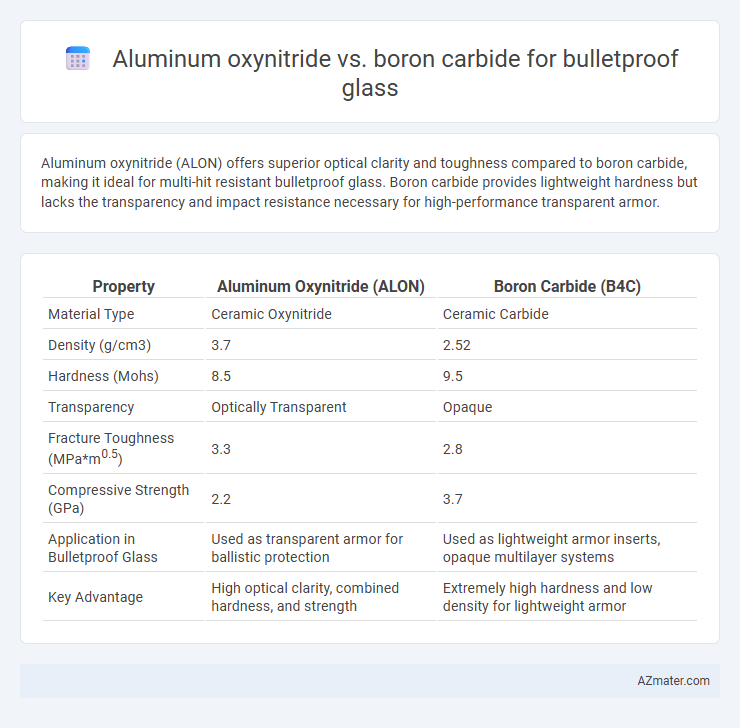
Aluminum oxynitride (ALON) offers superior optical clarity and toughness compared to boron carbide, making it ideal for multi-hit resistant bulletproof glass. Boron carbide provides lightweight hardness but lacks the transparency and impact resistance necessary for high-performance transparent armor.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminum Oxynitride (ALON) | Boron Carbide (B4C) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic Oxynitride | Ceramic Carbide |
| Density (g/cm3) | 3.7 | 2.52 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 8.5 | 9.5 |
| Transparency | Optically Transparent | Opaque |
| Fracture Toughness (MPa*m0.5) | 3.3 | 2.8 |
| Compressive Strength (GPa) | 2.2 | 3.7 |
| Application in Bulletproof Glass | Used as transparent armor for ballistic protection | Used as lightweight armor inserts, opaque multilayer systems |
| Key Advantage | High optical clarity, combined hardness, and strength | Extremely high hardness and low density for lightweight armor |
Introduction to Bulletproof Glass Materials
Aluminum oxynitride (ALON) and boron carbide represent advanced materials used in bulletproof glass applications, offering exceptional hardness and impact resistance. ALON, a transparent ceramic composed of aluminum, oxygen, and nitrogen, provides superior optical clarity combined with high strength and durability, making it ideal for transparent armor systems. Boron carbide, a dense ceramic renowned for its extreme hardness and lightweight properties, is commonly used as a backing material to absorb and dissipate ballistic energy in multi-layered armor composites.
Overview of Aluminum Oxynitride (ALON)
Aluminum Oxynitride (ALON) is a transparent ceramic known for its exceptional hardness, high optical clarity, and superior ballistic resistance, making it a prime candidate for bulletproof glass applications. ALON exhibits excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, thermal shock, and abrasion, outperforming traditional materials like Boron Carbide in optical transparency and durability under impact. Its ability to combine lightweight properties with multi-hit ballistic protection offers significant advantages in military and aerospace armor systems.
Overview of Boron Carbide
Boron carbide is a highly effective material for bulletproof glass due to its exceptional hardness, ranking third behind diamond and cubic boron nitride, which provides superior ballistic protection and lightweight characteristics. Its chemical stability and low density make it ideal for armor applications, offering enhanced resistance against high-velocity projectiles compared to aluminum oxynitride. The combination of toughness and wear resistance allows boron carbide to maintain structural integrity under extreme impact conditions, making it a preferred choice in military and security industries.
Comparative Ballistic Performance
Aluminum oxynitride (ALON) offers superior transparency and higher hardness compared to boron carbide, contributing to enhanced ballistic resistance in bulletproof glass applications. Boron carbide, while also extremely hard and lightweight, tends to have slightly lower fracture toughness than ALON, affecting its performance against high-velocity projectiles. The combination of clarity and toughness makes ALON a preferred choice for transparent armor systems requiring both optical clarity and robust ballistic protection.
Transparency and Optical Properties
Aluminum oxynitride (ALON) offers superior transparency in the visible and near-infrared spectrum with excellent optical clarity and minimal light scattering compared to boron carbide, which is primarily valued for its hardness rather than optical performance. ALON exhibits a high refractive index and low birefringence, making it ideal for bulletproof glass applications requiring clear visibility and minimal distortion. Boron carbide's optical properties are limited, resulting in reduced transparency and increased opacity, restricting its use in transparent ballistic armor.
Weight and Thickness Considerations
Aluminum oxynitride (ALON) offers a significant advantage in bulletproof glass applications due to its lighter weight and reduced thickness compared to boron carbide, enabling thinner, more lightweight armor solutions. ALON's density is approximately 3.7 g/cm3, considerably less than boron carbide's 2.52 g/cm3; however, boron carbide's exceptional hardness often compensates for weight when maximizing ballistic resistance is critical. The balance between ALON's higher optical clarity and lower thickness with boron carbide's superior hardness and hardness-to-weight ratio directly impacts design choices in lightweight, thin ballistic armor systems.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Aluminum oxynitride (ALON) exhibits superior durability for bulletproof glass, offering high hardness and strong impact resistance while maintaining optical clarity. Boron carbide, although extremely hard and lightweight, can be more prone to brittle failure under extreme impacts compared to ALON. Both materials demonstrate excellent environmental resistance, but ALON outperforms boron carbide in resisting moisture, chemical corrosion, and thermal variations, making it more reliable for long-term outdoor applications.
Manufacturing Process and Cost Efficiency
Aluminum oxynitride (ALON) manufacturing involves complex sintering and hot pressing processes, requiring high temperatures and precise control, which contribute to its higher production cost compared to boron carbide. Boron carbide is produced through carbothermal reduction and reaction sintering, a more established and cost-efficient method, making it more economically viable for large-scale bulletproof glass applications. Despite its lower cost, boron carbide's manufacturing limitations in clarity and uniformity contrast with ALON's superior optical properties, influencing the cost-performance balance in armored glazing solutions.
Applications in Security and Defense
Aluminum oxynitride (ALON) offers superior optical clarity and high ballistic resistance, making it ideal for transparent armor in security and defense applications such as military vehicle windows and face shields. Boron carbide, known for its extreme hardness and lightweight properties, is commonly used in lightweight body armor and vehicle armoring where maximum protection against high-velocity projectiles is required. Both materials enhance survivability in combat scenarios, with ALON providing enhanced visibility and toughness, while boron carbide delivers cost-effective protection and low weight.
Future Trends in Transparent Armor Technology
Aluminum oxynitride (ALON) and boron carbide remain pivotal materials in advancing bulletproof glass due to their exceptional hardness and optical clarity. Future trends emphasize enhancing ALON's scalable manufacturing processes and integrating nanostructured boron carbide composites to improve ballistic resistance while reducing weight. Innovations in hybrid layering techniques also target optimizing the transparency and impact absorption capabilities of next-generation transparent armor systems.
Infographic: Aluminum oxynitride vs Boron carbide for Bulletproof glass
 azmater.com
azmater.com