Ceramic resin offers superior fracture toughness and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-speed cutting applications. Alumina provides exceptional hardness and wear resistance but is more brittle, suitable for precision machining of harder materials.
Table of Comparison
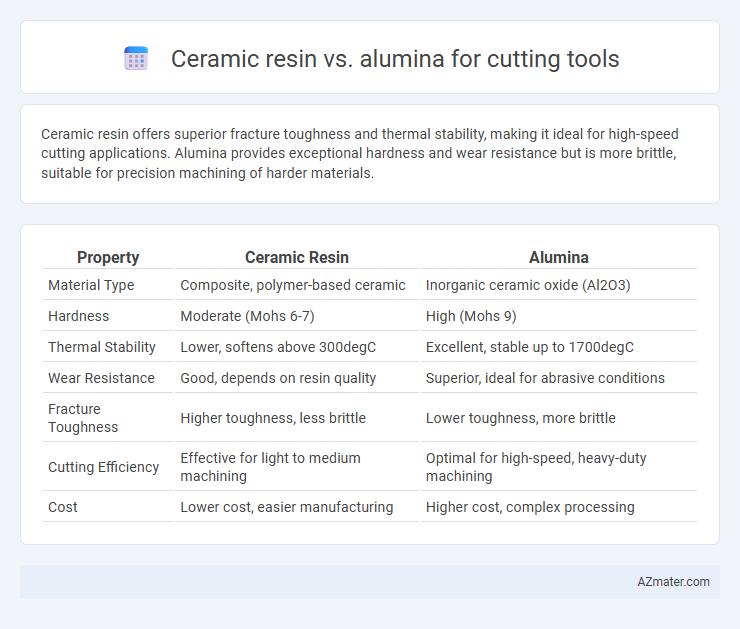
| Property | Ceramic Resin | Alumina |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Composite, polymer-based ceramic | Inorganic ceramic oxide (Al2O3) |
| Hardness | Moderate (Mohs 6-7) | High (Mohs 9) |
| Thermal Stability | Lower, softens above 300degC | Excellent, stable up to 1700degC |
| Wear Resistance | Good, depends on resin quality | Superior, ideal for abrasive conditions |
| Fracture Toughness | Higher toughness, less brittle | Lower toughness, more brittle |
| Cutting Efficiency | Effective for light to medium machining | Optimal for high-speed, heavy-duty machining |
| Cost | Lower cost, easier manufacturing | Higher cost, complex processing |
Introduction to Cutting Tool Materials
Cutting tool materials such as ceramic resin and alumina play a crucial role in machining performance, with ceramic resin offering enhanced toughness and thermal stability for high-speed applications. Alumina, or aluminum oxide, is prized for its exceptional hardness and resistance to wear, making it suitable for cutting abrasive materials. The choice between ceramic resin and alumina depends on machining conditions, material hardness, and desired tool life, impacting overall precision and productivity.
Overview of Ceramic Resin in Cutting Tools
Ceramic resin in cutting tools offers excellent wear resistance and thermal stability, making it suitable for high-speed machining applications. Compared to alumina, ceramic resin provides improved toughness and reduced brittleness, enhancing tool life under intermittent cutting conditions. Its composite structure allows for better shock absorption and dimensional stability in precision cutting tasks.
What is Alumina and Its Role in Cutting Tools
Alumina, or aluminum oxide (Al2O3), is a widely used ceramic material in cutting tools due to its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. Its role in cutting tools is to enhance durability and maintain sharpness during high-temperature machining, especially for hard metals. Alumina-based tools offer superior toughness compared to traditional ceramic resins, providing increased efficiency and lifespan in precision cutting applications.
Material Properties: Ceramic Resin vs Alumina
Ceramic resin offers enhanced toughness and flexibility compared to alumina, making it suitable for cutting tools that require resistance to chipping and cracking. Alumina provides superior hardness and thermal stability, ensuring high wear resistance and cutting precision at elevated temperatures. The choice between ceramic resin and alumina depends on the desired balance between impact resistance and cutting performance under extreme conditions.
Wear Resistance Comparison
Ceramic resin cutting tools exhibit moderate wear resistance suitable for machining softer materials but degrade rapidly under high thermal and mechanical stress. Alumina cutting tools provide superior wear resistance due to their high hardness and thermal stability, maintaining edge sharpness longer in abrasive and high-temperature conditions. The alumina's durable oxide composition makes it ideal for heavy-duty cutting applications, outperforming ceramic resin in lifespan and wear rate metrics.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Ceramic resin exhibits moderate heat resistance but faces thermal degradation at temperatures surpassing 200degC, limiting its suitability for high-temperature cutting applications. Alumina, with exceptional thermal stability and a melting point around 2072degC, withstands extreme heat and ensures durability in cutting tools operating under severe thermal conditions. This superior heat resistance and thermal stability make alumina the preferred material for high-performance cutting tools requiring sustained efficiency and wear resistance.
Cutting Performance and Efficiency
Ceramic resin cutting tools provide enhanced toughness and thermal shock resistance, resulting in longer tool life and reduced wear during high-speed machining. Alumina-based cutting tools excel in hardness and heat resistance, enabling superior cutting performance in abrasive and high-temperature conditions but may have lower impact resistance. Selecting between ceramic resin and alumina depends on the balance between cutting efficiency, tool longevity, and the specific material being machined.
Cost Analysis: Ceramic Resin vs Alumina
Ceramic resin cutting tools often have a lower initial cost compared to alumina-based tools due to less expensive raw materials and manufacturing processes. However, alumina tools typically offer longer tool life and higher wear resistance, reducing replacement frequency and overall operational costs in high-speed or abrasive machining applications. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including tool durability and performance efficiency, often favors alumina despite higher upfront investment.
Suitable Applications for Each Material
Ceramic resin cutting tools excel in applications requiring high toughness and thermal stability, making them ideal for machining hardened steels and cast irons at moderate speeds. Alumina cutting tools offer superior hardness and wear resistance, suited for high-speed machining of abrasive materials such as stainless steel and superalloys. Selecting between ceramic resin and alumina depends on workpiece material, cutting speed, and tool life requirements to optimize performance and cost-efficiency.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Cutting Tools
Ceramic resin offers excellent toughness and thermal resistance, making it ideal for cutting tools exposed to high temperatures and shock loads, while alumina excels in hardness and wear resistance for precision machining. Selecting the right material depends on the application's specific requirements, such as cutting speed, workpiece material, and tool life expectations. Optimal performance is achieved by balancing alumina's durability with ceramic resin's resilience to ensure efficiency and cost-effectiveness in machining operations.
Infographic: Ceramic resin vs Alumina for Cutting tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com