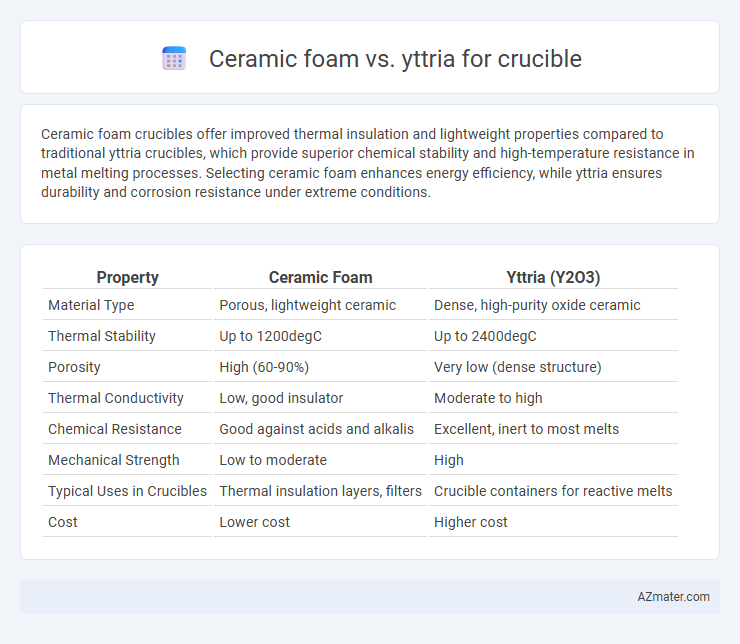
Ceramic foam crucibles offer improved thermal insulation and lightweight properties compared to traditional yttria crucibles, which provide superior chemical stability and high-temperature resistance in metal melting processes. Selecting ceramic foam enhances energy efficiency, while yttria ensures durability and corrosion resistance under extreme conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Foam | Yttria (Y2O3) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Porous, lightweight ceramic | Dense, high-purity oxide ceramic |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1200degC | Up to 2400degC |
| Porosity | High (60-90%) | Very low (dense structure) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low, good insulator | Moderate to high |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and alkalis | Excellent, inert to most melts |
| Mechanical Strength | Low to moderate | High |
| Typical Uses in Crucibles | Thermal insulation layers, filters | Crucible containers for reactive melts |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Crucible Materials
Crucible materials must withstand extreme temperatures and chemical corrosion during metal melting processes. Ceramic foam offers high porosity and thermal insulation, making it ideal for efficient heat management, while yttria boasts superior chemical stability and resistance to thermal shock, crucial for handling reactive metals like titanium. Selecting between ceramic foam and yttria depends on the specific demands for thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and chemical compatibility in high-temperature applications.
Overview of Ceramic Foam Crucibles
Ceramic foam crucibles offer superior thermal insulation and excellent resistance to thermal shock compared to traditional yttria crucibles. Their porous structure reduces heat loss while maintaining structural integrity at high temperatures, making them ideal for advanced metallurgical and high-temperature processes. This innovative material enhances energy efficiency and extends crucible lifespan in industrial applications.
Properties of Yttria Crucibles
Yttria crucibles exhibit exceptional high-temperature stability, maintaining integrity beyond 2200degC, making them ideal for melting reactive metals and superalloys. Their excellent thermal shock resistance and chemical inertness prevent contamination and degradation during prolonged use. Compared to ceramic foam, yttria's superior purity and crystallographic structure provide enhanced mechanical strength and corrosion resistance in aggressive environments.
Thermal Stability Comparison
Ceramic foam crucibles exhibit superior thermal stability due to their high porosity and low thermal conductivity, effectively resisting thermal shock in high-temperature applications. Yttria crucibles offer exceptional thermal stability through their high melting point of approximately 2430degC and excellent chemical inertness, making them ideal for extreme environments. Comparing both, yttria's dense structure provides greater thermal durability and resistance to corrosion, while ceramic foam emphasizes rapid heat dissipation and lightweight design.
Chemical Resistance: Ceramic Foam vs Yttria
Ceramic foam crucibles exhibit superior chemical resistance due to their porous structure, allowing better thermal shock absorption and resistance to corrosive slags compared to dense yttria crucibles. Yttria crucibles offer high chemical inertness against acidic and basic melts but are more susceptible to localized corrosion under fluctuating thermal conditions. The choice between ceramic foam and yttria depends on the specific melt chemistry and operational temperature, with ceramic foam favored for aggressive slag environments and yttria for stability in inert or mildly reactive melts.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Ceramic foam crucibles offer high porosity and lightweight structure but generally exhibit lower mechanical strength and durability compared to yttria crucibles, which possess superior thermal and chemical stability due to yttria's high melting point and resistance to slag infiltration. Yttria crucibles demonstrate enhanced mechanical strength, maintaining integrity under extreme thermal shock and corrosion conditions, making them ideal for high-temperature metallurgical processes. The dense microstructure of yttria increases durability, whereas ceramic foam's porous nature limits its application to less demanding environments.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Ceramic foam crucibles exhibit excellent thermal insulation and resistance to thermal shock, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 1600degC, ideal for metallurgical processes requiring rapid heat dissipation. Yttria-based crucibles, known for their superior chemical stability and high melting point around 2430degC, outperform ceramic foam in environments involving extreme temperatures and corrosive molten metals such as superalloys and rare-earth element processing. Performance comparisons highlight yttria crucibles' durability under prolonged high-temperature exposure, while ceramic foam offers enhanced energy efficiency through its porous structure, reducing heat loss during thermal cycles.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Ceramic foam crucibles generally offer lower material and manufacturing costs compared to yttria crucibles due to the abundance and lower price of raw materials like alumina or silica. Yttria crucibles, despite their superior high-temperature stability and chemical resistance, often face supply constraints and higher costs driven by the scarcity and complex refining of yttrium oxide. Availability of ceramic foam crucibles is more consistent globally, making them a cost-effective choice for applications with moderate thermal demands, while yttria crucibles remain pricier and less accessible but necessary for ultra-high-temperature environments.
Common Applications and Industries
Ceramic foam crucibles are widely used in metal casting, foundries, and filtration industries due to their excellent thermal shock resistance and porosity, which facilitates efficient gas release and slag containment. Yttria-based crucibles are preferred in aerospace, electronics, and specialty metal industries for melting reactive and high-temperature metals like titanium and superalloys, owing to their superior chemical stability and resistance to molten metal corrosion. Both materials serve critical roles in metallurgy, but ceramic foam is ideal for filtration and lightweight applications, while yttria excels in high-purity and high-temperature environments.
Choosing the Right Crucible: Key Considerations
Selecting the right crucible involves evaluating material properties like thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. Ceramic foam offers superior heat insulation and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for high-temperature processes requiring rapid temperature changes. Yttria crucibles provide exceptional resistance to molten metals and corrosive environments, ensuring durability and purity in metal casting and refining applications.
Infographic: Ceramic foam vs Yttria for Crucible
 azmater.com
azmater.com