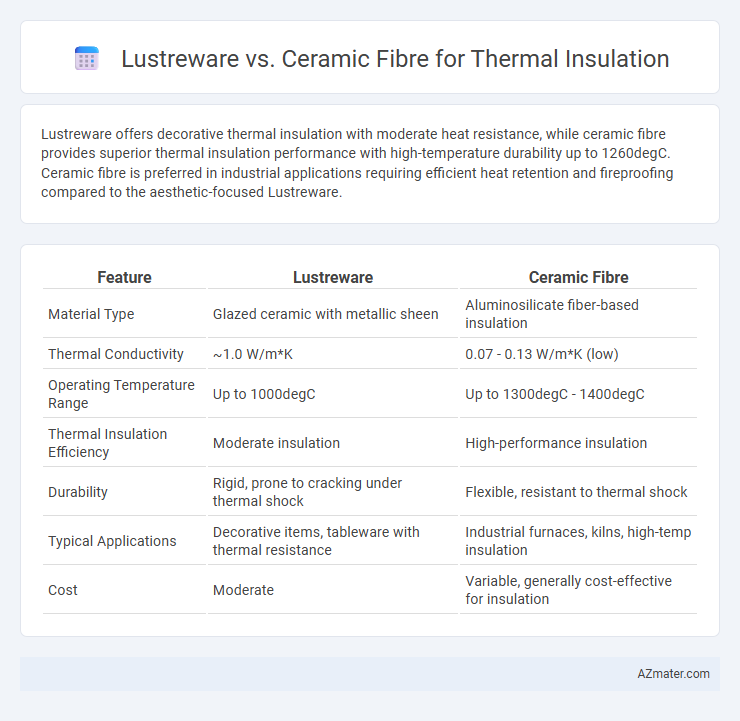
Lustreware offers decorative thermal insulation with moderate heat resistance, while ceramic fibre provides superior thermal insulation performance with high-temperature durability up to 1260degC. Ceramic fibre is preferred in industrial applications requiring efficient heat retention and fireproofing compared to the aesthetic-focused Lustreware.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lustreware | Ceramic Fibre |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed ceramic with metallic sheen | Aluminosilicate fiber-based insulation |
| Thermal Conductivity | ~1.0 W/m*K | 0.07 - 0.13 W/m*K (low) |
| Operating Temperature Range | Up to 1000degC | Up to 1300degC - 1400degC |
| Thermal Insulation Efficiency | Moderate insulation | High-performance insulation |
| Durability | Rigid, prone to cracking under thermal shock | Flexible, resistant to thermal shock |
| Typical Applications | Decorative items, tableware with thermal resistance | Industrial furnaces, kilns, high-temp insulation |
| Cost | Moderate | Variable, generally cost-effective for insulation |
Introduction to Thermal Insulation Materials
Thermal insulation materials like Lustreware and ceramic fibre play crucial roles in minimizing heat loss and enhancing energy efficiency across industrial applications. Lustreware, known for its glossy, durable surface and moderate insulating properties, is typically used in decorative and functional contexts where aesthetics and thermal resistance are needed. Ceramic fibre offers superior thermal insulation with high-temperature tolerance, low thermal conductivity, and lightweight characteristics, making it ideal for demanding environments such as furnaces, kilns, and heat shields.
What is Lustreware?
Lustreware is a type of ceramic material known for its iridescent glaze that enhances both aesthetic appeal and thermal insulation properties. Unlike ceramic fibre, which is primarily used for high-temperature insulation due to its fibrous and porous structure, lustreware combines decorative elements with moderate thermal resistance suitable for cookware and ornamental pieces. Its unique glaze composition allows it to withstand and reflect heat efficiently while providing a visually striking finish.
What is Ceramic Fibre?
Ceramic fibre is a high-temperature insulation material composed primarily of alumina and silica, known for its excellent thermal stability and low thermal conductivity. It is commonly used in industrial furnaces, kilns, and heat treatment processes due to its ability to withstand temperatures exceeding 1,200degC (2,192degF). Compared to lustreware, ceramic fibre offers superior resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making it ideal for demanding thermal insulation applications.
Material Composition and Properties
Lustreware is a type of glazed ceramic material primarily composed of clay with metallic oxide glazes that create a reflective, decorative surface but offer limited thermal insulation properties. Ceramic fibre, made from alumina and silica fibers, provides excellent thermal resistance with low thermal conductivity and high temperature stability, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation applications. The porous, fibrous structure of ceramic fibre contributes to superior heat retention and durability compared to the rigid, non-porous composition of lustreware.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Lustreware offers moderate thermal insulation primarily suited for decorative and light thermal barrier applications, with typical thermal conductivity ranging from 0.2 to 0.3 W/m*K. Ceramic fibre provides superior thermal insulation performance due to its low thermal conductivity between 0.05 and 0.15 W/m*K, enabling it to withstand high temperatures up to 1260degC while minimizing heat loss. Comparing thermal insulation efficiency, ceramic fibre surpasses lustreware significantly, making it ideal for industrial and high-temperature insulation needs.
Heat Resistance and Operating Temperature Range
Lustreware exhibits moderate heat resistance with an operating temperature range typically up to 500degC, making it suitable for decorative and low-heat insulation applications. Ceramic fibre offers superior thermal insulation capabilities, withstands temperatures up to 1260degC, and maintains structural integrity under extreme thermal stress. The choice between lustreware and ceramic fibre depends on the required heat resistance and maximum operating temperature of the insulation environment.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Lustreware offers moderate durability with resistance to high temperatures but may suffer from cracking or chipping under rapid thermal cycling compared to ceramic fibre. Ceramic fibre excels in longevity due to its superior thermal shock resistance, low thermal conductivity, and ability to maintain structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1000degC. For applications demanding sustained high-temperature performance and extended service life, ceramic fibre provides a more reliable thermal insulation solution than lustreware.
Installation and Application Methods
Lustreware offers lightweight and flexible installation, making it ideal for complex shapes and tight spaces, with adhesive bonding or mechanical fastening methods commonly used. Ceramic fibre products, known for their high-temperature resistance, typically require careful cutting, compression fitting, or anchoring with specialized hardware for optimal thermal performance. Both materials are widely applied in industrial furnaces, kilns, and thermal processing equipment, but Lustreware excels in ease of installation while Ceramic fibre suits more extreme temperature environments.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Lustreware offers superior safety in thermal insulation due to its non-toxic, chemical-free composition compared to Ceramic Fibre, which can release harmful silica dust posing respiratory risks. Environmentally, Lustreware is more sustainable as it is often made from recyclable materials with lower emissions during production, whereas Ceramic Fibre production involves high energy consumption and generates significant hazardous waste. Choosing Lustreware enhances workplace safety and supports eco-friendly insulation solutions, minimizing health hazards and environmental impact.
Cost-effectiveness and Practical Applications
Lustreware offers a cost-effective solution for thermal insulation with moderate durability and is ideal for low-heat industrial applications, while ceramic fibre provides superior thermal resistance and longevity at a higher initial investment, suitable for high-temperature environments such as furnaces and kilns. Ceramic fibre insulation excels in energy efficiency and longevity, reducing maintenance costs over time despite higher upfront expenses. Lustreware remains practical for applications where budget constraints prevail and temperature exposure is limited, balancing affordability with adequate performance.
Infographic: Lustreware vs Ceramic Fibre for Thermal Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com