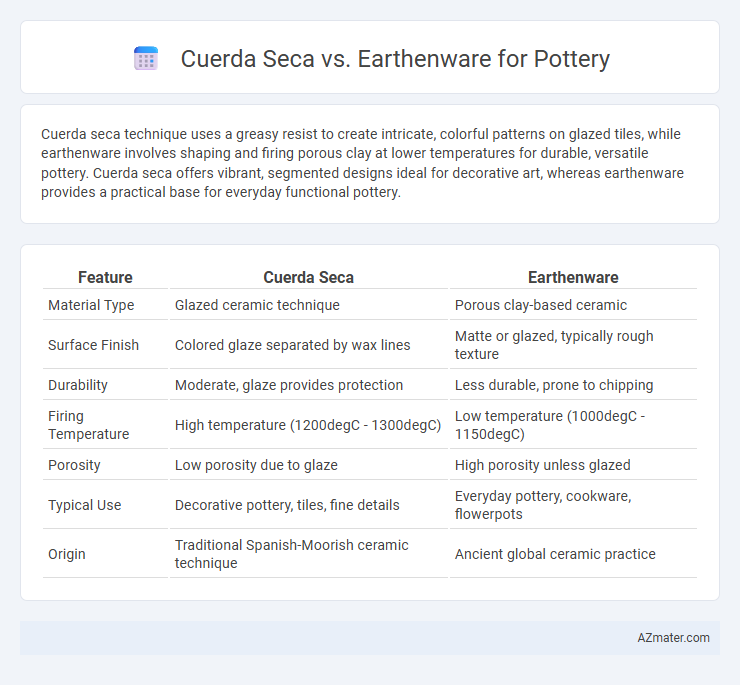
Cuerda seca technique uses a greasy resist to create intricate, colorful patterns on glazed tiles, while earthenware involves shaping and firing porous clay at lower temperatures for durable, versatile pottery. Cuerda seca offers vibrant, segmented designs ideal for decorative art, whereas earthenware provides a practical base for everyday functional pottery.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cuerda Seca | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed ceramic technique | Porous clay-based ceramic |
| Surface Finish | Colored glaze separated by wax lines | Matte or glazed, typically rough texture |
| Durability | Moderate, glaze provides protection | Less durable, prone to chipping |
| Firing Temperature | High temperature (1200degC - 1300degC) | Low temperature (1000degC - 1150degC) |
| Porosity | Low porosity due to glaze | High porosity unless glazed |
| Typical Use | Decorative pottery, tiles, fine details | Everyday pottery, cookware, flowerpots |
| Origin | Traditional Spanish-Moorish ceramic technique | Ancient global ceramic practice |
Introduction to Cuerda Seca and Earthenware
Cuerda seca is a decorative pottery technique originating from Moorish Spain, characterized by its colorful, segmented designs created using a greasy substance that prevents glaze colors from mixing during firing. Earthenware, a porous ceramic material fired at lower temperatures (typically between 1,000degC and 1,150degC), is known for its durability and versatility, often used for both functional and artistic pottery. The cuerda seca method is frequently applied on earthenware surfaces to achieve vibrant, intricate patterns that stand out due to the material's natural absorbency and warmth.
Historical Background of Cuerda Seca
The Cuerda Seca technique, developed in Islamic Spain during the 10th century, is historically significant for its use of greasy lines to separate colored glazes on pottery, preventing colors from mixing during firing. This method contrasts with traditional earthenware, which involves a single firing and often lacks the intricate color separation that characterizes Cuerda Seca ceramics. The historical evolution of Cuerda Seca highlights its importance in creating vivid, detailed designs that were highly valued across the medieval Islamic world.
Origins and Evolution of Earthenware
Earthenware pottery originated around 10,000 BCE in Neolithic cultures, characterized by its porous and low-fired clay composition, making it one of the oldest forms of ceramic art. Cuerda seca, developed later during the Islamic Golden Age, is a decorative technique used to create intricate, colored tile patterns on earthenware surfaces by isolating glazes with greasy lines. This evolution reflects a shift from simple utilitarian earthenware to sophisticated artistry combining function and ornamentation.
Materials and Techniques Used in Cuerda Seca
Cuerda seca pottery employs a unique technique that uses a greasy resist line made from a mixture of manganese oxide and grease to create distinct separated color areas on glazed tiles, preventing colors from mixing during firing. The primary materials include earthenware clay bodies that are formed, dried, and then decorated with thick linings of the greasy resist to outline intricate patterns before applying colored glazes within the separated compartments. This method contrasts with traditional earthenware glazing, which often involves direct application of colored glazes without resist lines, resulting in more blended or less defined color transitions.
Crafting Process of Earthenware Pottery
Earthenware pottery involves shaping clay, typically composed of natural materials like kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, which is fired at lower temperatures between 1,000degC and 1,150degC. The crafting process includes hand-building or wheel-throwing techniques, followed by bisque firing, glazing, and a final firing to achieve a porous, durable finish. Earthenware's porous nature requires glazing to create a waterproof surface, making it distinct from the Cuerda Seca method, which uses specific colored slip lines to create intricate designs on ceramics.
Key Differences in Aesthetic Appeal
Cuerda seca pottery showcases intricate, colorful patterns created using a resist technique that separates glazes with thin black lines, producing vibrant, detailed designs ideal for decorative art. Earthenware pottery typically features a more rustic and organic aesthetic with natural earth tones and textured surfaces, emphasizing simplicity and traditional craftsmanship. The key aesthetic difference lies in cuerda seca's bold, precise, and ornamental visual appeal versus earthenware's understated, tactile, and earthy charm.
Durability and Practicality Comparison
Cuerda seca pottery, featuring intricate designs separated by wax lines, offers moderate durability but tends to be more delicate due to the glazed surface and raised patterns prone to chipping. Earthenware, fired at lower temperatures, is generally more porous and less durable but highly practical for everyday use and repairable with sealants or glazes. For long-term use, earthenware provides greater practicality and resilience, while cuerda seca excels in decorative appeal but requires careful handling.
Artistic Uses and Applications
Cuerda seca technique enhances pottery by creating vivid, multi-colored designs using a resist line that separates glazes, ideal for intricate decorative patterns on tiles and vases. Earthenware offers a versatile canvas with its porous, low-fired body, supporting a wide range of glazing and painting methods tailored to both functional and artistic pottery. Artists favor cuerda seca for precise, vibrant motifs in traditional and contemporary ceramics, while earthenware's earthy texture complements rustic and tactile art pieces.
Cost and Accessibility Factors
Cuerda seca pottery involves intricate glazing techniques that tend to increase production costs compared to simpler earthenware methods. Earthenware is widely accessible due to the abundance of natural clay materials and straightforward firing processes, making it more affordable for beginners and mass production. Cost efficiency and material availability make earthenware a popular choice for budget-conscious artisans, while cuerda seca appeals to those prioritizing detailed, colorful designs despite higher expenses.
Choosing the Right Pottery Technique
Cuerda seca and earthenware are distinct pottery techniques that influence the aesthetic and durability of ceramic pieces. Cuerda seca involves creating intricate, separated colored patterns using a greasy resist line to prevent glaze mixing, ideal for detailed decorative art. Earthenware uses porous clay fired at lower temperatures, offering versatility and affordability but requiring glazing for water resistance, making it suitable for both functional and decorative pottery.
Infographic: Cuerda seca vs Earthenware for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com