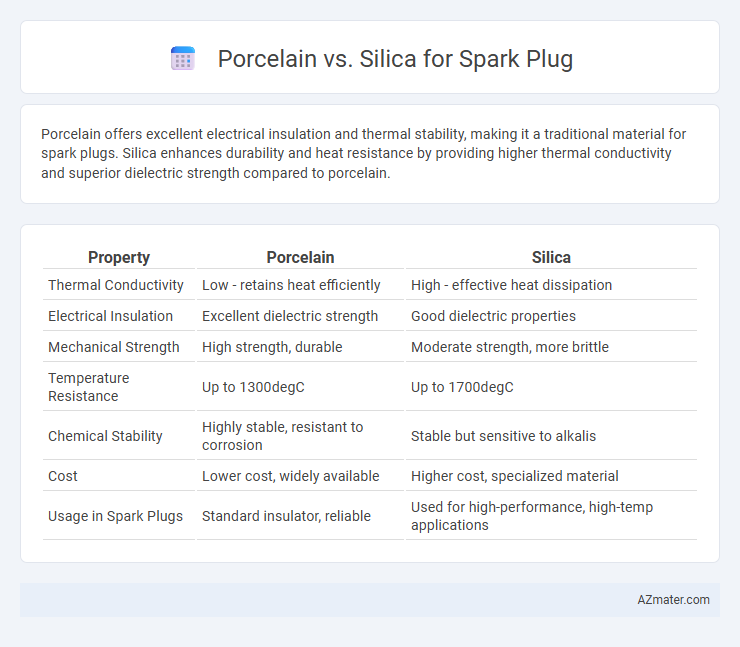
Porcelain offers excellent electrical insulation and thermal stability, making it a traditional material for spark plugs. Silica enhances durability and heat resistance by providing higher thermal conductivity and superior dielectric strength compared to porcelain.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Porcelain | Silica |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Low - retains heat efficiently | High - effective heat dissipation |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength | Good dielectric properties |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength, durable | Moderate strength, more brittle |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1300degC | Up to 1700degC |
| Chemical Stability | Highly stable, resistant to corrosion | Stable but sensitive to alkalis |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, specialized material |
| Usage in Spark Plugs | Standard insulator, reliable | Used for high-performance, high-temp applications |
Introduction to Spark Plug Insulation Materials
Spark plug insulation materials primarily include porcelain and silica, each offering distinct thermal and electrical properties essential for optimal engine performance. Porcelain insulation is widely used due to its excellent dielectric strength, mechanical durability, and resistance to high temperatures, which effectively prevents electrical leakage and withstands combustion pressures. Silica-based insulators provide superior thermal conductivity and enhanced heat dissipation, making them ideal for high-performance or racing engines that operate at higher temperatures and demand rapid heat transfer.
What is Porcelain in Spark Plugs?
Porcelain in spark plugs serves as the insulator material surrounding the central electrode, providing high electrical resistance and thermal stability essential for efficient ignition. It is typically composed of a ceramic compound containing kaolin, quartz, feldspar, and alumina, engineered to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures within the combustion chamber. This material ensures durability, prevents electrical leakage, and maintains consistent spark performance in automotive engines.
Understanding Silica-Based Spark Plug Insulators
Silica-based spark plug insulators offer superior thermal conductivity and enhanced electrical insulation compared to traditional porcelain, resulting in better heat dissipation and improved engine performance. Their high purity and optimized microstructure reduce thermal expansion and minimize the risk of cracking under extreme combustion temperatures. These properties make silica insulators ideal for high-performance and high-efficiency engines requiring reliable ignition and durability.
Key Properties: Porcelain vs Silica
Porcelain spark plug insulators offer excellent electrical insulation, high mechanical strength, and superior thermal stability, making them ideal for enduring high-temperature combustion environments. Silica-based insulators provide enhanced heat resistance and improved thermal conductivity but tend to be less durable under mechanical stress compared to porcelain. Considering factors like dielectric strength, thermal expansion, and fracture toughness, porcelain remains the preferred material for most spark plug applications due to its balanced performance and reliability.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Performance
Porcelain spark plug insulators offer superior heat resistance due to their dense ceramic composition, enabling stable performance in high-temperature combustion environments. Silica insulators, while providing good thermal conductivity, generally exhibit lower heat tolerance, making them more suitable for moderate-temperature applications. Optimal thermal performance depends on matching the insulator material to engine operating conditions to ensure effective heat dissipation and combustion efficiency.
Electrical Insulation Efficiency Comparison
Porcelain spark plug insulators offer high dielectric strength and excellent thermal conductivity, maintaining stable electrical insulation under extreme combustion pressures and temperatures. Silica-based insulators provide superior resistance to electrical leakage due to their higher purity and lower porosity, enhancing long-term durability and performance in high-voltage applications. Comparative tests reveal silica insulators typically exhibit up to 15% better insulation efficiency, reducing misfires and improving spark consistency in advanced ignition systems.
Durability and Longevity: Which Lasts Longer?
Porcelain spark plugs feature excellent insulation and heat resistance but are more prone to cracking under extreme conditions, which can limit their durability. Silica-based spark plugs demonstrate superior thermal stability and resistance to wear, leading to enhanced longevity in high-performance engines. Overall, silica spark plugs tend to last longer due to their robust composition that withstands combustion stress and temperature fluctuations more effectively.
Cost Differences and Economic Impact
Porcelain spark plugs generally have a lower manufacturing cost compared to silica-based spark plugs due to simpler material processing and widespread availability of raw materials. Silica spark plugs, often used for high-performance or industrial applications, command higher prices because of enhanced durability and thermal resistance, impacting overall vehicle maintenance budgets. Choosing porcelain over silica can reduce upfront expenses but may increase long-term economic costs related to replacement frequency and engine efficiency.
Applications: Best Use Cases for Each Material
Porcelain spark plugs offer superior insulation and thermal resistance, making them ideal for high-performance engines and harsh environments where heat dissipation is critical. Silica spark plugs excel in standard automotive applications by providing reliable conductivity and durability at a lower cost, suited for everyday driving conditions. Each material's unique properties optimize engine efficiency and longevity based on specific temperature ranges and usage demands.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Insulator for Your Engine
Porcelain insulators offer excellent durability and high dielectric strength, making them ideal for high-temperature engine environments and ensuring reliable spark delivery. Silica insulators provide superior thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock, which enhances engine performance by effectively dissipating heat. Selecting the right spark plug insulator depends on engine operating conditions, with porcelain best suited for heavy-duty applications and silica preferred for engines requiring rapid heat dissipation and improved ignition efficiency.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Silica for Spark Plug
 azmater.com
azmater.com