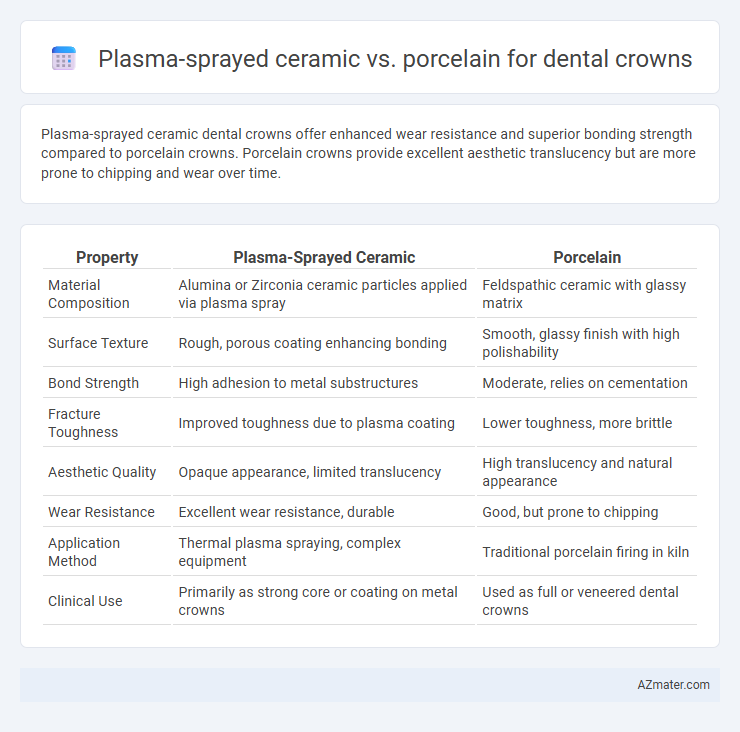
Plasma-sprayed ceramic dental crowns offer enhanced wear resistance and superior bonding strength compared to porcelain crowns. Porcelain crowns provide excellent aesthetic translucency but are more prone to chipping and wear over time.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Alumina or Zirconia ceramic particles applied via plasma spray | Feldspathic ceramic with glassy matrix |
| Surface Texture | Rough, porous coating enhancing bonding | Smooth, glassy finish with high polishability |
| Bond Strength | High adhesion to metal substructures | Moderate, relies on cementation |
| Fracture Toughness | Improved toughness due to plasma coating | Lower toughness, more brittle |
| Aesthetic Quality | Opaque appearance, limited translucency | High translucency and natural appearance |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent wear resistance, durable | Good, but prone to chipping |
| Application Method | Thermal plasma spraying, complex equipment | Traditional porcelain firing in kiln |
| Clinical Use | Primarily as strong core or coating on metal crowns | Used as full or veneered dental crowns |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Dental crowns require materials that balance durability, biocompatibility, and aesthetic appeal, with plasma-sprayed ceramics and porcelain representing prominent options. Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings provide enhanced fracture resistance and strong adhesion to metal substructures, ideal for robustness in posterior crowns. Porcelain crowns deliver superior translucency and natural appearance, favored in anterior restorations where aesthetic outcomes are critical.
Overview of Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic Crowns
Plasma-sprayed ceramic crowns offer a highly durable and wear-resistant dental restoration, utilizing a technique that applies ceramic materials at high temperatures to create a dense, strong coating. This method enhances the crown's adhesion to the underlying structure and provides superior resistance to fracture compared to traditional porcelain crowns. Plasma-sprayed ceramics exhibit improved biocompatibility and aesthetic qualities while maintaining functional integrity under occlusal forces.
Key Features of Porcelain Dental Crowns
Porcelain dental crowns are highly valued for their exceptional aesthetics, closely mimicking the natural translucency and color of real teeth, making them ideal for visible areas. These crowns offer strong biocompatibility, minimizing the risk of gum irritation and allergic reactions. Porcelain provides moderate durability suitable for typical biting forces, though it may be less resistant to chipping compared to plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings.
Aesthetic Differences: Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic vs Porcelain
Plasma-sprayed ceramic dental crowns exhibit a unique textured surface and matte finish, offering enhanced durability but often less natural translucency compared to porcelain. Porcelain crowns deliver superior esthetics with their high translucency and ability to mimic the natural enamel's luster and coloration, making them ideal for visible anterior teeth restorations. The choice between plasma-sprayed ceramic and porcelain predominantly impacts the crown's visual integration with surrounding teeth and overall smile aesthetics.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Plasma-sprayed ceramic dental crowns exhibit higher fracture toughness and superior wear resistance compared to porcelain crowns, making them more resilient to chipping and cracking under chewing forces. The plasma-spraying process creates a dense, uniform ceramic coating with enhanced bond strength to the metal substructure, contributing to longer-lasting durability in clinical applications. Porcelain crowns, while aesthetically pleasing, tend to have lower flexural strength and are more prone to surface degradation over time, especially in patients with bruxism or heavy occlusal load.
Biocompatibility and Patient Safety
Plasma-sprayed ceramic dental crowns exhibit superior biocompatibility due to their enhanced surface roughness and controlled porosity, promoting better gum tissue integration and reducing inflammatory responses. Porcelain crowns, while aesthetically appealing, may pose a slightly higher risk of hypersensitivity reactions and marginal microleakage, impacting long-term patient safety. The plasma-spray technique also allows for stronger adhesion and durability, minimizing the potential for crown failure and improving overall clinical outcomes.
Longevity and Wear Resistance
Plasma-sprayed ceramic dental crowns offer superior wear resistance due to their dense and homogenous microstructure, enhancing longevity in high-stress oral environments. Porcelain crowns, while aesthetically pleasing with their natural translucency, tend to exhibit higher brittleness and lower fracture toughness, which may reduce their lifespan under continuous mastication forces. Clinical studies indicate plasma-sprayed ceramics maintain structural integrity for over 10 years, outperforming traditional porcelain crowns in durability and resistance to chipping.
Cost Considerations and Value
Plasma-sprayed ceramic dental crowns typically involve higher manufacturing costs due to advanced technology and material expenses, resulting in a higher price point compared to traditional porcelain crowns. Porcelain crowns offer a cost-effective solution with satisfactory esthetics and durability, making them a popular choice for patients seeking value without compromising quality. Evaluating cost versus longevity and appearance, plasma-sprayed ceramic crowns may provide superior wear resistance and customization, justifying their premium pricing in complex restorative cases.
Clinical Indications for Each Material
Plasma-sprayed ceramic crowns are primarily indicated for posterior teeth requiring high fracture resistance and excellent wear properties under heavy occlusal forces. Porcelain crowns are clinically favored for anterior teeth due to their superior esthetic qualities, including translucency and color matching with natural dentition. Selection depends on balancing mechanical strength requirements with esthetic demands, where plasma-sprayed ceramics offer durability in load-bearing restorations and porcelain ensures optimal visual integration in the smile zone.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Crown Material
Plasma-sprayed ceramic crowns offer superior strength and bonding capabilities compared to traditional porcelain crowns, making them ideal for patients requiring durable restoration in high-stress areas. Porcelain crowns provide excellent esthetic qualities and biocompatibility, suitable for visible front teeth where appearance is critical. Choosing between these materials ultimately depends on balancing mechanical demands, esthetic preferences, and long-term clinical performance for each individual case.
Infographic: Plasma-sprayed ceramic vs Porcelain for Dental crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com