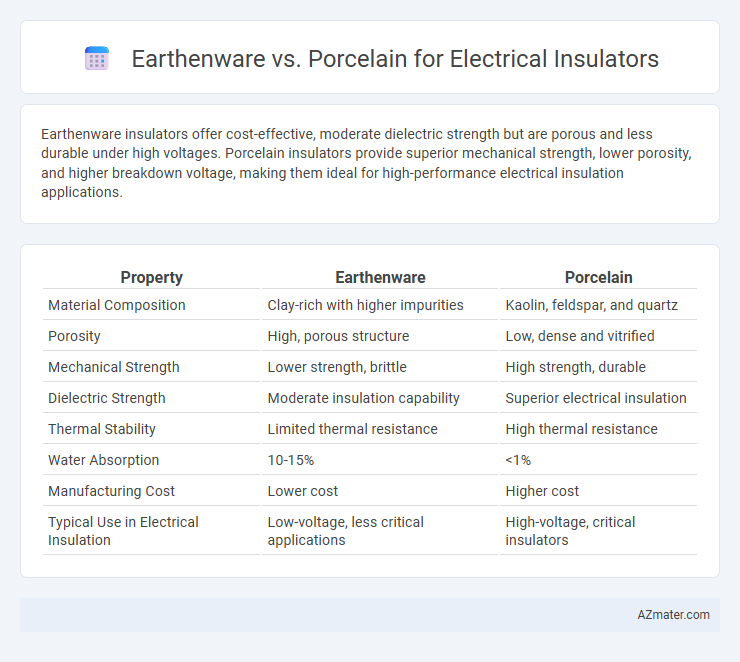
Earthenware insulators offer cost-effective, moderate dielectric strength but are porous and less durable under high voltages. Porcelain insulators provide superior mechanical strength, lower porosity, and higher breakdown voltage, making them ideal for high-performance electrical insulation applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Earthenware | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay-rich with higher impurities | Kaolin, feldspar, and quartz |
| Porosity | High, porous structure | Low, dense and vitrified |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower strength, brittle | High strength, durable |
| Dielectric Strength | Moderate insulation capability | Superior electrical insulation |
| Thermal Stability | Limited thermal resistance | High thermal resistance |
| Water Absorption | 10-15% | <1% |
| Manufacturing Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Typical Use in Electrical Insulation | Low-voltage, less critical applications | High-voltage, critical insulators |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators are critical components designed to prevent unwanted flow of current in electrical systems, ensuring safety and functionality. Earthenware and porcelain, two commonly used materials for insulators, differ significantly in dielectric strength, mechanical durability, and moisture resistance. Porcelain offers higher dielectric strength and superior weather resistance compared to earthenware, making it the preferred choice for high-voltage applications.
Overview of Earthenware Insulators
Earthenware insulators, made from clay-based ceramics, offer excellent electrical resistance and mechanical strength for low to medium voltage applications. Their porous nature requires glazing to enhance moisture resistance and durability in outdoor conditions. Earthenware insulators provide cost-effective insulation solutions but are generally less robust and heat-resistant compared to porcelain counterparts.
Overview of Porcelain Insulators
Porcelain insulators exhibit exceptional dielectric strength and mechanical durability, making them ideal for high-voltage electrical applications compared to earthenware. Their vitrified, non-porous surface resists moisture absorption and environmental contaminants, significantly enhancing insulation performance and longevity. Advanced compositions of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz contribute to porcelain's superior thermal stability and resistance to electrical tracking, crucial for reliable insulator function in power transmission systems.
Material Composition and Properties
Earthenware insulators primarily consist of clay mixed with natural minerals, exhibiting high porosity and lower mechanical strength, which limits their electrical insulation capabilities under high voltage. Porcelain insulators are made from refined kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, providing a dense, vitrified structure that offers superior dielectric strength, mechanical durability, and moisture resistance. The superior chemical stability and low water absorption of porcelain make it the preferred material for high-performance electrical insulators in demanding environments.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Earthenware insulators exhibit higher porosity and lower dielectric strength compared to porcelain, resulting in reduced electrical performance and increased risk of moisture absorption and leakage currents. Porcelain insulators offer superior insulation properties due to their dense, vitrified structure, which provides high dielectric strength, low water absorption, and excellent resistance to electrical stress and environmental degradation. The enhanced electrical performance of porcelain makes it the preferred choice for high-voltage and critical electrical insulation applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Porcelain exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to earthenware, making it the preferred choice for electrical insulators in high-stress environments. Porcelain's dense vitrified structure enhances its resistance to mechanical shock, weathering, and electrical conductivity degradation. Earthenware, being more porous and brittle, is less capable of withstanding mechanical loads and environmental wear, reducing its effectiveness and lifespan as an insulator.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Earthenware insulators are generally less expensive due to lower raw material costs and simpler manufacturing processes, making them suitable for budget-sensitive applications. Porcelain insulators require higher-quality kaolin clay and more precise firing at elevated temperatures, resulting in increased production costs but superior mechanical strength and electrical insulation properties. The choice between earthenware and porcelain depends on balancing cost efficiency with performance requirements in electrical insulation.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Earthenware insulators exhibit lower weather resistance due to their porous structure, making them prone to moisture absorption and degradation over time. Porcelain insulators provide superior weather resistance with a dense, vitrified surface that prevents water ingress and withstands extreme environmental conditions. Longevity of porcelain insulators significantly exceeds earthenware, maintaining structural integrity and insulating properties for decades even in harsh outdoor settings.
Applications Best Suited for Each Material
Earthenware insulators are best suited for low-voltage, indoor electrical applications due to their porous nature and lower mechanical strength, making them ideal for decorative or light-duty use in residential and commercial settings. Porcelain insulators, with their high dielectric strength, low porosity, and excellent mechanical durability, are preferred for high-voltage outdoor applications such as power transmission lines, substations, and industrial equipment. The superior thermal and weather resistance of porcelain ensures long-term reliability in harsh environmental conditions where earthenware would degrade.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Insulator Material
Porcelain offers superior mechanical strength, high dielectric strength, and better moisture resistance compared to earthenware, making it the preferred choice for high-voltage electrical insulators. Earthenware, while less expensive and adequate for low-voltage applications, lacks the durability and insulating properties required for demanding environments. Selecting the right insulator material depends on application voltage, environmental conditions, and budget constraints, with porcelain generally providing more reliable long-term performance.
Infographic: Earthenware vs Porcelain for Electrical Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com