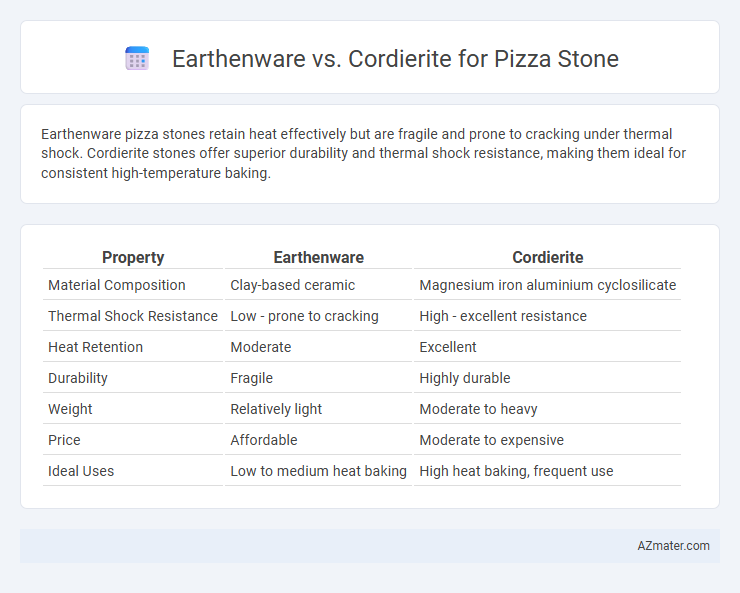
Earthenware pizza stones retain heat effectively but are fragile and prone to cracking under thermal shock. Cordierite stones offer superior durability and thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for consistent high-temperature baking.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Earthenware | Cordierite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay-based ceramic | Magnesium iron aluminium cyclosilicate |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low - prone to cracking | High - excellent resistance |
| Heat Retention | Moderate | Excellent |
| Durability | Fragile | Highly durable |
| Weight | Relatively light | Moderate to heavy |
| Price | Affordable | Moderate to expensive |
| Ideal Uses | Low to medium heat baking | High heat baking, frequent use |
Introduction to Pizza Stones: Earthenware vs Cordierite
Pizza stones are essential tools for achieving a crispy crust and evenly baked pizza by mimicking the effects of a brick oven. Earthenware pizza stones, made from natural clay, offer excellent heat retention and impart a rustic flavor but are more prone to cracking under thermal shock. Cordierite stones, composed of a mineral known for superior heat resistance, provide greater durability, even heat distribution, and are less likely to break when exposed to sudden temperature changes.
What is Earthenware?
Earthenware pizza stones are made from porous clay that absorbs moisture during baking, which helps create a crisp crust but makes them more prone to cracking under high heat. Cordierite, a mineral known for exceptional thermal shock resistance, outperforms earthenware by withstanding rapid temperature changes without breaking, making it a durable choice for frequent pizza baking. Earthenware is often favored for its natural heat retention and traditional aesthetic, though cordierite's strength and longevity make it ideal for long-term use.
What is Cordierite?
Cordierite is a mineral known for its exceptional thermal shock resistance and durability, making it an ideal material for pizza stones. Unlike earthenware, cordierite can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking, ensuring consistent heat distribution for evenly cooked pizzas. Its low thermal expansion and high heat retention improve baking performance, providing a more reliable and long-lasting cooking surface.
Heat Retention and Thermal Performance
Cordierite pizza stones exhibit superior heat retention and thermal shock resistance compared to earthenware, maintaining consistent high temperatures ideal for evenly baking pizzas. Earthenware heats quickly but tends to lose heat faster and may crack under rapid temperature changes, making it less durable for frequent use. The thermal conductivity of cordierite ensures efficient heat transfer, enhancing the crust's crispness and overall cooking performance.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Cordierite pizza stones exhibit superior durability and longevity compared to earthenware, due to their high thermal shock resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperature changes without cracking. Earthenware stones, while effective at heat retention, tend to be more porous and brittle, making them prone to chipping and cracking over time with repeated use. Consequently, cordierite is favored for long-term performance and resilience in pizza stone applications.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
Cordierite pizza stones exhibit superior resistance to thermal shock compared to earthenware, making them less prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes. Earthenware stones tend to absorb heat unevenly, increasing the risk of fractures when exposed to sudden heat spikes or cold water. Cordierite's crystalline structure allows it to withstand high temperatures and rapid cooling, ensuring greater durability and longevity in pizza baking applications.
Cooking Results: Crust Texture and Browning
Earthenware pizza stones excel in creating a crispy crust with a slightly softer interior due to their excellent heat retention but slower heat transfer, resulting in even browning without charring. Cordierite stones offer superior thermal shock resistance and faster heat conduction, producing a crust with a well-defined crispness and enhanced browning, ideal for high-temperature baking. Both materials contribute to distinct crust textures, with earthenware delivering traditional crunch and cordierite favoring a more robust, browned finish.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Earthenware pizza stones require careful maintenance, including avoiding thermal shock and thorough drying after each use to prevent cracking and mold growth. Cordierite stones are more durable and resistant to thermal shock, allowing easier cleaning by simply scrubbing with a brush and avoiding soap to maintain seasoning. Both materials benefit from regular removal of food residues but cordierite generally demands less delicate handling and upkeep.
Price Range and Accessibility
Earthenware pizza stones are generally more affordable, with prices typically ranging from $20 to $50, making them accessible for casual home bakers. Cordierite stones, priced between $40 and $100, offer superior thermal shock resistance and durability, but at a higher cost. Earthenware is widely available in most kitchenware stores, while cordierite stones may require shopping at specialty retailers or online platforms.
Which Pizza Stone Should You Choose?
Earthenware pizza stones offer excellent heat retention and a natural, porous surface that absorbs moisture for crispy crusts, making them ideal for home bakers seeking traditional results. Cordierite pizza stones provide superior thermal shock resistance and durability, allowing for frequent use at very high temperatures without cracking, perfect for busy kitchens and outdoor ovens. Choose earthenware for authentic texture and flavor or cordierite for long-lasting performance and consistent heat distribution.
Infographic: Earthenware vs Cordierite for Pizza Stone
 azmater.com
azmater.com