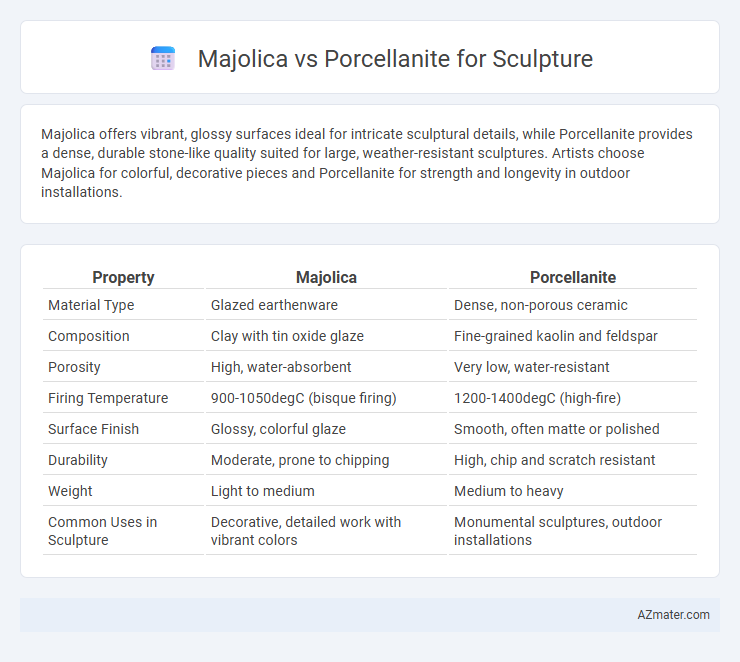
Majolica offers vibrant, glossy surfaces ideal for intricate sculptural details, while Porcellanite provides a dense, durable stone-like quality suited for large, weather-resistant sculptures. Artists choose Majolica for colorful, decorative pieces and Porcellanite for strength and longevity in outdoor installations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Majolica | Porcellanite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed earthenware | Dense, non-porous ceramic |
| Composition | Clay with tin oxide glaze | Fine-grained kaolin and feldspar |
| Porosity | High, water-absorbent | Very low, water-resistant |
| Firing Temperature | 900-1050degC (bisque firing) | 1200-1400degC (high-fire) |
| Surface Finish | Glossy, colorful glaze | Smooth, often matte or polished |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to chipping | High, chip and scratch resistant |
| Weight | Light to medium | Medium to heavy |
| Common Uses in Sculpture | Decorative, detailed work with vibrant colors | Monumental sculptures, outdoor installations |
Introduction to Majolica and Porcellanite
Majolica is a type of earthenware pottery characterized by its porous body and vibrant, lead-glazed surface, making it ideal for detailed, colorful sculptures due to its ability to hold intricate designs and bright finishes. Porcellanite, a dense, fine-grained sedimentary rock, offers exceptional durability and a smooth, porcelain-like texture favored for sculptures requiring enhanced strength and a polished appearance. Comparing their properties, Majolica suits decorative, ornamental artwork requiring vivid coloration, while Porcellanite caters to robust, long-lasting sculptural forms with a natural stone aesthetic.
Historical Development of Majolica and Porcellanite
Majolica, originating in Renaissance Italy during the 15th century, is a tin-glazed pottery known for its vibrant colors and intricate designs, historically used for both functional ware and decorative sculpture. Porcellanite, a dense, fine-grained sedimentary rock formed through the lithification of clay, gained prominence in prehistoric and ancient sculptural works due to its durability and smooth finish. The evolution of majolica highlights advances in ceramic glazing techniques, while porcellanite's use reflects early human innovation in selecting natural stone materials for sculptural expression.
Material Composition: Majolica vs Porcellanite
Majolica is a type of earthenware pottery characterized by its porous clay body and a tin glaze that creates a glossy, colorful surface, making it lighter and more fragile compared to other ceramics. Porcellanite, on the other hand, is a dense, natural stone resembling porcelain with a composition primarily of microcrystalline quartz, offering superior hardness and durability ideal for outdoor or large-scale sculptures. Understanding the differences in mineral content and porosity between Majolica's clay and Porcellanite's stone base is crucial for selecting the appropriate material based on the sculpture's intended use and environmental exposure.
Sculptural Techniques with Majolica
Majolica offers unique advantages for sculptural techniques due to its porous body and vibrant glaze application, enabling artists to achieve detailed textures and rich color effects through layered glazing and firing processes. Unlike the dense and hard Porcellanite, which demands carving and polishing, Majolica's malleability when wet allows for intricate modeling, sculpting fine details, and adding relief elements before kiln firing. The interplay of tin-opacified glazes with the porous bisque surface enhances surface decoration, making Majolica ideal for expressive, colorful ceramic sculptures.
Sculptural Techniques with Porcellanite
Porcellanite offers exceptional hardness and durability, allowing sculptors to achieve fine, detailed carvings and intricate textures that withstand weathering. Its dense, non-porous surface supports high precision tools and polishing techniques, resulting in smooth finishes and sharp edges ideal for outdoor sculptures. In contrast, Majolica's brittle, glazed surface limits extensive carving but excels in colorful surface treatments, emphasizing decorative rather than structural sculptural techniques.
Aesthetic Qualities in Sculpture
Majolica offers vibrant, glossy surfaces with rich, colorful glazes that enhance sculptural detail and evoke a dynamic visual appeal. Porcellanite, with its smooth, fine-grained texture and subtle translucency, imparts a refined, elegant aesthetic often favored for minimalist and modern sculptures. The choice between Majolica and Porcellanite significantly impacts the sculpture's visual tone, from vivid expressiveness to understated sophistication.
Durability and Maintenance Comparison
Majolica, characterized by its porous and glazed surface, offers vibrant color options but demands frequent sealing to prevent moisture absorption and surface damage. Porcellanite, a dense and non-porous ceramic, excels in durability, resisting weathering, stains, and scratches with minimal maintenance over time. Sculptors seeking long-lasting outdoor pieces often prefer Porcellanite due to its superior strength and low upkeep requirements compared to Majolica.
Artistic Applications and Styles
Majolica offers vibrant, glossy surfaces ideal for colorful, decorative sculptures with intricate detailing and expressive glazing techniques, making it suited for ornamental and whimsical artistic styles. Porcellanite provides a dense, fine-grained texture that supports smooth carving and polished finishes, favored in minimalist and contemporary sculptural forms emphasizing subtlety and durability. Both materials enable diverse artistic applications, but Majolica excels in vivid, tactile aesthetics while Porcellanite caters to refined, elegant structural works.
Cost and Accessibility for Sculptors
Majolica clay offers a cost-effective option for sculptors due to its affordability and widespread availability in most art supply stores, making it accessible for both beginners and professionals. Porcellanite, on the other hand, is more expensive and harder to source, often requiring specialized suppliers or custom orders, which can limit accessibility. Choosing Majolica helps artists maintain budget control without compromising on creative potential, while Porcellanite suits projects demanding higher durability and a refined finish despite higher costs.
Choosing the Right Material for Sculpture
Majolica offers vibrant coloration and a glossy finish suitable for decorative sculptures but lacks the durability needed for outdoor installations. Porcellanite provides exceptional hardness, frost resistance, and minimal porosity, making it ideal for sculptures exposed to harsh weather conditions. Selecting between Majolica and Porcellanite depends on balancing aesthetic appeal with environmental resilience and longevity requirements.
Infographic: Majolica vs Porcellanite for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com