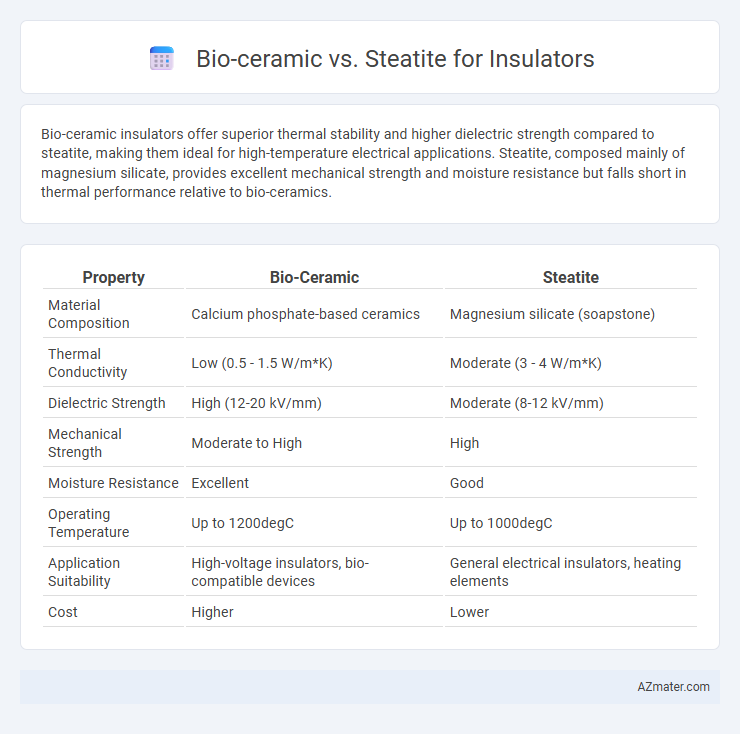
Bio-ceramic insulators offer superior thermal stability and higher dielectric strength compared to steatite, making them ideal for high-temperature electrical applications. Steatite, composed mainly of magnesium silicate, provides excellent mechanical strength and moisture resistance but falls short in thermal performance relative to bio-ceramics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bio-Ceramic | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Calcium phosphate-based ceramics | Magnesium silicate (soapstone) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (0.5 - 1.5 W/m*K) | Moderate (3 - 4 W/m*K) |
| Dielectric Strength | High (12-20 kV/mm) | Moderate (8-12 kV/mm) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate to High | High |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1000degC |
| Application Suitability | High-voltage insulators, bio-compatible devices | General electrical insulators, heating elements |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators are critical components in preventing undesired current flow in electrical systems, with bio-ceramic and steatite being prominent materials. Bio-ceramics offer enhanced thermal stability and higher dielectric strength compared to traditional steatite, which is valued for its cost-effectiveness and mechanical robustness. The choice between bio-ceramic and steatite insulators depends on factors such as operating temperature, electrical load requirements, and environmental conditions.
What are Bio-ceramic Insulators?
Bio-ceramic insulators are advanced materials composed of biocompatible ceramic compounds that offer exceptional electrical insulation and thermal resistance. These insulators are engineered for high durability and minimal environmental impact, making them ideal for medical devices and sensitive electronic applications. Compared to steatite, bio-ceramic insulators provide superior mechanical strength and enhanced performance in high-temperature environments.
Overview of Steatite as an Insulator
Steatite, a dense ceramic composed primarily of talc and other silicates, exhibits excellent electrical insulation properties with high dielectric strength and low dielectric losses. Its thermal stability and resistance to moisture make it ideal for high-voltage and high-temperature applications in electrical components and insulators. Compared to bio-ceramic insulators, steatite offers superior mechanical strength and durability under harsh environmental conditions.
Material Composition: Bio-ceramic vs Steatite
Bio-ceramic insulators primarily consist of advanced ceramic materials infused with bioactive compounds enhancing thermal stability and mechanical strength. Steatite insulators are made from natural steatite clay, rich in magnesium silicate, providing excellent dielectric properties and resistance to high voltage. The key difference in material composition lies in bio-ceramics' engineered microstructure for superior performance, while steatite relies on naturally occurring minerals for cost-effective insulation solutions.
Mechanical and Thermal Properties Comparison
Bio-ceramic insulators exhibit superior mechanical strength and higher fracture toughness compared to steatite, enhancing durability under mechanical stress. Thermal conductivity of bio-ceramics is generally lower, providing better thermal insulation, while steatite offers moderate thermal stability with higher thermal conductivity. Both materials perform well in electrical insulation, but bio-ceramic's enhanced thermal shock resistance makes it preferable for high-temperature applications.
Electrical Performance and Dielectric Strength
Bio-ceramic insulators typically offer superior electrical performance with higher dielectric strength, often exceeding 15 kV/mm, making them ideal for high-voltage applications. Steatite insulators, composed mainly of magnesium silicate, provide moderate dielectric strength around 8-12 kV/mm but excel in thermal stability and mechanical robustness. The choice between bio-ceramic and steatite depends on specific requirements for dielectric strength and electrical insulation in demanding environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bio-ceramic insulators derived from natural materials demonstrate lower environmental impact due to their biodegradability and reduced manufacturing emissions compared to steatite, which involves energy-intensive processing of raw mineral clays. Steatite insulators provide excellent thermal and electrical properties, but their extraction and processing contribute to resource depletion and higher carbon footprints. Sustainable applications increasingly favor bio-ceramics for insulation due to their eco-friendly lifecycle, minimized waste production, and compatibility with circular economy principles.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Bio-ceramic insulators generally exhibit higher initial costs due to advanced materials and manufacturing processes, while steatite offers a more budget-friendly option with moderate performance characteristics. Availability-wise, steatite is widely accessible and produced in large quantities globally, reducing lead times, whereas bio-ceramic materials may face limited regional production and longer procurement periods. Cost analysis favors steatite for large-scale, cost-sensitive projects, whereas bio-ceramic is preferred when superior insulation properties justify the investment.
Typical Applications in Industry
Bio-ceramic insulators are widely used in high-temperature industrial applications such as furnace linings, medical devices, and electronic components due to their excellent thermal stability and biocompatibility. Steatite insulators find typical applications in electrical equipment, high-voltage insulators, and heating elements for industrial ovens thanks to their high dielectric strength and thermal resistance. Both materials are essential in the electrical and thermal insulation sectors but are chosen based on specific thermal and electrical performance requirements.
Choosing the Right Insulator: Bio-ceramic or Steatite?
Bio-ceramic insulators offer superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, making them ideal for high-voltage and high-temperature applications, while steatite insulators excel in cost-efficiency and electrical insulation at moderate temperatures. Choosing between bio-ceramic and steatite depends on factors such as operating voltage, temperature range, and environmental conditions to ensure optimal performance and durability. Bio-ceramic materials provide enhanced resistance to chemical corrosion and wear, whereas steatite is preferred for applications demanding budget-friendly yet reliable insulation.
Infographic: Bio-ceramic vs Steatite for Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com