Porcelain furnace tubes offer excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability, but sillimanite tubes provide superior high-temperature strength and thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for extreme furnace environments. Choosing sillimanite enhances tube longevity and performance in continuous high-heat applications compared to porcelain.
Table of Comparison
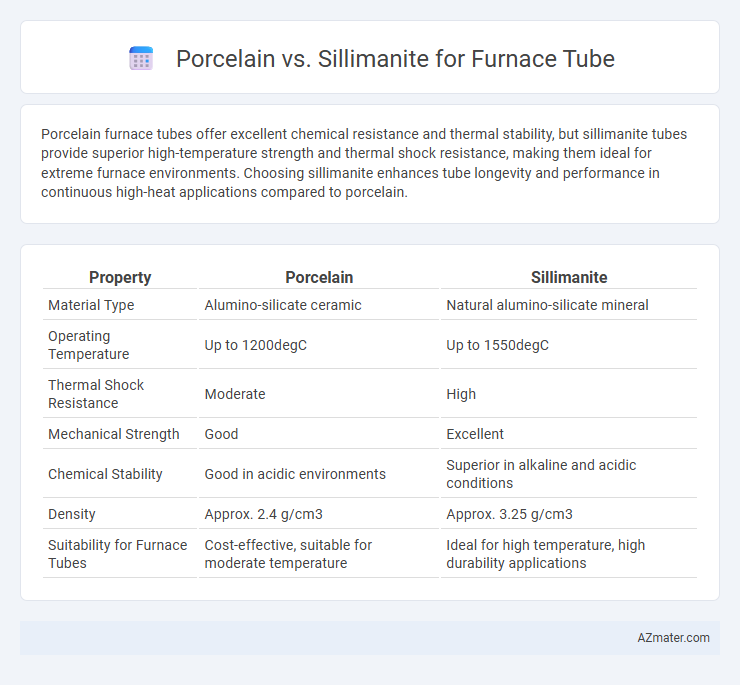
| Property | Porcelain | Sillimanite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Alumino-silicate ceramic | Natural alumino-silicate mineral |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1550degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Stability | Good in acidic environments | Superior in alkaline and acidic conditions |
| Density | Approx. 2.4 g/cm3 | Approx. 3.25 g/cm3 |
| Suitability for Furnace Tubes | Cost-effective, suitable for moderate temperature | Ideal for high temperature, high durability applications |
Introduction: Importance of Material Selection for Furnace Tubes
Furnace tubes demand materials with exceptional thermal resistance and mechanical strength to endure high-temperature operations in industrial furnaces. Porcelain offers excellent electrical insulation and thermal stability but can suffer from brittleness under thermal shock conditions. Sillimanite, a high-alumina silicate mineral, provides superior thermal shock resistance and structural integrity, making it a preferred choice for prolonged exposure to intense heat in furnace tubes.
Overview of Porcelain and Sillimanite Materials
Porcelain, a ceramic material composed primarily of kaolin clay, feldspar, and quartz, offers excellent electrical insulation, high mechanical strength, and resistance to thermal shock, making it suitable for furnace tubes in moderate temperature applications. Sillimanite, an alumino-silicate mineral rich in aluminum oxide, provides superior refractory properties, high melting points above 1750degC, and excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, ideal for high-temperature furnace tubes. The choice between porcelain and sillimanite depends on specific operating temperatures and environmental conditions in furnace applications.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Porcelain furnace tubes primarily consist of kaolinite, feldspar, and quartz, forming a dense, glassy structure with excellent insulation properties but limited thermal shock resistance. In contrast, sillimanite tubes boast a high alumina silicate content (Al2O3*SiO2) with a fibrous crystalline structure, providing superior thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion at elevated temperatures. The chemical composition of sillimanite enhances its structural integrity, making it better suited for high-temperature furnace applications compared to porcelain.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Performance
Porcelain furnace tubes exhibit high thermal resistance but are prone to thermal shock, limiting their performance under rapid temperature fluctuations. Sillimanite furnace tubes offer superior heat performance with excellent thermal stability and resistance to high-temperature corrosion, making them ideal for prolonged exposure to extreme heat. The crystalline structure of sillimanite ensures enhanced durability and dimensional stability compared to porcelain in high-temperature furnace applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Sillimanite furnace tubes exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to porcelain due to their higher resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, making them ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. The inherent durability of sillimanite, derived from its alumino-silicate composition, ensures enhanced longevity under cyclic heating and cooling conditions, outperforming porcelain's comparatively brittle nature. While porcelain offers good corrosion resistance, sillimanite's robust crystalline structure significantly reduces the risk of cracking and deformation, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs.
Corrosion and Chemical Attack Resistance
Sillimanite furnace tubes exhibit superior corrosion and chemical attack resistance compared to porcelain, owing to their high alumina content and dense crystalline structure that withstands acidic and alkaline environments effectively. Porcelain tubes, although corrosion-resistant to some extent, are more susceptible to degradation in aggressive chemical atmospheres due to their lower mechanical strength and porosity. The enhanced durability of sillimanite translates into longer service life and reduced maintenance in high-temperature, chemically harsh industrial settings.
Cost Effectiveness and Economic Considerations
Porcelain furnace tubes offer lower initial costs and ease of fabrication, making them budget-friendly for short-term or low-temperature applications. Sillimanite tubes, though more expensive upfront, provide superior thermal stability and longer service life, resulting in reduced maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Economic considerations favor sillimanite in high-temperature environments where durability offsets the higher initial investment.
Applications in Industrial Furnace Operations
Porcelain furnace tubes offer excellent electrical insulation and high resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for applications requiring reliable insulation and moderate temperature endurance up to 1300degC. Sillimanite tubes excel in high-temperature stability and chemical resistance, supporting continuous operation in industrial furnaces exceeding 1400degC, especially in metallurgical and ceramic manufacturing processes. Choosing between porcelain and sillimanite depends on specific furnace temperatures and chemical environments, with sillimanite preferred for more aggressive, higher-temperature industrial furnace operations.
Maintenance, Lifespan, and Replacement Factors
Porcelain furnace tubes offer moderate durability with a lifespan typically around 1 to 2 years under high-temperature conditions, requiring frequent maintenance due to their susceptibility to thermal shock and cracking. Sillimanite tubes provide superior thermal stability and resistance to corrosion, extending lifespan to 3 to 5 years and reducing downtime associated with replacements. Replacement factors hinge on operational temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress, with sillimanite favored for high-temperature maintenance reduction and long-term cost efficiency.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Furnace Tubes
Porcelain offers excellent thermal insulation and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it suitable for lower temperature furnace applications. Sillimanite, with its superior high-temperature strength and resistance to thermal shock, is ideal for demanding, high-temperature furnace tubes. Selecting the right material depends on operational temperature, mechanical stress, and chemical exposure to ensure optimal performance and longevity of furnace tubes.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Sillimanite for Furnace tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com