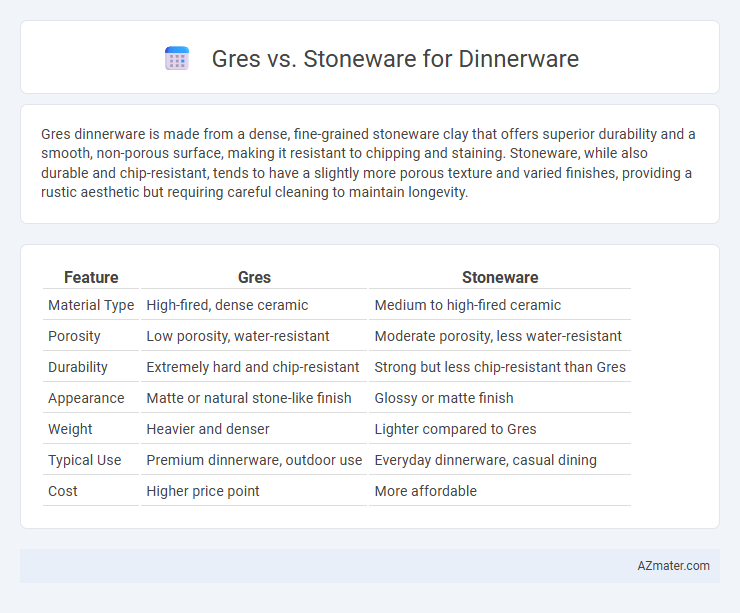
Gres dinnerware is made from a dense, fine-grained stoneware clay that offers superior durability and a smooth, non-porous surface, making it resistant to chipping and staining. Stoneware, while also durable and chip-resistant, tends to have a slightly more porous texture and varied finishes, providing a rustic aesthetic but requiring careful cleaning to maintain longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gres | Stoneware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-fired, dense ceramic | Medium to high-fired ceramic |
| Porosity | Low porosity, water-resistant | Moderate porosity, less water-resistant |
| Durability | Extremely hard and chip-resistant | Strong but less chip-resistant than Gres |
| Appearance | Matte or natural stone-like finish | Glossy or matte finish |
| Weight | Heavier and denser | Lighter compared to Gres |
| Typical Use | Premium dinnerware, outdoor use | Everyday dinnerware, casual dining |
| Cost | Higher price point | More affordable |
Introduction to Gres and Stoneware
Gres and stoneware are both popular materials used in dinnerware, known for their durability and aesthetic appeal. Gres, a type of porcelain, is fired at higher temperatures making it highly dense, non-porous, and resistant to chipping, ideal for everyday use and elegant table settings. Stoneware, fired at slightly lower temperatures, offers a rustic charm with its thicker, more textured surface and excellent heat retention, making it well-suited for casual dining and heavy use.
What is Gres Dinnerware?
Gres dinnerware refers to a type of ceramic made from high-quality stoneware clay fired at high temperatures, resulting in a durable, dense, and non-porous material. This makes gres dinnerware highly resistant to chips, scratches, and thermal shock, ideal for everyday use and professional settings. Compared to traditional stoneware, gres typically offers a smoother, more refined finish with enhanced strength and longevity.
What is Stoneware Dinnerware?
Stoneware dinnerware is a type of pottery made from dense, non-porous clay fired at high temperatures between 1200degC and 1300degC, resulting in a durable and chip-resistant finish. Its natural iron content gives it a characteristic earthy tone, often with a glazed surface for added strength and ease of cleaning. Stoneware is known for excellent heat retention, making it ideal for everyday use and ideal for oven-to-table serving.
Key Material Differences: Gres vs Stoneware
Gres and stoneware differ primarily in their firing temperatures and composition, with gres being fired at higher temperatures, resulting in a denser and more vitrified material. Stoneware typically contains a mix of clay and other natural materials, making it more porous and less durable than gres. The higher vitrification in gres provides superior resistance to chipping and water absorption, making it ideal for long-lasting dinnerware.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Gres and stoneware both offer high durability for dinnerware, but gres is fired at higher temperatures, resulting in a denser, less porous material that resists chipping and cracking more effectively. Stoneware, while also strong, tends to be slightly more porous and can be more susceptible to chipping under heavy use. The superior vitrification in gres enhances its strength, making it a preferred choice for longevity in daily dining environments.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Gres dinnerware offers a unique, rustic aesthetic with natural textures and earthy tones that appeal to minimalist and organic design preferences. Stoneware provides a versatile range of finishes, including glossy, matte, and patterned glazes, catering to both modern and traditional table settings. The durability and rich color variations in stoneware enhance its ability to complement diverse interior styles, making it a popular choice for customizable dinnerware collections.
Performance: Heat and Scratch Resistance
Gres dinnerware exhibits superior heat resistance, making it ideal for oven and microwave use without risk of cracking or thermal shock. Stoneware also offers good heat retention but is generally less resistant to high temperatures compared to gres. When considering scratch resistance, gres typically outperforms stoneware due to its denser, less porous surface, which reduces susceptibility to surface damage from daily utensils.
Care and Maintenance Needs
Gres dinnerware typically requires more delicate handling due to its porous surface, necessitating hand washing and avoiding abrasive cleaners to maintain its finish. Stoneware is generally more durable and resistant to chipping, allowing for dishwasher use and microwave safety without compromising longevity. Both materials benefit from avoiding sudden temperature changes to prevent cracking, but stoneware's denser composition offers greater ease in everyday care and maintenance.
Cost Comparison: Gres vs Stoneware
Gres dinnerware typically costs more than standard stoneware due to its higher firing temperature and denser composition, resulting in greater durability and resistance to chipping. Stoneware offers a more budget-friendly option while still providing decent strength and aesthetic versatility for everyday use. When comparing costs, consider the long-term investment in gres for longevity versus the initial savings with stoneware for frequent replacements.
Which is Better for Your Table: Final Verdict
Stoneware offers superior durability and chip resistance, making it ideal for everyday dinnerware that withstands frequent use and dishwasher cleaning. Gres, a type of stoneware fired at higher temperatures, provides enhanced strength and a more refined, glass-like finish suitable for elegant table settings. Choosing between gres and traditional stoneware depends on your priorities for durability, aesthetic appeal, and usage frequency, with stoneware excelling in practicality and gres in sophistication.
Infographic: Gres vs Stoneware for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com