Gres cookware, made from dense stoneware clay, offers superior durability and heat retention compared to porous ware, which is more absorbent and prone to staining or cracking under high heat. Porous ware requires sealing to prevent moisture absorption, whereas gres is inherently non-porous, ensuring better longevity and resistance to thermal shock.
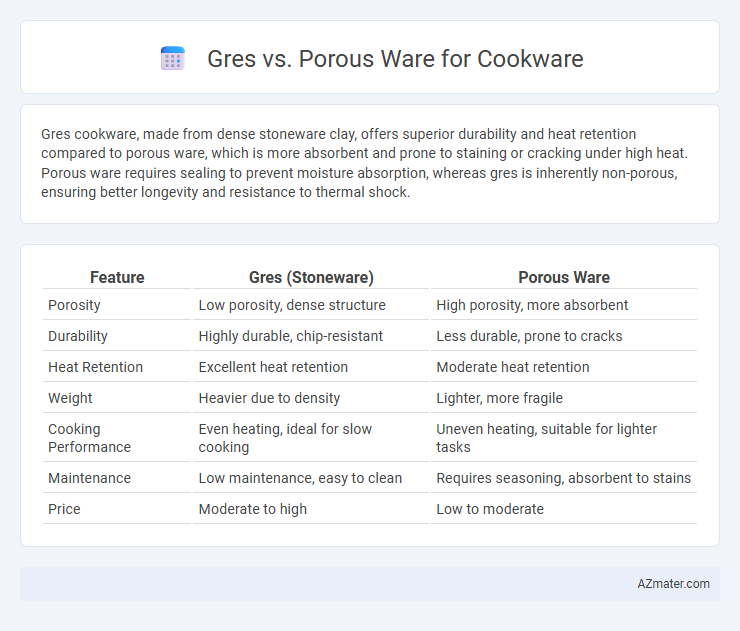
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gres (Stoneware) | Porous Ware |
|---|---|---|
| Porosity | Low porosity, dense structure | High porosity, more absorbent |
| Durability | Highly durable, chip-resistant | Less durable, prone to cracks |
| Heat Retention | Excellent heat retention | Moderate heat retention |
| Weight | Heavier due to density | Lighter, more fragile |
| Cooking Performance | Even heating, ideal for slow cooking | Uneven heating, suitable for lighter tasks |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Requires seasoning, absorbent to stains |
| Price | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Gres and Porous Ware Cookware
Gres cookware, made from dense, non-porous stoneware clay, offers excellent durability and heat retention for even cooking. Porous ware cookware, characterized by its micro-porous structure, absorbs moisture and flavors, which can enhance the taste of slow-cooked dishes but requires seasoning and careful maintenance. Both types provide distinct advantages in heat distribution and cooking techniques, catering to different culinary preferences and usage needs.
Material Composition: Gres vs Porous Ware
Gres cookware is made from high-density ceramic clay fired at extremely high temperatures, resulting in a dense, non-porous surface that resists water absorption and enhances durability. Porous ware, in contrast, consists of ceramics with a more open microstructure, allowing liquid absorption that can affect heat retention and cause staining over time. The material composition difference directly impacts cooking performance, maintenance, and longevity, with gres offering superior resistance to thermal shock and moisture infiltration compared to porous ware.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Gres cookware is manufactured through high-temperature firing of refined clay, resulting in a dense, non-porous ceramic that enhances durability and heat retention. Porous ware, by contrast, involves less refined clay and lower firing temperatures, creating a more porous structure that absorbs moisture and may affect cooking performance. The distinct firing techniques and clay refinement in gres production lead to superior thermal conductivity and a longer lifespan compared to porous ware cookware.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Performance
Gres cookware, made from high-density stoneware clay, offers superior heat resistance due to its ability to withstand temperatures up to 1300degC without cracking, making it ideal for high-heat cooking and oven use. Porous ware, typically crafted from less dense clay, absorbs moisture more readily, which can reduce thermal performance by causing uneven heat distribution and increasing the risk of thermal shock under rapid temperature changes. The dense, vitrified structure of gres enhances thermal retention and stability, ensuring consistent heat flow and durability during prolonged cooking compared to the more fragile porous ware.
Porosity and Moisture Absorption Differences
Gres cookware, characterized by low porosity, exhibits minimal moisture absorption, enhancing durability and resistance to staining. Porous ware, in contrast, has higher porosity levels, leading to increased moisture absorption that can result in faster wear and potential bacterial growth. Selecting low-porosity gres materials ensures better hygiene and longevity in cookware applications.
Durability and Longevity in Daily Use
Gres cookware, made from dense stoneware, offers superior durability and resistance to chipping and cracking, making it ideal for daily use and high-temperature cooking. Porous ware, with its more porous ceramic structure, tends to absorb moisture and can degrade faster over time, especially with frequent washing and exposure to thermal shocks. Choosing gres cookware ensures longer-lasting performance and maintains structural integrity through repeated use and cleaning cycles.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Gres (stoneware) cookware offers excellent safety due to its non-porous surface, which resists bacterial absorption and chemical leaching, ensuring food compatibility and hygiene during cooking. Porous cookware, by contrast, can absorb oils, liquids, and bacteria, increasing the risk of contamination and altering flavors over time, making it less ideal for consistent food safety. Selecting non-porous gres cookware minimizes chemical reactions and enhances durability, providing safer food preparation options in the kitchen.
Cleaning and Maintenance Requirements
Gres cookware, made from dense stoneware, offers superior resistance to stains and scratches, making it easier to clean and maintain with simple hand washing or dishwasher use. Porous ware, often made from earthenware or unglazed clay, requires careful cleaning to prevent absorption of oils and odors, typically needing gentle detergents and thorough drying to avoid mold or cracking. Regular sealing or seasoning of porous cookware enhances its durability and reduces cleaning challenges compared to the low-maintenance, non-porous surface of gres cookware.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Gres cookware features a sleek, smooth surface with a glossy finish that enhances modern kitchen aesthetics, while porous ware offers a rustic, textured look prized for its natural, handcrafted charm. Gres designs often come in vibrant colors and intricate patterns, allowing for a wide range of stylish, contemporary options, whereas porous ware leans towards earthy tones and organic shapes that emphasize artisanal appeal. Selecting between gres and porous ware depends on whether you prioritize refined elegance or authentic, nature-inspired kitchen decor.
Choosing the Right Cookware: Gres or Porous Ware?
Gres cookware, made from dense stoneware clay, offers superior heat retention and durability, making it ideal for slow cooking and consistent heat distribution. Porous ware, known for its porous ceramic structure, allows better moisture absorption and breathability, enhancing flavors but requiring careful seasoning and maintenance to prevent cracking. Selecting between gres and porous ware depends on cooking style: gres suits prolonged, even cooking, while porous ware excels in recipes benefiting from moisture control and subtle heat variations.
Infographic: Gres vs Porous ware for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com