melting points and excellent insulating properties, ensuring structural integrity and energy efficiency in extreme heat environments. Unlike Zellige tiles, which are decorative and not heat-resistant, refractory bricks provide durability and safety in industrial furnace applications.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Zellige tiles offer moderate thermal resistance suitable for decorative furnace walls but fall short compared to refractory bricks, which are engineered to withstand extreme temperatures exceeding 1500degC. Refractory bricks possess dense, insulating properties that reduce heat loss and enhance furnace efficiency by maintaining stable internal temperatures. When selecting materials for furnace walls, refractory bricks ensure superior thermal resistance and durability over zellige tiles, making them the preferred choice for high-temperature applications.
Durability and Longevity
Zellige tiles, made from natural clay and fired at high temperatures, offer moderate durability but are primarily designed for aesthetic wall finishes rather than high-heat environments. Refractory bricks, composed of alumina, silica, and other heat-resistant materials, exhibit superior thermal stability and longevity, making them ideal for furnace walls subjected to extreme temperatures. Their ability to withstand thermal cycling and chemical corrosion ensures enhanced structural integrity and extended service life in furnace applications.
Installation Methods
Zellige tiles require skilled artisans for precise hand-cutting and individual placement using a mortar bed, ensuring watertight grout with traditional cement or lime-based grout mixtures. Refractory bricks are installed by stacking and firing with heat-resistant refractory mortar, creating durable bonds that withstand intense furnace temperatures and thermal cycling. The method for refractory bricks prioritizes heat expansion accommodation and structural integrity, while Zellige's installation emphasizes aesthetic alignment and moisture resistance.
Maintenance Requirements
Zellige tiles used in furnace walls require regular cleaning and minimal sealing to maintain their aesthetic and heat resistance, though they may be more prone to surface chipping compared to refractory bricks. Refractory bricks exhibit superior durability with low maintenance demands, resisting thermal shock and chemical degradation, which reduces the frequency of repairs in high-temperature furnace environments. Choosing refractory bricks improves long-term reliability by minimizing maintenance costs related to cracking and spalling under intense heat cycles.
Cost Analysis
Zellige tiles typically cost more due to their handcrafted nature and aesthetic appeal, whereas refractory bricks provide a more budget-friendly solution with higher thermal resistance suited for furnace walls. Refractory bricks offer better durability under extreme temperatures and thermal cycling, reducing long-term maintenance expenses despite a higher initial bulk purchase. Cost analysis must consider both upfront material prices and lifecycle performance, with refractory bricks often proving more cost-effective for industrial furnace applications.
Suitability for Industrial Furnaces
Zellige tiles, known for their aesthetic appeal and glazed finish, lack the high thermal resistance required for industrial furnace walls, making them unsuitable for such applications. Refractory bricks are specifically engineered to withstand extreme heat, thermal cycling, and chemical corrosion, rendering them ideal for use in industrial furnace linings. Their dense, insulating properties ensure durability and energy efficiency in high-temperature environments essential for industrial processes.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Furnace Walls
Refractory bricks are the best choice for furnace walls due to their superior heat resistance, thermal conductivity, and durability compared to Zellige tiles, which are decorative and not designed for extreme temperatures. The high alumina content and dense structure of refractory bricks ensure prolonged performance under intense thermal stress, making them essential for industrial and high-temperature furnace applications. Opting for refractory bricks enhances furnace efficiency and longevity, reducing maintenance and replacement costs over time.
Infographic: Zellige vs Refractory brick for Furnace wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com