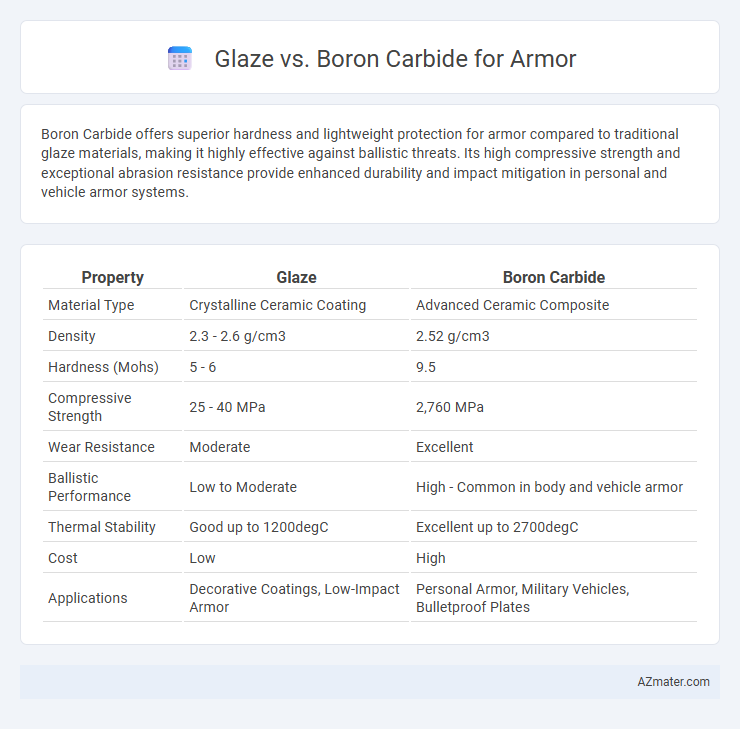
Boron Carbide offers superior hardness and lightweight protection for armor compared to traditional glaze materials, making it highly effective against ballistic threats. Its high compressive strength and exceptional abrasion resistance provide enhanced durability and impact mitigation in personal and vehicle armor systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glaze | Boron Carbide |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Crystalline Ceramic Coating | Advanced Ceramic Composite |
| Density | 2.3 - 2.6 g/cm3 | 2.52 g/cm3 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 5 - 6 | 9.5 |
| Compressive Strength | 25 - 40 MPa | 2,760 MPa |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Ballistic Performance | Low to Moderate | High - Common in body and vehicle armor |
| Thermal Stability | Good up to 1200degC | Excellent up to 2700degC |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Applications | Decorative Coatings, Low-Impact Armor | Personal Armor, Military Vehicles, Bulletproof Plates |
Introduction to Armor Materials
Glaze and boron carbide are advanced materials used in armor systems for enhanced ballistic protection. Boron carbide, known for its extreme hardness and low density, is widely favored in personal and vehicle armor to effectively stop high-velocity projectiles. Glaze, often a ceramic-based coating, contributes by improving surface hardness and resistance to wear, complementing the structural properties of core materials like boron carbide.
Overview of Glaze Armor Technology
Glaze armor technology utilizes a hard, glass-like ceramic layer fused onto a metal backing to effectively dissipate the energy from high-velocity impacts. This ceramic glaze provides exceptional hardness and abrasion resistance, making it highly efficient at shattering and spreading the force of incoming projectiles. Compared to boron carbide, glaze armor offers a more cost-effective solution with robust thermal stability and thinner profiles for enhanced mobility without significant weight increase.
Understanding Boron Carbide in Armor Applications
Boron carbide is a lightweight, highly durable ceramic material known for its exceptional hardness and resistance to ballistic impacts in armor applications. It offers superior protection by effectively dispersing energy from high-velocity projectiles, making it a preferred choice for personal and vehicle armor systems. Unlike traditional glaze coatings, boron carbide provides a balance of strength and weight reduction, enhancing mobility without compromising defense capabilities.
Comparative Hardness and Strength
Boron carbide exhibits superior hardness, ranking around 9.5 on the Mohs scale, outpacing most ceramic glazes used in armor applications. Its exceptional compressive strength, often exceeding 2,500 MPa, provides enhanced resistance against high-velocity impacts compared to traditional glazes. While glaze materials offer moderate hardness and cost efficiency, boron carbide's combination of lightweight properties and extreme strength makes it the preferred choice for advanced armor systems requiring maximum ballistic protection.
Weight Considerations for Mobility
Boron carbide offers superior hardness and protection at a significantly lower weight compared to traditional ceramic glazes, enhancing soldier mobility without compromising armor effectiveness. The reduced density of boron carbide allows for lighter armor plates, which decreases fatigue and improves agility during extended missions. This weight advantage makes boron carbide the preferred choice for modern tactical body armor where mobility is critical.
Ballistic Protection Performance
Boron carbide offers superior ballistic protection due to its high hardness and lightweight properties, making it ideal for stopping high-velocity projectiles. Glaze ceramics, while effective, generally provide less impact resistance and toughness compared to boron carbide, reducing their effectiveness against armor-piercing rounds. The combination of boron carbide's exceptional hardness (around 9.5 Mohs) and low density enables enhanced energy dispersion and minimal weight, critical for advanced personal and vehicle armor applications.
Durability and Lifespan
Boron carbide offers superior durability and lifespan compared to conventional ceramic glazes, making it a preferred material in high-performance armor applications. Its exceptional hardness and resistance to wear and abrasion enable boron carbide armor to maintain structural integrity and protective capabilities over extended periods under extreme conditions. In contrast, glaze coatings, while providing some surface hardness and corrosion resistance, tend to degrade faster and are less effective in sustaining long-term impact resistance.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Boron carbide armor offers exceptional hardness and lightweight protection but comes at a significantly higher cost due to complex manufacturing and scarce raw materials. Glaze armor provides a more affordable alternative with decent ballistic resistance, benefiting from widespread availability of materials and simpler production processes. The cost-effectiveness and ready availability of glaze make it suitable for applications where budget constraints are critical, while boron carbide is preferred for premium, high-performance armor solutions.
Typical Use Cases: Military and Civilian
Glaze armor is typically used in military applications requiring lightweight protection against ballistic threats, such as in combat vehicles and personal body armor, due to its hardness and ability to shatter projectiles on impact. Boron carbide, valued for its superior wear resistance and extreme hardness, is commonly applied in both military armor systems and civilian ballistic panels for vehicles, providing enhanced protection against high-velocity rounds and shrapnel. Civilian uses often include protective gear for law enforcement and security personnel, leveraging the materials' balance of weight and durability for improved mobility and safety.
Choosing the Right Armor Material
Choosing the right armor material depends on balancing protection, weight, and cost, where boron carbide excels due to its exceptional hardness and lightweight properties, making it ideal for ballistic protection. While ceramic glazes offer good surface hardness and can be more affordable, they generally lack the extreme durability and multi-hit resistance of boron carbide composites. Evaluating threat levels and application environments is critical when selecting between ceramic glazes and boron carbide for armor solutions.
Infographic: Glaze vs Boron Carbide for Armor
 azmater.com
azmater.com