Faience bricks offer a glossy, vitrified surface ideal for decorative applications, while fireclay bricks provide superior heat resistance and durability suited for high-temperature environments. Fireclay bricks contain high alumina content, enhancing thermal shock resistance compared to the more porous faience material.
Table of Comparison
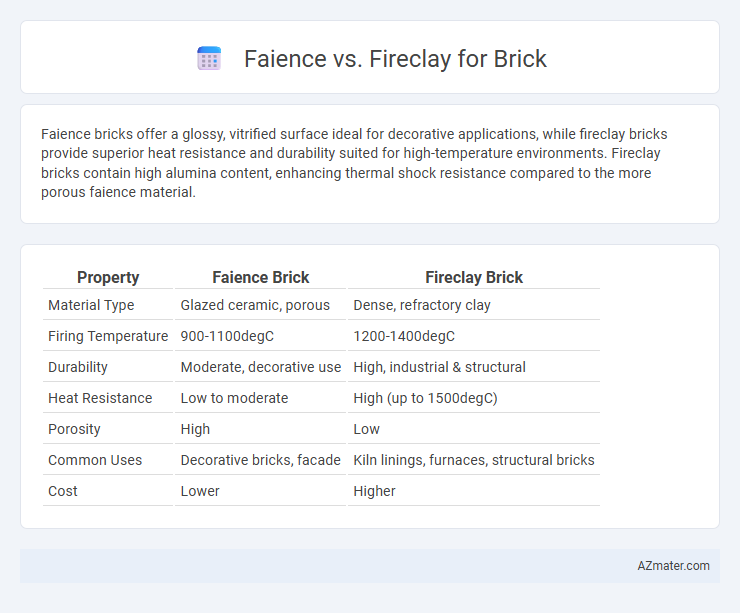
| Property | Faience Brick | Fireclay Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed ceramic, porous | Dense, refractory clay |
| Firing Temperature | 900-1100degC | 1200-1400degC |
| Durability | Moderate, decorative use | High, industrial & structural |
| Heat Resistance | Low to moderate | High (up to 1500degC) |
| Porosity | High | Low |
| Common Uses | Decorative bricks, facade | Kiln linings, furnaces, structural bricks |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Faience and Fireclay Bricks
Faience bricks are ceramic tiles glazed with a colorful, glass-like coating that offers vibrant aesthetics and moisture resistance, commonly used for decorative facades and interior accents. Fireclay bricks, composed of refractory clay, withstand high temperatures and thermal shock, making them essential for industrial furnaces, kilns, and fireplaces. Both materials differ in composition and application, with faience excelling in ornamental appeal and fireclay providing structural durability under extreme heat.
Composition and Raw Materials
Faience bricks are primarily composed of glazed ceramic materials using finely ground quartz, feldspar, and clay, which are fired at high temperatures to achieve a glossy, decorative finish. Fireclay bricks consist mainly of fire-resistant clay enriched with alumina and silica, known for their ability to withstand extreme heat and thermal shock. The raw materials for faience emphasize decorative aesthetics, while fireclay prioritizes thermal stability and durability for industrial applications.
Manufacturing Processes
Faience bricks are produced through a glazing process where a vitreous coating is fused onto the surface during high-temperature firing, resulting in a glossy, decorative finish. Fireclay bricks undergo a more intensive manufacturing process involving the firing of refractory clay at extremely high temperatures, enhancing their heat resistance and durability for industrial applications. The distinct firing temperatures and raw material compositions in each process directly influence the structural properties and intended use of faience versus fireclay bricks.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Faience bricks exhibit moderate porosity and lower compressive strength, making them less durable under heavy mechanical stress compared to fireclay bricks. Fireclay bricks possess high density, low porosity, and superior thermal shock resistance, offering enhanced compressive strength typically above 20 MPa. The physical robustness of fireclay bricks makes them ideal for high-temperature applications, while faience bricks are better suited for decorative purposes due to their glazed surface and lower mechanical resilience.
Aesthetic Qualities and Finishes
Faience bricks offer a vibrant, glossy surface achieved through a tin glaze, providing rich colors and intricate patterns ideal for decorative installations. Fireclay bricks feature a more natural, matte finish with earthy tones, delivering a rustic and durable appearance suited for traditional or industrial aesthetics. The choice between faience and fireclay bricks depends on the desired visual impact, with faience emphasizing ornamental appeal and fireclay prioritizing robust, understated texture.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Faience bricks, known for their glazed surface, offer excellent weather resistance by preventing moisture penetration and resisting frost damage, making them suitable for exterior applications in harsh climates. Fireclay bricks, composed of refractory clays, provide superior durability due to their high firing temperatures, resulting in enhanced strength and thermal stability under extreme conditions. Both materials excel in longevity, but faience's moisture-resistant glaze offers a distinct advantage in wet or freeze-thaw environments.
Application Areas in Construction
Faience bricks are primarily used for decorative facades, ornamental detailing, and interior wall cladding due to their glazed finish and aesthetic appeal, making them ideal for architectural accents and heritage restoration projects. Fireclay bricks, known for their high heat resistance and durability, are extensively applied in industrial settings such as kilns, furnaces, fireplaces, and heat-intensive environments, providing structural support and insulation. The choice between faience and fireclay bricks in construction is driven by the specific application requirements of visual finish versus thermal performance.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Faience bricks typically cost more due to their intricate glazing and decorative finishes, making them less widely available than fireclay bricks. Fireclay bricks, made from high-quality clay with excellent refractory properties, are generally more affordable and easier to source in bulk for industrial and construction use. Availability of fireclay bricks spans most regions, while faience bricks often require custom orders or specialty suppliers, impacting both price and lead time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Faience bricks, made from glazed ceramic materials, typically require higher energy consumption during the firing process due to their elaborate glazing and finishing techniques, contributing to a larger carbon footprint compared to fireclay bricks. Fireclay bricks are composed of natural clay with minimal processing, which results in lower energy usage and enhanced sustainability through their durability and recyclability in construction. The environmental impact of fireclay bricks is generally reduced by their longer lifespan and potential for reuse, making them a more eco-friendly option in sustainable building practices.
Choosing the Right Material: Faience or Fireclay
Faience bricks offer a glazed, decorative finish with high resistance to weathering and stain, making them ideal for ornamental facades and architectural details. Fireclay bricks provide exceptional thermal shock resistance and durability, suited for high-temperature applications like fireplaces and industrial furnaces. Selecting between faience and fireclay depends on the project's aesthetic requirements and performance needs, balancing visual appeal with thermal resistance.
Infographic: Faience vs Fireclay for Brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com