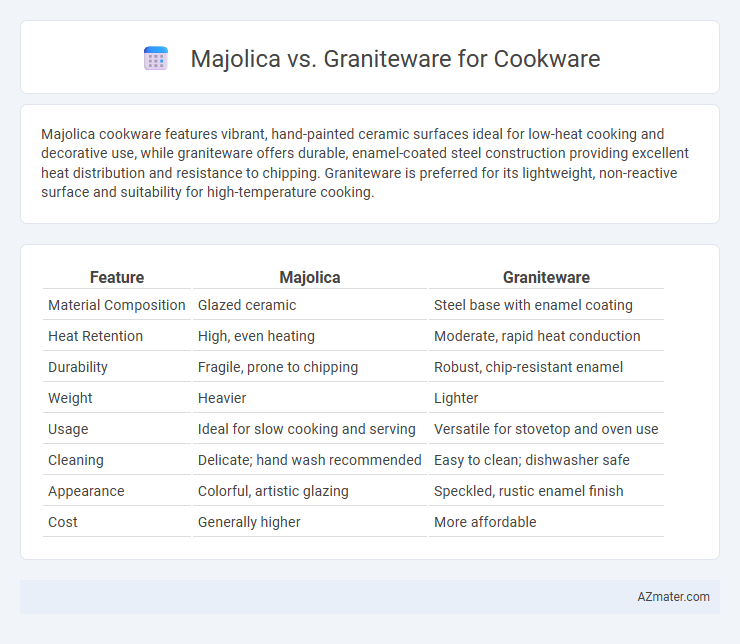
Majolica cookware features vibrant, hand-painted ceramic surfaces ideal for low-heat cooking and decorative use, while graniteware offers durable, enamel-coated steel construction providing excellent heat distribution and resistance to chipping. Graniteware is preferred for its lightweight, non-reactive surface and suitability for high-temperature cooking.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Majolica | Graniteware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Glazed ceramic | Steel base with enamel coating |
| Heat Retention | High, even heating | Moderate, rapid heat conduction |
| Durability | Fragile, prone to chipping | Robust, chip-resistant enamel |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Usage | Ideal for slow cooking and serving | Versatile for stovetop and oven use |
| Cleaning | Delicate; hand wash recommended | Easy to clean; dishwasher safe |
| Appearance | Colorful, artistic glazing | Speckled, rustic enamel finish |
| Cost | Generally higher | More affordable |
Introduction to Majolica and Graniteware
Majolica cookware is known for its vibrant, colorful ceramic glaze that provides excellent heat retention and an attractive finish suitable for both cooking and serving. Graniteware, typically made from steel coated with enamel, offers durability and resistance to chipping, making it ideal for everyday use and outdoor cooking. Both materials provide unique benefits, with Majolica excelling in aesthetic appeal and slow, even heating, while Graniteware emphasizes practicality and ruggedness.
Historical Background of Majolica Cookware
Majolica cookware traces its origins to Renaissance Italy, characterized by vibrant, hand-painted earthenware crafted using tin-glazed pottery techniques dating back to the 15th century. This traditional ceramic method involves applying a white, opaque glaze that creates a glossy surface ideal for intricate, colorful designs, making Majolica both functional and decorative. In contrast, graniteware emerged in the 19th century as a durable, enamel-coated steel product designed for mass production and everyday use, emphasizing practicality over ornamental appeal.
Origins and Evolution of Graniteware
Graniteware cookware originated in the early 19th century as a durable and affordable alternative to traditional cast iron and copper pots, crafted by applying a protective enamel coating over steel or iron. Its evolution was marked by advancements in enamel technology, which improved resistance to chipping and rust, making graniteware popular in both household and commercial kitchens. Compared to Majolica, known for its ornate, colorful ceramic-coated earthenware from Renaissance Italy, graniteware emphasizes functionality and durability, evolving from industrial roots to become a staple in modern cookware collections.
Material Composition: Majolica vs Graniteware
Majolica cookware features a ceramic base coated with colorful lead-free glazes, offering excellent heat retention and even cooking due to its porous material. Graniteware cookware consists of steel or iron coated with a thick layer of enamel fused with granite or other minerals, providing a durable, non-reactive surface resistant to chipping and rust. While Majolica excels in aesthetics and gentle heat distribution, Graniteware is more robust and suitable for high-heat cooking and outdoor use.
Cooking Performance Comparison
Majolica cookware offers excellent heat retention and even distribution due to its ceramic glaze, making it ideal for slow cooking and simmering delicate sauces. Graniteware, constructed from steel coated with durable enamel, heats up quickly and provides a non-stick surface suited for high-heat searing and frying. Both materials excel in oven safety and durability, but graniteware generally outperforms Majolica in responsiveness to temperature changes and quick cooking tasks.
Durability and Longevity
Majolica cookware, crafted from glazed earthenware, offers vibrant aesthetics but tends to be more fragile and prone to chipping compared to graniteware. Graniteware, made from steel coated with enamel, provides exceptional durability and resistance to scratches, making it ideal for long-lasting use in busy kitchens. The longevity of graniteware surpasses majolica due to its robust construction and ability to withstand high-temperature cooking without damage.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Differences
Majolica cookware features vibrant, hand-painted designs with intricate patterns and glossy enamel finishes that create a rustic, artisanal appearance ideal for decorative tablescapes. Graniteware cookware offers a speckled, durable enamel-coated surface in solid or mottled colors, providing a vintage farmhouse charm with a more understated and utilitarian aesthetic. The choice between Majolica's colorful, detailed artistry and Graniteware's simple, rugged appeal depends on whether bold visual statement or classic practicality suits the kitchen decor.
Safety and Health Considerations
Majolica cookware features a lead-free, non-toxic glaze that ensures food safety by preventing harmful substances from leaching during cooking, making it ideal for health-conscious users. Graniteware often contains a porcelain enamel coating fused to steel, providing a durable, non-reactive surface that resists chipping and scratching, minimizing exposure to potentially hazardous metals. Both materials offer safe, toxin-free cooking options when properly maintained, but it is crucial to avoid damaged enamel in graniteware to prevent contamination.
Maintenance and Care Tips
Majolica cookware requires gentle hand washing with mild detergents to preserve its vibrant glaze and prevent chipping, while avoiding abrasive scrubbers is essential. Graniteware, known for its durability and chip-resistant surface, can often be cleaned with non-abrasive sponges and is generally dishwasher safe, but prolonged soaking should be avoided to maintain its enamel coating. Proper drying and storage of both materials prevent rusting of exposed metal edges and extend the cookware's lifespan.
Which Cookware to Choose: Majolica or Graniteware?
Majolica cookware offers vibrant, hand-painted ceramic designs that provide excellent heat retention and even cooking, ideal for slow-cooking and serving directly from the oven to the table. Graniteware, made from enameled steel, is lightweight, durable, and resistant to chipping, making it suitable for high-heat stovetop use and outdoor cooking. Choose Majolica for aesthetic appeal and heat retention, while Graniteware suits practical, everyday use with its robustness and versatility.
Infographic: Majolica vs Graniteware for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com