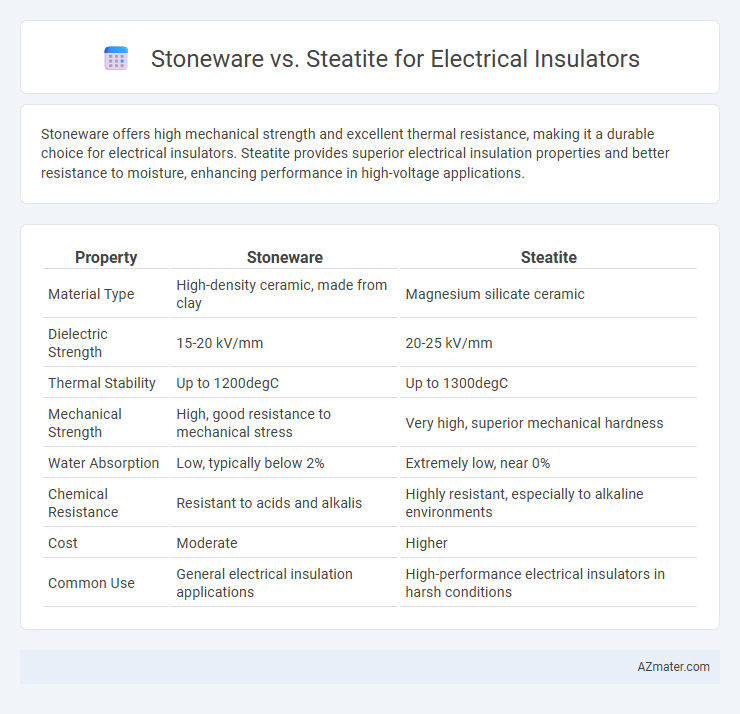
Stoneware offers high mechanical strength and excellent thermal resistance, making it a durable choice for electrical insulators. Steatite provides superior electrical insulation properties and better resistance to moisture, enhancing performance in high-voltage applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stoneware | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-density ceramic, made from clay | Magnesium silicate ceramic |
| Dielectric Strength | 15-20 kV/mm | 20-25 kV/mm |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1300degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High, good resistance to mechanical stress | Very high, superior mechanical hardness |
| Water Absorption | Low, typically below 2% | Extremely low, near 0% |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids and alkalis | Highly resistant, especially to alkaline environments |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Common Use | General electrical insulation applications | High-performance electrical insulators in harsh conditions |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators are materials that resist the flow of electric current, ensuring safety and functionality in electrical systems. Stoneware and steatite are two commonly used ceramic insulators that vary in properties such as dielectric strength, mechanical durability, and thermal stability. Stoneware offers high mechanical strength and moisture resistance, making it suitable for outdoor applications, while steatite provides superior dielectric properties and thermal shock resistance, ideal for high-voltage and precision insulation needs.
What is Stoneware?
Stoneware is a dense, non-porous ceramic material fired at high temperatures between 1200degC and 1300degC, making it highly durable and resistant to electrical conductivity. Its microstructure consists of vitrified particles that provide excellent insulation properties, ideal for electrical insulator applications. Compared to steatite, stoneware offers superior mechanical strength and moisture resistance, essential for maintaining electrical insulation in harsh environments.
What is Steatite?
Steatite, also known as soapstone, is a dense, heat-resistant ceramic material composed primarily of magnesium silicate. Its exceptional electrical insulating properties and high thermal stability make it ideal for use as an electrical insulator in high-temperature and high-voltage applications. Compared to stoneware, steatite offers superior mechanical strength and lower dielectric loss, enhancing performance in demanding electrical environments.
Key Material Properties: Stoneware vs Steatite
Stoneware offers high mechanical strength, excellent wear resistance, and good thermal stability, making it suitable for heavy-duty electrical insulators. Steatite provides superior dielectric strength, low dielectric loss, and exceptional electrical insulation properties with moderate mechanical durability. Both materials offer corrosion resistance, but steatite's finer grain structure enhances its electrical performance compared to the denser stoneware.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Stoneware offers high dielectric strength and excellent resistance to electrical leakage, making it suitable for medium-voltage insulators. Steatite exhibits superior electrical insulation properties due to its exceptionally low electrical conductivity and high dielectric constant, enhancing performance in high-frequency and high-voltage applications. The choice between stoneware and steatite depends on voltage requirements, with steatite favored for better insulation stability under fluctuating electrical stresses.
Thermal Resistance and Durability
Stoneware offers high thermal resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 1200degC, making it suitable for heavy-duty electrical insulators exposed to high heat. Steatite excels in durability due to its dense, non-porous structure, providing superior mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock in electrical insulation applications. Both materials ensure reliable insulation, but stoneware is preferred for extreme thermal environments, while steatite is favored for enhanced durability and longevity.
Mechanical Strength and Reliability
Stoneware exhibits high mechanical strength and excellent durability, making it a reliable choice for electrical insulators exposed to mechanical stress and harsh environmental conditions. Steatite offers good mechanical robustness but generally has lower strength compared to stoneware, which may limit its use in high-load or high-impact applications. The superior mechanical strength and long-term reliability of stoneware ensure consistent performance and reduced risk of failure in critical electrical insulation systems.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Stoneware offers lower production costs due to abundant raw materials and simpler firing processes, making it economically favorable for mass production of electrical insulators. Steatite, composed primarily of talc, requires more precise processing and higher firing temperatures, increasing manufacturing expenses but providing superior mechanical strength and thermal stability. Cost-efficiency in stoneware aligns with high-volume applications, while steatite suits specialized insulators demanding enhanced performance despite higher production costs.
Common Applications in Electrical Systems
Stoneware and steatite are widely used materials for electrical insulators due to their excellent dielectric properties and mechanical strength. Stoneware is commonly employed in high-voltage power line insulators, transformer bushings, and switchgear components, where its durability and resistance to environmental stress are critical. Steatite finds applications in electronic substrates, high-frequency insulators, and thermal insulator supports within electrical systems, prized for its high dielectric strength and thermal stability.
Choosing the Right Insulator: Stoneware or Steatite?
Stoneware offers excellent mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for high-voltage insulators in power transmission. Steatite provides superior thermal stability and dielectric properties, ideal for applications requiring high resistance to electrical and thermal stress. Selecting the right insulator depends on specific operational demands, such as environmental conditions and electrical load requirements, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Stoneware vs Steatite for Electrical Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com