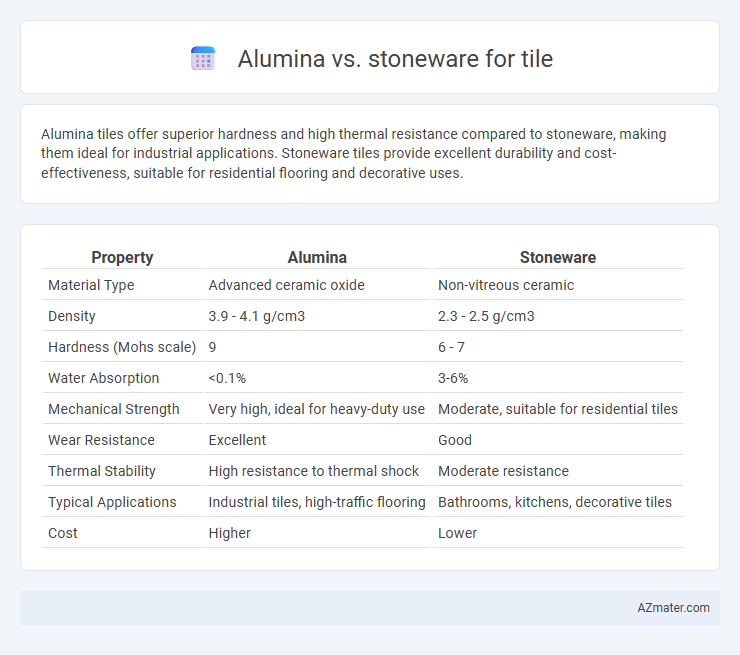
Alumina tiles offer superior hardness and high thermal resistance compared to stoneware, making them ideal for industrial applications. Stoneware tiles provide excellent durability and cost-effectiveness, suitable for residential flooring and decorative uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alumina | Stoneware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Advanced ceramic oxide | Non-vitreous ceramic |
| Density | 3.9 - 4.1 g/cm3 | 2.3 - 2.5 g/cm3 |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 9 | 6 - 7 |
| Water Absorption | <0.1% | 3-6% |
| Mechanical Strength | Very high, ideal for heavy-duty use | Moderate, suitable for residential tiles |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Thermal Stability | High resistance to thermal shock | Moderate resistance |
| Typical Applications | Industrial tiles, high-traffic flooring | Bathrooms, kitchens, decorative tiles |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Alumina and Stoneware Tiles
Alumina tiles are made from aluminum oxide, offering exceptional hardness, chemical resistance, and durability suitable for high-wear applications. Stoneware tiles consist of dense, fine-grained clay fired at high temperatures, providing a strong, water-resistant surface with natural textures and patterns. Both materials offer unique benefits for flooring and wall coverings, with alumina excelling in industrial settings and stoneware favored for aesthetic versatility in residential and commercial spaces.
Composition and Material Properties
Alumina tiles, composed primarily of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), offer exceptional hardness, high wear resistance, and superior thermal stability compared to stoneware tiles made from clay and other natural minerals. Stoneware's dense, vitrified structure provides moderate strength and water resistance but lacks the extreme durability and chemical resistance characteristic of alumina. The advanced ceramic composition of alumina tiles makes them ideal for industrial and high-stress environments, while stoneware suits residential applications requiring aesthetic appeal and moderate durability.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Alumina tiles exhibit superior durability due to their high alumina content, which enhances resistance to wear, heat, and chemical corrosion compared to stoneware. Stoneware tiles, while robust and resistant to moisture, tend to be less dense and more prone to chipping under heavy impact than alumina tiles. The structural composition of alumina provides greater strength, making it an ideal choice for high-traffic or industrial flooring environments where long-term performance is critical.
Aesthetic Options and Finishes
Alumina tiles offer a sleek, modern aesthetic with smooth, uniform finishes that enhance contemporary designs, available in high-gloss or matte options ideal for minimalist spaces. Stoneware tiles provide a natural, earthy look with rich textures and a wide variety of finishes, including rustic, matte, and glazed, perfectly suited for traditional or eclectic interiors. Both materials support diverse color palettes, but alumina excels in vibrant, consistent hues while stoneware showcases organic variations and handcrafted charm.
Water Absorption and Porosity
Alumina tiles exhibit significantly lower water absorption rates, typically below 0.5%, due to their dense, non-porous microstructure, making them highly resistant to moisture penetration. Stoneware tiles generally have higher porosity, with water absorption rates ranging from 3% to 7%, which can affect durability and stain resistance. The reduced porosity of alumina enhances its performance in wet and high-traffic environments, providing superior protection against water damage compared to stoneware.
Resistance to Chemicals and Stains
Alumina tiles exhibit superior resistance to chemicals and stains due to their dense, non-porous structure and high alumina content, making them ideal for environments with harsh chemical exposure. Stoneware tiles, while durable and resistant to everyday stains, are more porous and can absorb chemicals, which may cause surface damage or discoloration over time. The advanced chemical resistance of alumina tiles ensures longer-lasting aesthetics and reduced maintenance costs compared to stoneware in chemically intensive applications.
Thermal Performance and Heat Resistance
Alumina tiles exhibit superior thermal performance and heat resistance due to their high melting point around 2072degC and excellent thermal conductivity, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. Stoneware tiles, while durable and moderately heat-resistant, typically withstand temperatures up to approximately 1200degC but may suffer from thermal shock under rapid temperature changes. The denser microstructure of alumina enhances stability during thermal cycling, reducing the risk of cracking compared to the more porous stoneware.
Installation Methods and Considerations
Alumina tiles require adhesive installation due to their lightweight and uniform composition, allowing for precise alignment and reduced grout lines, while stoneware tiles often benefit from mortar or thinset methods because of their heavier weight and porous nature, enhancing durability and water resistance. Alumina's minimal porosity demands less sealing maintenance compared to stoneware, which typically requires pre-installation sealing to prevent moisture absorption and staining. Selecting the appropriate installation method hinges on substrate type, environmental conditions, and the tile's absorption rate, ensuring optimal adhesion and longevity for both alumina and stoneware tiles.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value
Alumina tiles typically demand a higher upfront cost due to advanced manufacturing processes and superior durability compared to stoneware, which proves more budget-friendly initially. Over time, alumina's exceptional hardness and resistance to abrasion result in lower maintenance expenses and longer replacement cycles, enhancing long-term value. Stoneware, while economical initially, may incur higher cumulative costs due to increased susceptibility to chipping and wear, reducing its overall cost efficiency in high-traffic applications.
Ideal Applications for Alumina vs Stoneware Tiles
Alumina tiles are ideal for high-traffic commercial spaces and industrial environments due to their superior hardness, abrasion resistance, and capacity to withstand heavy mechanical stress. Stoneware tiles excel in residential and light commercial applications, offering excellent water resistance and durability suitable for kitchens, bathrooms, and living areas. The choice between alumina and stoneware depends on the required wear resistance, with alumina preferred for extreme conditions and stoneware favored for aesthetic versatility and moderate durability.
Infographic: Alumina vs Stoneware for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com