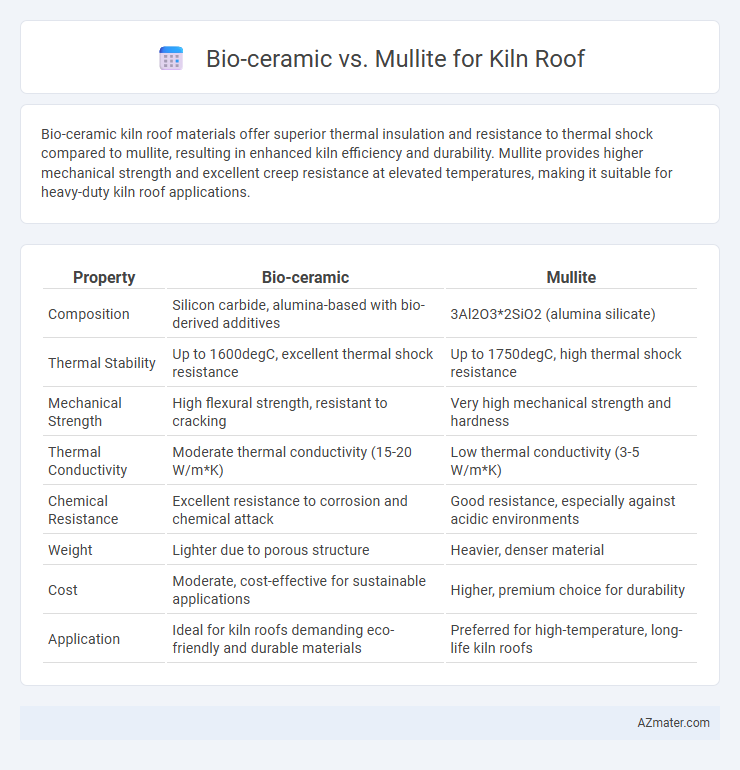
Bio-ceramic kiln roof materials offer superior thermal insulation and resistance to thermal shock compared to mullite, resulting in enhanced kiln efficiency and durability. Mullite provides higher mechanical strength and excellent creep resistance at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for heavy-duty kiln roof applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bio-ceramic | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silicon carbide, alumina-based with bio-derived additives | 3Al2O3*2SiO2 (alumina silicate) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1600degC, excellent thermal shock resistance | Up to 1750degC, high thermal shock resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | High flexural strength, resistant to cracking | Very high mechanical strength and hardness |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate thermal conductivity (15-20 W/m*K) | Low thermal conductivity (3-5 W/m*K) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to corrosion and chemical attack | Good resistance, especially against acidic environments |
| Weight | Lighter due to porous structure | Heavier, denser material |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective for sustainable applications | Higher, premium choice for durability |
| Application | Ideal for kiln roofs demanding eco-friendly and durable materials | Preferred for high-temperature, long-life kiln roofs |
Introduction to Kiln Roof Materials
Kiln roof materials play a crucial role in maintaining thermal efficiency and structural integrity under extreme temperatures. Bio-ceramic linings offer advanced thermal insulation and chemical resistance, making them ideal for high-performance kilns with rapid heating and cooling cycles. Mullite, a traditional ceramic material, provides excellent mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance, commonly used in industrial kiln roofs for durability and long service life.
Overview of Bio-ceramic and Mullite
Bio-ceramic materials for kiln roofs offer exceptional thermal insulation and resistance to chemical corrosion, typically composed of advanced aluminosilicate compounds designed to endure high temperatures up to 1600degC. Mullite, a silica-aluminum oxide mineral, provides excellent thermal shock resistance, mechanical strength, and stability in kiln environments, capable of withstanding temperatures around 1700degC with minimal deformation. Both materials are chosen for their durability and thermal performance, but bio-ceramics excel in insulation while mullite is favored for structural integrity in kiln roof applications.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Bio-ceramic kiln roofs offer superior thermal insulation due to their low thermal conductivity and ability to withstand rapid temperature fluctuations without degrading. Mullite, known for its excellent thermal stability and resistance to high temperatures up to 1800degC, provides strong insulation but generally has higher thermal conductivity compared to bio-ceramic materials. The choice between bio-ceramic and mullite depends on specific kiln operating temperatures and insulation efficiency requirements, with bio-ceramics often favored for enhanced energy savings and durability in variable thermal conditions.
Heat Resistance Comparison
Bio-ceramic offers superior heat resistance compared to mullite, withstanding temperatures up to 1650degC, making it ideal for high-temperature kiln roofs. Mullite, known for its excellent thermal stability and low thermal expansion, performs effectively up to about 1400degC but may degrade faster under extreme conditions. The enhanced insulating properties of bio-ceramics contribute to reduced energy consumption and prolonged kiln lifespan in high-temperature applications.
Structural Integrity and Strength
Bio-ceramic materials for kiln roofs provide superior thermal shock resistance and maintain structural integrity under rapid temperature fluctuations due to their fine microstructure and high compressive strength. Mullite, while also offering excellent high-temperature stability, excels in creep resistance and long-term stability at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for prolonged kiln operations. The choice between bio-ceramic and mullite depends on specific kiln conditions, with bio-ceramics favored for enhanced durability during thermal cycling and mullite preferred for robust performance under sustained heat load.
Energy Efficiency in Kiln Operations
Bio-ceramic kiln roofs provide superior insulation and lower thermal conductivity compared to mullite, resulting in enhanced energy efficiency during kiln operations. The bio-ceramic material minimizes heat loss, maintaining higher internal temperatures with less fuel consumption. In contrast, mullite, while durable and thermally stable, exhibits higher heat dissipation, leading to increased energy requirements and operational costs.
Lifespan and Durability
Bio-ceramic kiln roof materials offer superior lifespan and durability compared to Mullite due to their enhanced thermal shock resistance and lower thermal conductivity. Mullite, while stable at high temperatures, tends to develop micro-cracks over prolonged use, reducing its durability under cyclic thermal loads. The bio-ceramic composition effectively minimizes structural degradation, extending kiln roof service life and reducing maintenance costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bio-ceramic kiln roofs offer superior environmental benefits due to their lower energy consumption during manufacturing and enhanced thermal insulation, reducing overall kiln fuel usage. Mullite, derived from alumina and silica, requires higher processing temperatures which increase carbon emissions, though it provides excellent durability and thermal stability. Choosing bio-ceramic materials supports sustainability initiatives by minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting eco-friendly kiln operation.
Cost Analysis: Bio-ceramic vs Mullite
Bio-ceramic kiln roof materials typically offer a higher initial cost compared to mullite due to advanced manufacturing processes and superior thermal insulation properties. Mullite provides a more economical option with lower upfront expenses but may require more frequent maintenance and replacement, impacting long-term costs. When evaluating overall cost-efficiency, bio-ceramic's enhanced durability and energy savings often result in reduced operational expenses over the kiln's lifespan.
Choosing the Right Material for Kiln Roofs
Bio-ceramic materials provide superior thermal insulation and resistance to thermal shock compared to mullite, making them ideal for high-temperature kiln roofs where energy efficiency is critical. Mullite, known for its excellent mechanical strength and stability at elevated temperatures, is a preferred choice for kilns requiring durability under heavy load and abrasive conditions. Selecting the right kiln roof material depends on balancing thermal insulation needs with structural strength, where bio-ceramics excel in reducing heat loss and mullite ensures long-term mechanical integrity.
Infographic: Bio-ceramic vs Mullite for Kiln Roof
 azmater.com
azmater.com