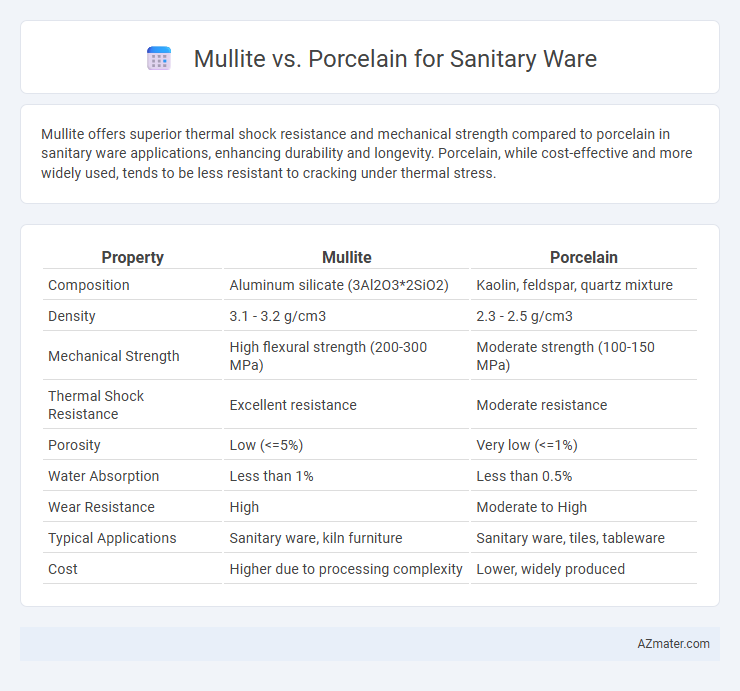
Mullite offers superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength compared to porcelain in sanitary ware applications, enhancing durability and longevity. Porcelain, while cost-effective and more widely used, tends to be less resistant to cracking under thermal stress.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Mullite | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminum silicate (3Al2O3*2SiO2) | Kaolin, feldspar, quartz mixture |
| Density | 3.1 - 3.2 g/cm3 | 2.3 - 2.5 g/cm3 |
| Mechanical Strength | High flexural strength (200-300 MPa) | Moderate strength (100-150 MPa) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent resistance | Moderate resistance |
| Porosity | Low (<=5%) | Very low (<=1%) |
| Water Absorption | Less than 1% | Less than 0.5% |
| Wear Resistance | High | Moderate to High |
| Typical Applications | Sanitary ware, kiln furniture | Sanitary ware, tiles, tableware |
| Cost | Higher due to processing complexity | Lower, widely produced |
Introduction to Mullite and Porcelain
Mullite is a highly durable alumino-silicate mineral known for its excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance sanitary ware applications. Porcelain, a fine, white ceramic material made from kaolin clay, feldspar, and quartz, is prized for its smooth surface, aesthetic appeal, and resistance to water and stains. Both materials offer distinct advantages in sanitary ware manufacturing, with mullite excelling in durability and porcelain favored for its refined finish and ease of cleaning.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Mullite, primarily composed of 3Al2O3*2SiO2, exhibits higher alumina content compared to porcelain, which contains a mixture of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz with alumina levels generally around 30-40%. This elevated alumina concentration in mullite contributes to superior chemical stability and resistance to acidic environments, making it ideal for sanitary ware applications requiring durability against harsh cleaning agents. In contrast, porcelain's balanced chemical composition offers good mechanical strength and aesthetic appeal but lower chemical resistance relative to mullite-based ceramics.
Manufacturing Processes
Mullite sanitary ware is produced using high-temperature sintering of alumino-silicate materials, resulting in superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength. Porcelain manufacturing involves the vitrification of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz at lower temperatures compared to mullite, producing a denser, more vitrified surface ideal for smooth finishes. The choice between mullite and porcelain impacts firing times, energy consumption, and the final product's durability in sanitary ware applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Mullite-based sanitary ware offers superior mechanical strength due to its unique crystalline structure, providing enhanced resistance to cracking and chipping compared to traditional porcelain. Porcelain, while exhibiting good hardness, tends to be more brittle and less durable under high-impact conditions, leading to increased wear over time. The thermal stability and fracture toughness of mullite make it an optimal choice for long-lasting sanitary applications requiring robust durability.
Water Absorption and Porosity
Mullite sanitary ware exhibits lower water absorption rates, typically below 0.5%, due to its dense microstructure and high-temperature firing process, compared to porcelain which generally shows water absorption around 0.5-2%. The reduced porosity in mullite contributes to enhanced durability and resistance to moisture penetration, making it ideal for sanitary applications requiring longevity and hygiene. Porcelain, while culturally popular and aesthetically versatile, has higher porosity levels that may affect its stain resistance and long-term performance in high-moisture environments.
Thermal Stability and Shock Resistance
Mullite offers superior thermal stability compared to porcelain, withstanding temperatures up to 1,800degC without deformation, making it ideal for high-heat sanitary ware applications. Its low thermal expansion coefficient enhances shock resistance, reducing the risk of cracks under rapid temperature changes. Porcelain, while durable and aesthetically pleasing, typically exhibits lower thermal shock resistance and may crack under sudden temperature fluctuations.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics
Mullite offers a smoother surface finish with higher resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for sanitary ware that demands durability and long-lasting aesthetics. Porcelain provides a glossy, refined appearance with exceptional color consistency and translucency, enhancing the visual appeal of bathroom fixtures. The choice between mullite and porcelain depends on whether the priority is surface resilience or superior, elegant aesthetics.
Cost-Efficiency Analysis
Mullite sanitary ware offers higher thermal stability and mechanical strength but comes at a greater initial cost compared to porcelain, which is more affordable and widely used in budget-friendly applications. Porcelain's lower production and material expenses make it a cost-efficient choice for standard sanitary ware, while mullite's durability reduces long-term maintenance and replacement costs in high-demand settings. Evaluating total lifecycle costs reveals porcelain excels in cost-efficiency for residential use, whereas mullite provides better value in commercial or industrial environments with rigorous usage.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Mullite sanitary ware offers superior thermal stability and durability, reducing replacement frequency and lowering long-term resource consumption compared to porcelain. Porcelain manufacturing typically demands higher energy input due to firing at elevated temperatures, resulting in increased carbon emissions relative to mullite-based products. Mullite's enhanced resistance to chemical erosion extends product lifespan, minimizing landfill waste and promoting sustainable bathroom fixtures.
Choosing the Right Material for Sanitary Ware
Mullite offers superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength compared to porcelain, making it ideal for demanding sanitary ware applications requiring durability and longevity. Porcelain, favored for its smooth surface finish and excellent whiteness, provides strong chemical resistance and aesthetic appeal but may be more prone to chipping under heavy impact. Selecting between mullite and porcelain depends on the specific sanitary ware use-case, balancing factors like mechanical stress, aesthetic requirements, and thermal performance to ensure optimal functionality and lifespan.
Infographic: Mullite vs Porcelain for Sanitary ware
 azmater.com
azmater.com