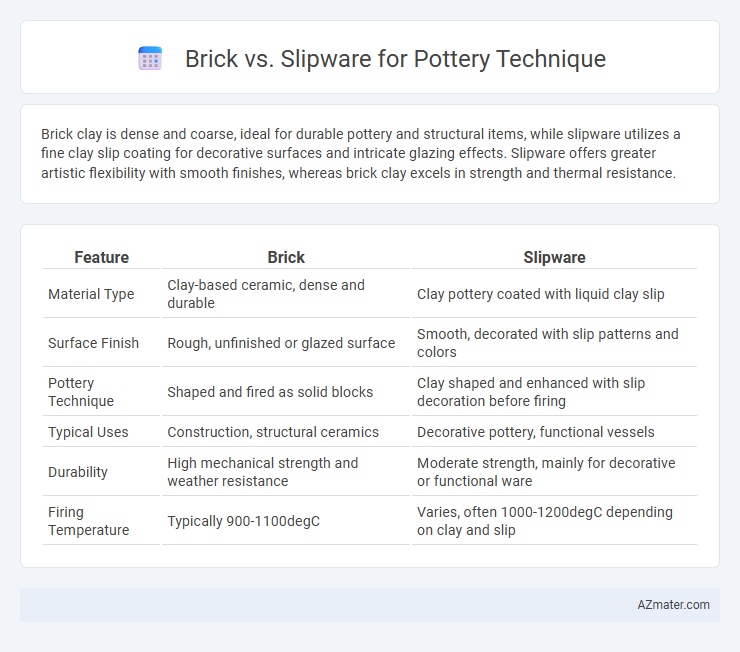
Brick clay is dense and coarse, ideal for durable pottery and structural items, while slipware utilizes a fine clay slip coating for decorative surfaces and intricate glazing effects. Slipware offers greater artistic flexibility with smooth finishes, whereas brick clay excels in strength and thermal resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Brick | Slipware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Clay-based ceramic, dense and durable | Clay pottery coated with liquid clay slip |
| Surface Finish | Rough, unfinished or glazed surface | Smooth, decorated with slip patterns and colors |
| Pottery Technique | Shaped and fired as solid blocks | Clay shaped and enhanced with slip decoration before firing |
| Typical Uses | Construction, structural ceramics | Decorative pottery, functional vessels |
| Durability | High mechanical strength and weather resistance | Moderate strength, mainly for decorative or functional ware |
| Firing Temperature | Typically 900-1100degC | Varies, often 1000-1200degC depending on clay and slip |
Introduction to Brick and Slipware Pottery
Brick pottery involves shaping clay into sturdy, uniform blocks typically used in construction, emphasizing durability and functionality. Slipware pottery is characterized by decorative techniques where liquid clay slip is applied to the surface, allowing intricate patterns and vibrant finishes. Both methods highlight distinct artistic and practical approaches within ceramic craftsmanship.
Historical Overview of Brick and Slipware Techniques
Brick-making techniques date back over 7,000 years, originating in ancient Mesopotamia where sun-dried and fired clay bricks were fundamental in building structures. Slipware pottery, emerging around the same period but more prominently in medieval Europe, involves coating ceramic pieces with liquid clay slip to create decorative patterns and smooth surfaces. Both methods showcase the evolution of clay utilization, with bricks emphasizing structural durability and slipware focusing on artistic expression.
Material Composition: Brick Clay vs Slipware Clay
Brick clay is typically composed of coarse-grained, iron-rich sediments that provide strength and reddish hues due to its high iron oxide content, making it ideal for durable pottery and construction materials. Slipware clay, on the other hand, utilizes finer, more plastic clays mixed with liquid slip--a suspension of clay particles in water--to create smooth surfaces suitable for decorative glazing and intricate designs. The distinct material compositions influence their respective functionalities: brick clay emphasizes structural integrity, while slipware clay prioritizes aesthetic appeal and surface refinement.
Formation and Construction Methods
Brick pottery techniques involve pressing clay into rectangular molds to create uniform, dense shapes suited for structural forms, emphasizing precision in mass production and consistency. Slipware pottery relies on applying liquid clay (slip) over a base form, often created through wheel throwing or hand-building, allowing for intricate surface decoration and varied textures. Formation in brick pottery is mostly mold-based with minimal shaping, while slipware focuses on layered construction and surface refinement through slip application.
Surface Decoration and Finishing Differences
Brick pottery exhibits a rough, matte surface achieved through minimal glazing and firing at lower temperatures, emphasizing texture over sheen. Slipware utilizes a liquid clay slip applied to clay bodies before firing, allowing intricate patterns and glossy finishes through controlled layering and polishing. Surface decoration on slipware demonstrates greater versatility with techniques like sgraffito and marbling, while brick pottery retains a rustic, earthy aesthetic due to its coarse finish and natural coloration.
Firing Processes: Temperatures and Effects
Brick firing typically occurs at high temperatures between 1000degC and 1100degC, resulting in a dense, durable ceramic body with a reddish hue due to iron content. Slipware firing is generally done at lower temperatures around 900degC to 1050degC, allowing the decorative slip to fuse smoothly to the surface without compromising intricate patterns. The difference in firing ranges affects the clay's porosity, strength, and color, with brick firings producing more robust pots and slipware emphasizing detailed surface aesthetics.
Durability and Functional Properties
Brick pottery demonstrates high durability due to its dense, fired clay composition, making it resistant to chipping and thermal shock, ideal for structural and heavy-use applications. Slipware, characterized by its decorative slip coating applied before firing, offers moderate durability but excels in aesthetic versatility and water resistance, suitable for functional tableware with artistic finishes. Both materials exhibit distinct functional properties: bricks prioritize strength and longevity, while slipware balances practical use with ornamental appeal.
Aesthetic Variations and Artistic Expression
Brick pottery emphasizes bold, structured forms with earthy textures and deep reddish-brown tones that highlight natural clay properties, creating a rustic aesthetic. Slipware technique utilizes fluid, colored slip to achieve intricate patterns, contrasting hues, and glossy surfaces, allowing for greater artistic expression and decorative complexity. The choice between brick and slipware significantly influences the visual impact and tactile experience of ceramic art.
Common Uses and Cultural Significance
Brick pottery, characterized by its dense, durable clay composition, is commonly used for structural and utilitarian items such as tiles, construction bricks, and heavy-duty vessels, reflecting its origins in ancient architectural practices. Slipware pottery, known for its decorative slip coating made from liquid clay, is predominantly crafted for ornamental and tableware purposes, showcasing intricate patterns and vibrant colors that highlight cultural artistry in regions like England and the Mediterranean. Both techniques hold significant cultural value: brick pottery symbolizes sustainable building traditions, while slipware represents artistic expression and social identity through its detailed surface designs.
Choosing the Right Technique: Brick or Slipware?
Choosing between brick and slipware pottery techniques depends on the desired aesthetic and function; brick pottery offers robust, structural qualities suited for utilitarian pieces, while slipware provides intricate decorative possibilities with colored slip application. Brick pottery involves shaping clay into dense, durable forms, emphasizing strength and simplicity, whereas slipware utilizes a liquid clay slip to create surface designs, allowing for vibrant patterns and textures. Considering the project's purpose, whether for everyday use or artistic display, guides the selection of the most appropriate technique.
Infographic: Brick vs Slipware for Pottery Technique
 azmater.com
azmater.com