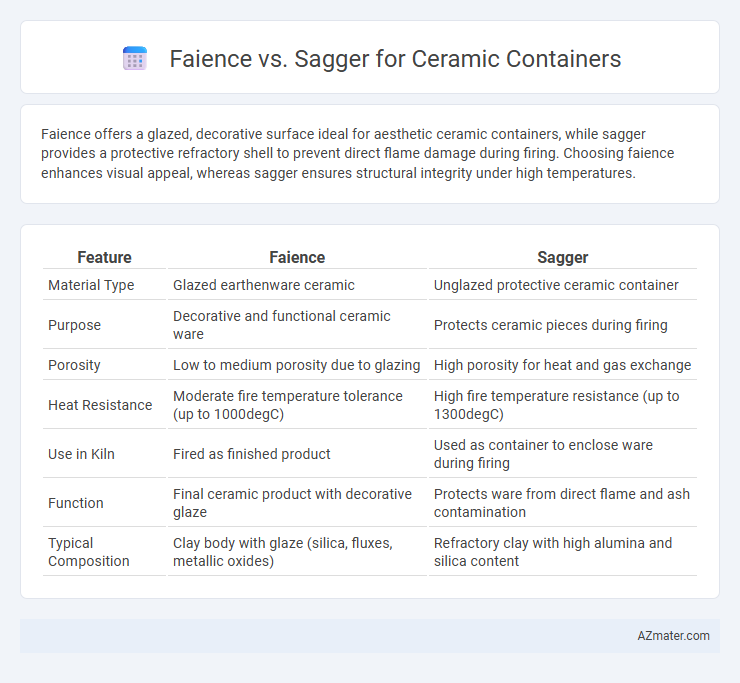
Faience offers a glazed, decorative surface ideal for aesthetic ceramic containers, while sagger provides a protective refractory shell to prevent direct flame damage during firing. Choosing faience enhances visual appeal, whereas sagger ensures structural integrity under high temperatures.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Faience | Sagger |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed earthenware ceramic | Unglazed protective ceramic container |
| Purpose | Decorative and functional ceramic ware | Protects ceramic pieces during firing |
| Porosity | Low to medium porosity due to glazing | High porosity for heat and gas exchange |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate fire temperature tolerance (up to 1000degC) | High fire temperature resistance (up to 1300degC) |
| Use in Kiln | Fired as finished product | Used as container to enclose ware during firing |
| Function | Final ceramic product with decorative glaze | Protects ware from direct flame and ash contamination |
| Typical Composition | Clay body with glaze (silica, fluxes, metallic oxides) | Refractory clay with high alumina and silica content |
Introduction to Ceramic Containers
Ceramic containers are crafted using diverse materials like faience and sagger, each offering unique properties for functionality and aesthetics. Faience is a glazed non-clay ceramic, known for its bright colors and decorative appeal, commonly utilized in ornamental containers. In contrast, saggers are refractory containers made from fireclay or other heat-resistant materials, designed primarily to protect ceramics during kiln firing, ensuring durability and structural integrity.
Defining Faience: Composition and Features
Faience is a glazed non-clay ceramic material primarily composed of ground quartz or sand, with small amounts of lime and soda serving as fluxes to lower the firing temperature. Its distinctive glassy surface and vibrant colors result from a silica-based body vitrified around 800-1000degC, offering a porous but durable finish suitable for decorative containers. Unlike sagger ceramics, which focus on protective firing enclosures, faience emphasizes aesthetic appeal through its translucent glaze and intricate surface designs.
Sagger Explained: Purpose and Material
Saggers serve as protective containers in ceramic firing, designed to shield delicate pieces from direct flame and ash contamination. Made typically from refractory clay, these containers withstand high temperatures while maintaining structural integrity in the kiln. Unlike faience, which is a glazed ceramic material, saggers focus on functionality to enhance ceramic quality during firing.
Historical Background: Faience and Sagger
Faience, a glazed non-clay ceramic known for its vibrant blue-green hues, traces back to ancient Egypt around 4000 BCE, serving both decorative and functional purposes in pottery and small vessels. The sagger, a protective ceramic container used in kilns, emerged prominently during the Song dynasty in China (960-1279 CE) to safeguard more delicate ceramics from direct flame and ash damage during firing. Both faience and saggers highlight the evolution of ceramic technologies, reflecting diverse cultural advancements in glazing techniques and kiln management.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Faience ceramic containers are created by applying a tin-based glaze over a low-fired clay body, producing a bright, opaque, and colorful surface, whereas sagger ceramic containers involve placing the clay pieces inside a protective container or sagger during firing to shield them from direct flame and ash contamination. The faience manufacturing process emphasizes decoration and surface finish through glazing techniques prior to firing, while the sagger process prioritizes protection, allowing for controlled atmospheres that affect the final texture and color of the ceramic. Faience requires precise glaze application and lower firing temperatures around 900-1050degC, while saggers are used in high-temperature firings up to 1300degC in kilns, making the production methods distinctly focused on finish versus firing environment control.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Faience ceramic containers offer moderate durability with a vitreous, glazed surface that resists water absorption but can be prone to chipping under impact. Sagger containers, made from dense, refractory clay, provide superior thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making them ideal for high-temperature firing and long-term use in kiln protection. The performance of sagger ware excels in environments requiring consistent thermal insulation and durability, whereas faience is preferred for decorative and less-intensive applications.
Visual and Aesthetic Distinctions
Faience ceramic containers showcase vibrant, glazed surfaces with intricate blue and green patterns, offering a glossy, decorative aesthetic that enhances visual appeal. Sagger ceramics exhibit a matte or unglazed finish with subtle color variations, emphasizing rustic textures and earthy tones for a natural, understated look. The choice between faience and sagger affects the overall visual impact, with faience providing bright, ornamental elegance and sagger delivering organic, tactile simplicity.
Applications in Modern Ceramics
Faience offers vibrant glazing and decorative appeal, making it ideal for ornamental ceramic containers used in interior design and artisanal crafts. Sagger firing provides enhanced thermal insulation and contamination protection, suited for technical ceramics requiring durability and purity in industrial applications. Modern ceramics leverage faience for aesthetic enhancements while utilizing sagger techniques to ensure functional performance under high-temperature conditions.
Cost and Accessibility Analysis
Faience ceramic containers typically involve higher production costs due to their glazed surfaces and intricate decorative techniques, which require specialized materials and skilled artisans, making them less accessible for mass-market consumers. In contrast, sagger-fired containers benefit from lower costs as the sagger protects the ware during the kiln firing process without additional glazing, allowing for simpler, more cost-effective production methods suited for bulk manufacturing. Accessibility of sagger ceramics is enhanced by the widespread availability of raw materials and less reliance on artisan craftsmanship, making them a more affordable option in both industrial and domestic markets.
Choosing Between Faience and Sagger
Choosing between faience and sagger for ceramic containers depends on the desired finish and firing process. Faience offers a vibrant, glazed surface ideal for decorative pieces, while saggers provide protective enclosures during firing, preventing direct flame contact and enhancing durability. Selecting faience is optimal for intricate designs, whereas saggers suit functional ceramics needing thermal protection.
Infographic: Faience vs Sagger for Ceramic Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com