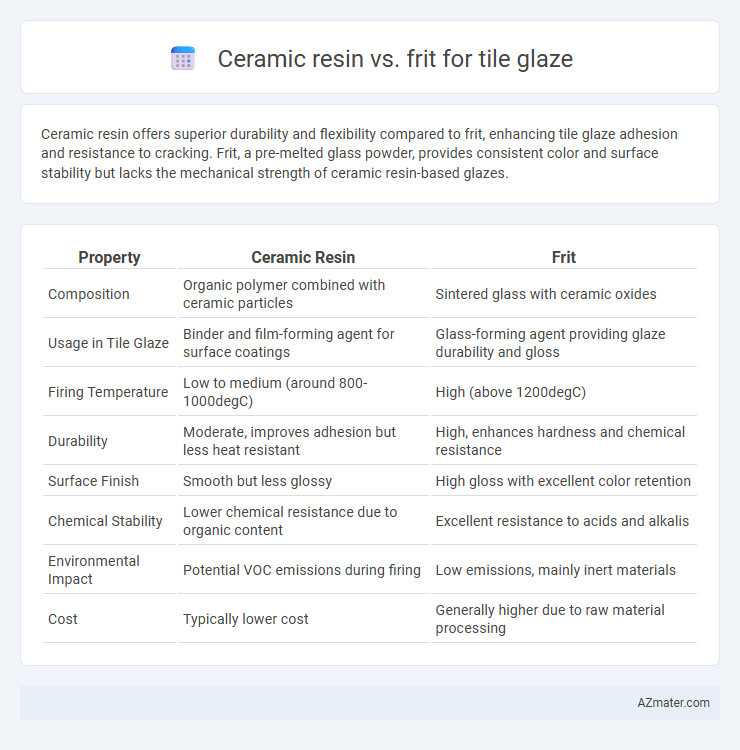
Ceramic resin offers superior durability and flexibility compared to frit, enhancing tile glaze adhesion and resistance to cracking. Frit, a pre-melted glass powder, provides consistent color and surface stability but lacks the mechanical strength of ceramic resin-based glazes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Resin | Frit |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Organic polymer combined with ceramic particles | Sintered glass with ceramic oxides |
| Usage in Tile Glaze | Binder and film-forming agent for surface coatings | Glass-forming agent providing glaze durability and gloss |
| Firing Temperature | Low to medium (around 800-1000degC) | High (above 1200degC) |
| Durability | Moderate, improves adhesion but less heat resistant | High, enhances hardness and chemical resistance |
| Surface Finish | Smooth but less glossy | High gloss with excellent color retention |
| Chemical Stability | Lower chemical resistance due to organic content | Excellent resistance to acids and alkalis |
| Environmental Impact | Potential VOC emissions during firing | Low emissions, mainly inert materials |
| Cost | Typically lower cost | Generally higher due to raw material processing |
Introduction to Ceramic Resin and Frit
Ceramic resin, a synthetic polymer, acts as a binder in tile glaze formulations, providing flexibility and enhanced adhesion properties during the firing process. Frits are powdered glass formulations fused and quenched, contributing crucial fluxing agents that lower the melting temperature and improve the glaze's durability and surface finish. Both components play essential roles in defining the chemical and physical characteristics of ceramic tile glazes.
Composition Differences Between Ceramic Resin and Frit
Ceramic resin primarily consists of organic polymers combined with inorganic fillers, offering flexibility and adhesion properties essential for tile glaze applications. In contrast, frit is a vitrified glass powder made from a mixture of silica, fluxes, and colorants, designed to melt and form a smooth, glassy coating upon firing. The fundamental composition difference lies in ceramic resin's polymer-based matrix versus frit's silicate-based glass structure, influencing their melting behavior and final glaze characteristics.
Functionality in Tile Glazing
Ceramic resin in tile glazing enhances adhesion and flexibility, allowing for better durability and resistance to cracking during firing. Frit, a glassy substance formed by melting raw materials, provides a stable, consistent surface with excellent chemical resistance and contributes to glaze hardness and smoothness. The combination of ceramic resin and frit optimizes the glaze's functionality by balancing flexibility and hardness, resulting in a durable, aesthetically pleasing tile finish.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Ceramic resin glazes exhibit superior flexibility and thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for tiles exposed to temperature fluctuations, while frit-based glazes provide exceptional hardness and chemical stability, enhancing scratch resistance and longevity. The inorganic nature of frit contributes to its high durability against UV degradation and moisture, whereas ceramic resin glazes may show slight wear over extended periods under harsh environmental conditions. Performance metrics indicate frit glazes maintain color vibrancy and structural integrity longer, making them preferable for high-traffic or outdoor applications.
Aesthetic Outcomes and Color Effects
Ceramic resin in tile glaze offers vibrant and consistent color saturation, enhancing intricate designs with smooth, glossy finishes that highlight fine details. Frits provide a broader range of matte and textured effects due to their varied chemical compositions, enabling unique, earthy color tones and natural variations. The choice between ceramic resin and frit impacts the depth and brilliance of tile glazes, influencing both the visual appeal and tactile experience of the final product.
Application Methods: Ceramic Resin vs Frit
Ceramic resin glazes are typically applied using screen printing or spraying techniques, allowing for precise control over thickness and design details. Frit-based glazes are commonly applied by dipping, brushing, or spraying, offering versatility but less precision compared to ceramic resins. The choice between ceramic resin and frit application methods depends on the desired finish, surface texture, and production scale in tile manufacturing.
Firing Temperatures and Compatibility
Frits for tile glaze typically have a lower melting point, firing between 1100degC and 1250degC, making them compatible with various ceramic bodies and allowing for energy-efficient firing cycles. Ceramic resins, composed of finely ground ceramic particles and binders, generally require higher firing temperatures around 1200degC to 1300degC to mature fully, ensuring strong adhesion and durability. Compatibility with specific clay bodies depends on matching thermal expansion coefficients, with frits offering more versatility across low to mid-fire ranges compared to resin-based glazes optimized for mid to high-fire applications.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Ceramic resin-based tile glazes typically have a lower environmental impact due to their reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and energy-efficient firing processes compared to frits, which require high-temperature melting of raw materials releasing more CO2. Frits often incorporate heavy metals like lead or cadmium, posing significant health risks during production and disposal, whereas ceramic resins generally use safer, non-toxic components. The use of ceramic resin glazes promotes safer working conditions and aligns better with eco-friendly manufacturing standards in the ceramic tile industry.
Cost and Accessibility
Ceramic resin offers a cost-effective solution for tile glaze production due to lower raw material expenses and simplified processing methods compared to frit, which involves higher manufacturing complexity and specialized equipment. Accessibility of ceramic resin is generally better, as it can be sourced from multiple suppliers with fewer restrictions, while frit often requires specific formulations and may have limited availability depending on regional manufacturing capabilities. For large-scale tile manufacturers, ceramic resin provides a more affordable and readily accessible option without sacrificing significant aesthetic quality.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Tile Project
Ceramic resin offers superior adhesion and flexibility for tile glaze applications, making it ideal for projects requiring durability and resistance to cracking. Frit, made from raw glass and minerals, provides exceptional chemical stability and vibrant, long-lasting color retention in high-temperature firings. Selecting between ceramic resin and frit depends on your tile project's specific needs for durability, color vibrancy, and firing conditions.
Infographic: Ceramic resin vs Frit for Tile glaze
 azmater.com
azmater.com