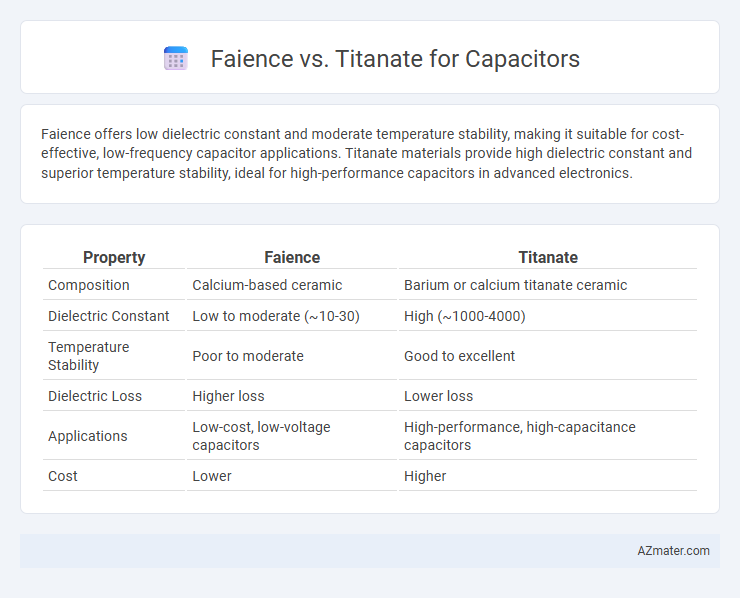
Faience offers low dielectric constant and moderate temperature stability, making it suitable for cost-effective, low-frequency capacitor applications. Titanate materials provide high dielectric constant and superior temperature stability, ideal for high-performance capacitors in advanced electronics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Faience | Titanate |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Calcium-based ceramic | Barium or calcium titanate ceramic |
| Dielectric Constant | Low to moderate (~10-30) | High (~1000-4000) |
| Temperature Stability | Poor to moderate | Good to excellent |
| Dielectric Loss | Higher loss | Lower loss |
| Applications | Low-cost, low-voltage capacitors | High-performance, high-capacitance capacitors |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Faience and Titanate Capacitors
Faience capacitors are ceramic-based components made from glazed earthenware materials offering moderate dielectric constants and reliability for general applications. Titanate capacitors utilize titanium-based dielectric compounds, such as barium titanate, providing high permittivity, excellent temperature stability, and enhanced capacitance density. These differences in dielectric composition result in distinct electrical properties, making titanate capacitors suitable for high-performance and precision electronic circuits while faience capacitors are often used in cost-sensitive, standard electronic devices.
Material Composition of Faience and Titanate
Faience capacitors are composed of glazed ceramic materials with a silica-based body and metallic oxide glazes, providing insulation and dielectric properties. Titanate capacitors primarily use barium titanate (BaTiO3) as the dielectric material, characterized by its high permittivity and temperature stability. The distinct material compositions influence their dielectric constants, temperature coefficients, and overall capacitor performance in electronic applications.
Electrical Properties Comparison
Faience capacitors exhibit moderate dielectric constant values typically ranging from 10 to 100, offering stable electrical performance and low dielectric losses under varying frequencies. Titanate capacitors, particularly those based on barium titanate, provide significantly higher dielectric constants often exceeding 1,000, resulting in greater capacitance density and enhanced energy storage capabilities. While faience materials present lower dielectric breakdown strength and limited temperature stability, titanate-based capacitors demonstrate superior electrical properties such as high permittivity, low leakage current, and improved temperature coefficients, making them ideal for high-performance electronic applications.
Capacitance Stability and Performance
Faience capacitors exhibit moderate capacitance stability but suffer from higher dielectric losses and limited temperature tolerance compared to titanate-based capacitors. Titanate capacitors, leveraging barium titanate or calcium titanate dielectrics, offer superior capacitance stability across varying temperatures and improved reliability due to their stable permittivity and low leakage current. Performance-wise, titanate capacitors provide enhanced frequency response and longer lifespan, making them preferable in precision and high-performance electronic applications.
Dielectric Constant Differences
Faience capacitors typically exhibit a lower dielectric constant ranging from 5 to 7, which limits their energy storage capacity compared to titanate capacitors that offer dielectric constants between 200 and 600. The high dielectric constant of titanate materials, such as barium titanate, significantly enhances the capacitance per unit volume, making them preferable for miniaturized and high-performance electronic applications. In contrast, faience materials, composed mainly of glazed ceramic, are less efficient in dielectric properties but provide better mechanical stability and temperature resilience.
Temperature and Voltage Behavior
Faience capacitors exhibit stable temperature coefficients but generally have lower voltage ratings and limited dielectric strength compared to titanate capacitors, which offer superior high-voltage tolerance and enhanced thermal stability across a wider temperature range. Titanate materials provide better dielectric constants, resulting in improved capacitance retention under elevated temperatures and high-voltage stress conditions. These properties make titanate capacitors more suitable for applications requiring robust performance in harsh thermal environments and high-voltage scenarios, whereas faience capacitors are ideal for moderate operating conditions with stable temperature behavior.
Reliability and Lifespan
Titanate capacitors offer superior reliability and longer lifespan compared to faience capacitors due to their robust dielectric properties and higher temperature tolerance. The stable permittivity of titanate materials reduces degradation over time, ensuring consistent performance in demanding environments. In contrast, faience capacitors are more susceptible to moisture and thermal stress, leading to shorter operational life and higher failure rates.
Manufacturing Costs and Availability
Faience capacitors typically feature lower manufacturing costs due to simpler raw materials and less complex processing techniques compared to titanate capacitors, which require rare-earth elements and advanced ceramic sintering. The availability of faience materials is generally higher, supporting mass production and cost efficiency, while titanate capacitors face supply chain constraints from limited sources of titanium compounds. Manufacturers often choose faience capacitors for cost-sensitive applications, whereas titanate variants are prioritized where superior dielectric properties justify higher expenses.
Common Applications in Electronics
Faience capacitors are widely used in vintage electronic equipment and high-frequency circuits due to their excellent dielectric properties and stability at elevated temperatures. Titanate capacitors, known for their high dielectric constant and temperature coefficient, find common applications in modern power electronics, filtering, and timing circuits where precise capacitance and reliability are crucial. Both capacitor types serve distinct roles in electronics, with faience favored in historical restorations and titanate dominating contemporary electronic designs.
Choosing the Right Capacitor: Faience vs Titanate
Selecting between faience and titanate capacitors depends largely on their dielectric properties and application requirements. Faience capacitors offer stable capacitance with lower dielectric losses, making them suitable for high-frequency and precision circuits. Titanate capacitors provide higher dielectric constants and greater capacitance per volume, ideal for compact designs requiring high capacitance and voltage ratings.
Infographic: Faience vs Titanate for Capacitor
 azmater.com
azmater.com